Fact: NASA takes the best before-and-after photos. Here are 10 of them.
Our world is changing every day.
Setiment in Louisiana
NASA satellites continually monitor the Earth, snapping photos and sending information to researchers on the ground.
Most of the time, things seem to be more or less the same as they were the day before, but the Earth is actually constantly changing. Sometimes it changes through discrete events, like landslides and floods. Other times, long-term trends, such as climate change, slowly reshape the land in ways that are difficult to see.
By zooming way out, we can get a new perspective of the events that have changed the Earth. These 10 before-and-after photos show the disasters, trends, and changes that have affected our planet, as seen from space.
1. In May 2016, NASA's satellites picked up the devastating 2016 Fort McMurray wildfire.
Before:
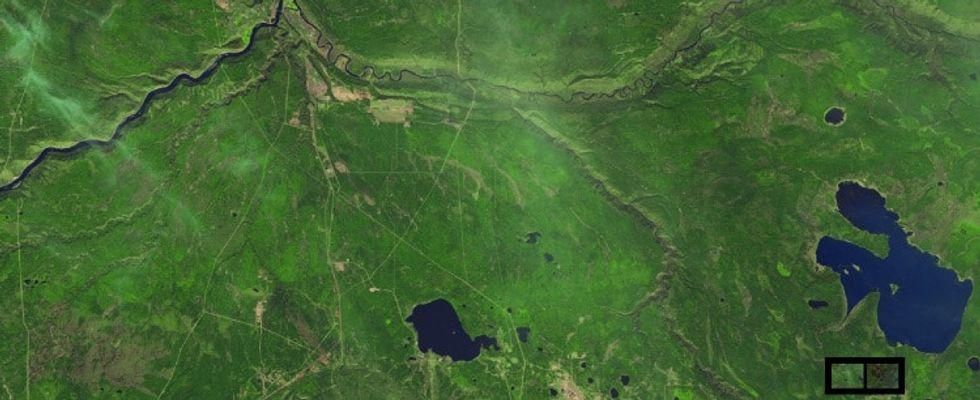

Satellite image from before the wildfire.
All images from NASA.
After:
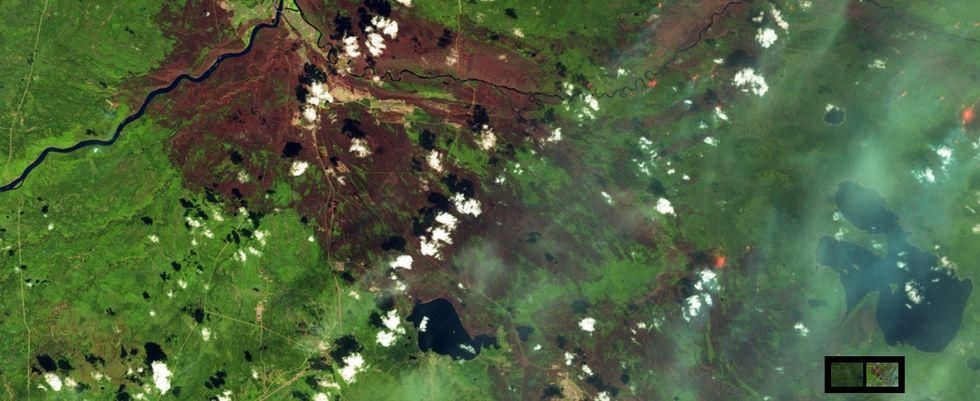

Satellite image after the devastating fire.
All images from NASA.
In May 2016, a wildfire broke out near Fort McMurray in Alberta, Canada. It destroyed more than 2,400 homes and businesses and burned through roughly 1,500,000 acres of land before it was under control. (Some of the pictures use false-color imaging to distinguish between land types, by the way).
2. The satellites also captured how landscapes eventually recover from fires, like in Yellowstone.
Before:
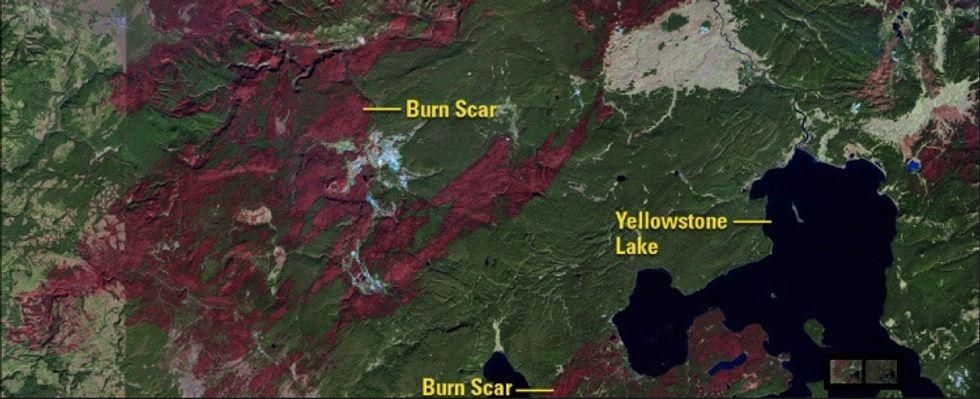
Satellite image after fire in Yellowstone.
All images from NASA.
After:
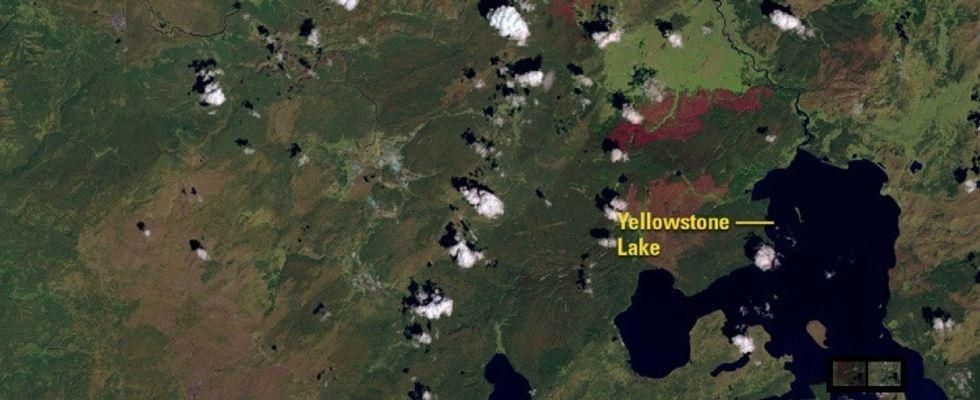
Nature returns to normal with time.
All images from NASA.
In 1988, wildfires burned through over a third of Yellowstone National Park. 28 years later, images show that much of the forest and plains have returned.
3. They saw drought shrink Utah's Great Salt Lake over the last 30 years ...
Before:

Image of the Utah’s Great Salt Lake before the drought.
All images from NASA.
After:
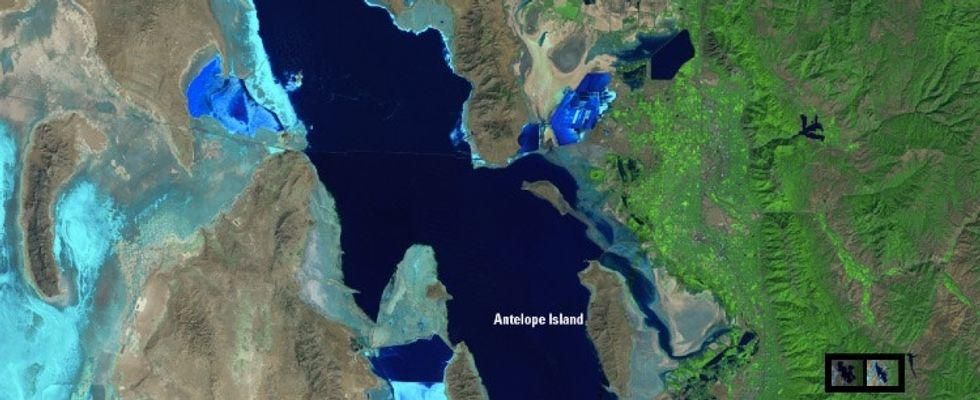

Water supplies have shrunk with a possible link to climate change.
All images from NASA.
Persistent drought has shrunk water supplies throughout much of the West. Scientists now think this may be linked to climate change.
4. And they showed the Mississippi pouring over its banks in March 2016.
Before:
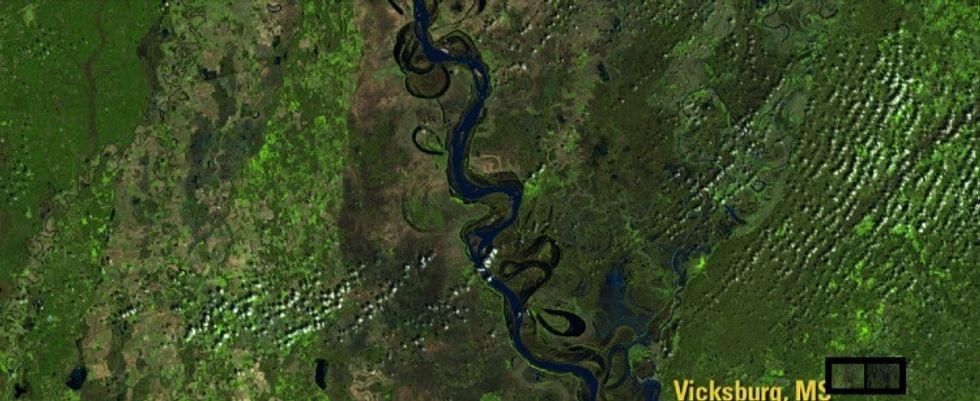

Satellite image of the Mississippi Delta and river.
All images from NASA.
After:
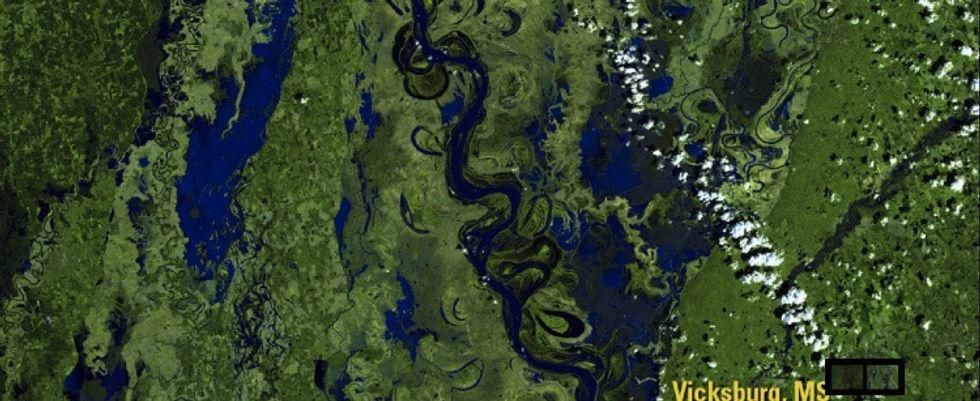

Rivers overflow their banks with spring run offs.
All images from NASA.
Record-breaking rain inundated much of the Mississippi Delta in the spring of 2016, causing the mighty river to spill over its banks.
5. In West Virginia, surface mining reshaped mountaintops.
Before:
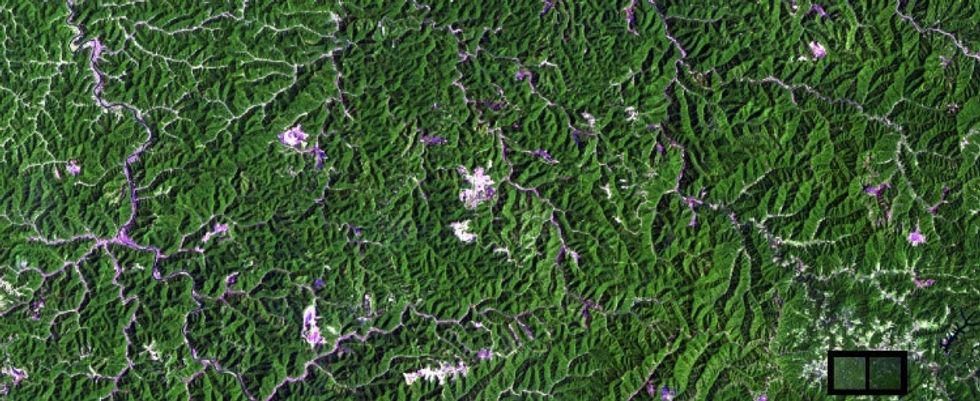

West Virginia before surface mining.
All images from NASA.
After:

West Virginia after surfacing mining for coal.
All images from NASA.
Mountaintop mining is often used to search for coal and can have lasting effects on the land.
6. In Washington state, the Oso mudslide changed the Earth back in 2014.
Before:

Mudslides can create significant change to an environment.
All images from NASA.
After:
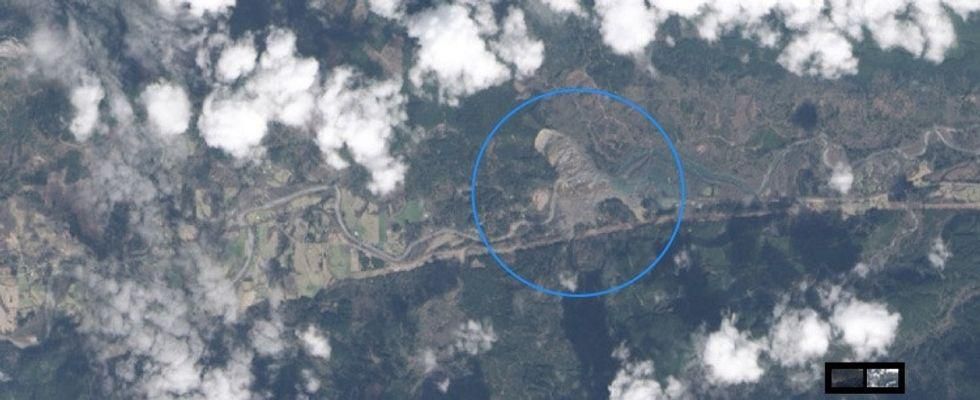

A landslide reshapes a community and kills 43 people in Washington state.
All images from NASA.
43 people were killed in the March 2014 landslide in western Washington.
7. In Louisiana, sediment carried by water created new land.
Before:

Water carries sediment which changes the topography.
All images from NASA.
After:
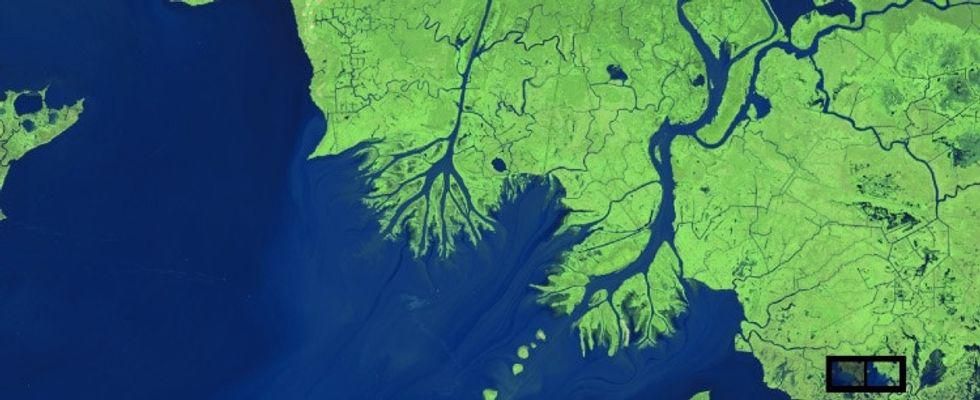

Sediment can create new land.
All images from NASA.
Rivers and streams often carry sediment with them. As they slow down and reach the coast, that sediment falls out of the water. Over time, this can create new land, as you can see above.
8. The images show Hurricane Isaac touching down in Louisiana.
Before:
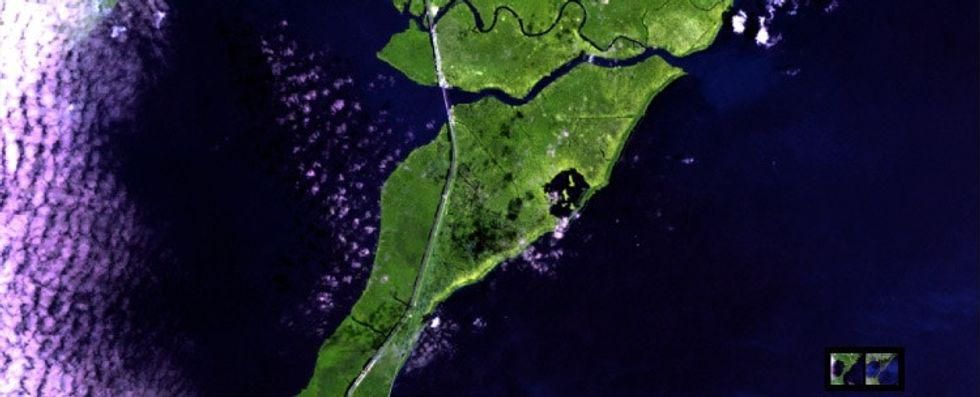
Satellite image before the hurricane.
All images from NASA.
After:
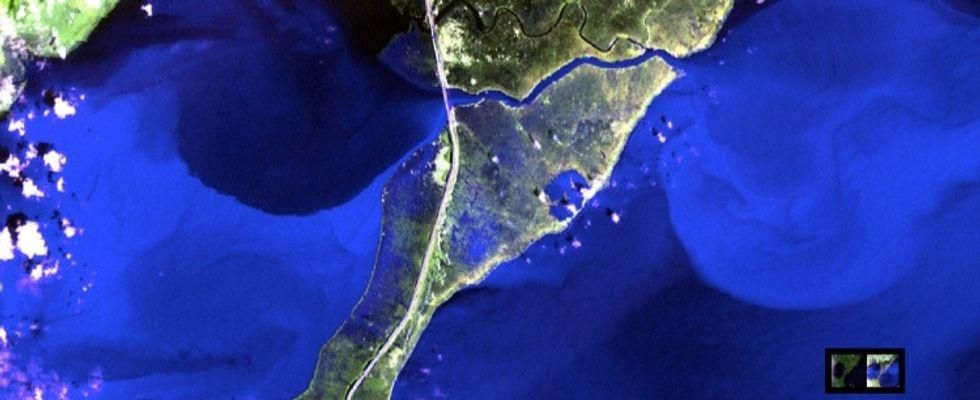

Image of the flooding of Louisiana after the hurricane.
All images from NASA.
Hurricane Isaac hit the gulf coast in August 2012. 41 people lost their lives and more than $2 billion worth of damage occurred. Above you can see the flooding that still lingered afterward.
9. And warming temperatures shrink Alaska's Columbia Glacier.
Before:
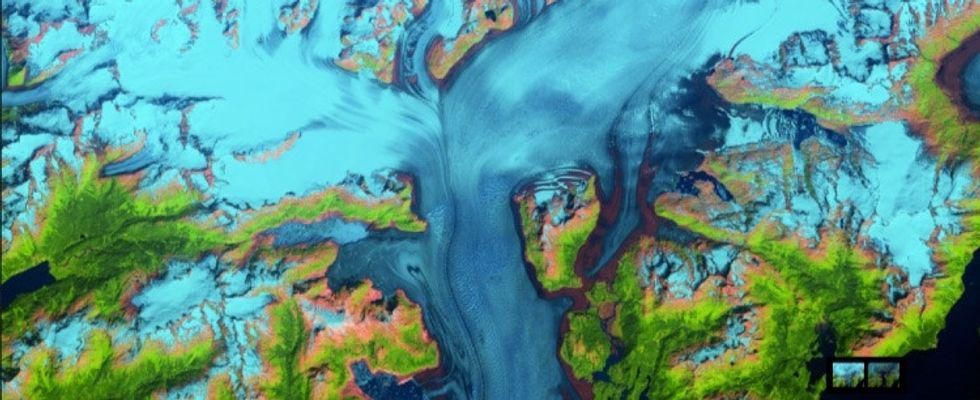

Alaska’s Columbia Glacier as seen from satellite.
All images from NASA.
After:
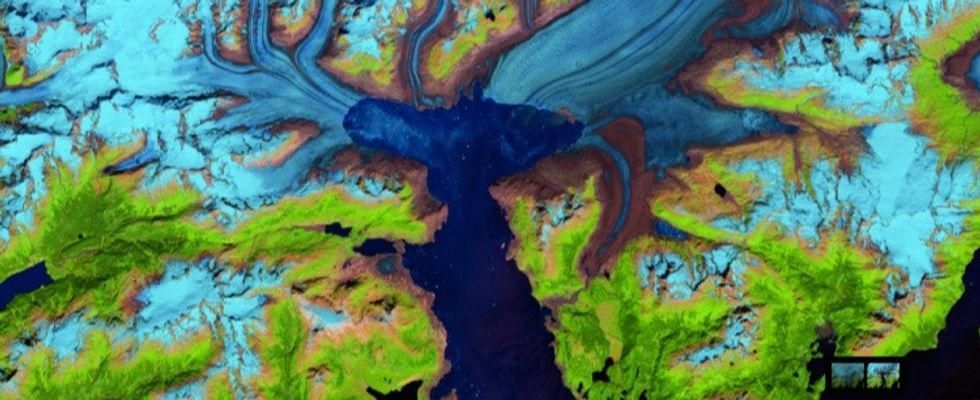

Warmer global temperatures have shrunk many glaciers.
All images from NASA.
Over the last 28 years, warmer global temperatures have shrunk many glaciers, including Alaska's Columbia Glacier. From above, the shrinkage is crystal clear.
10. Meanwhile, our cities grew and expanded, like this image of San Antonio, Texas, shows.
Before:
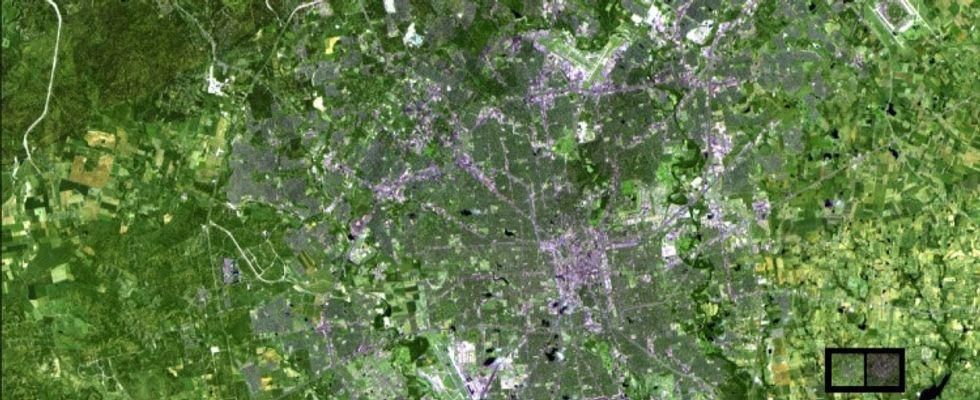

The growing community of San Antonio, Texas.
All images from NASA.
After:
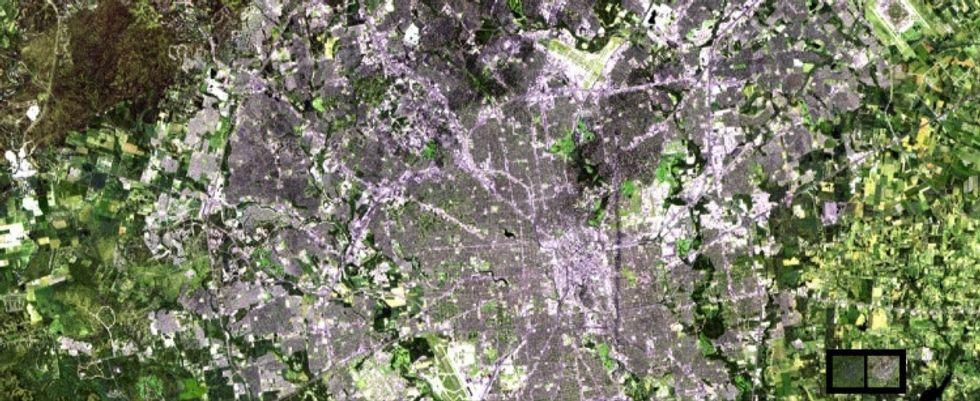

The city has started to take up more space than the natural environment.
All images from NASA.
San Antonio — home of the Alamo and the Spurs basketball team — had a population of just over 1 million people in 1991. Today, it's added another 400,000 people.
The above images are only a small set of the many pictures NASA released. Globally, there were a ton of other interesting sites, like entire lakes turning red in Iran, new islands being formed by ocean volcanoes, and dams flooding rainforests in Brazil.
The world — and our country — is constantly changing, and we play a part in that.
Sometimes nature changes us, such as people having to respond to floodwaters, but we also know humans affect the Earth as well. And while it's true that the Earth has gone through natural cycles, we know it's now happening faster than ever before.
As the Earth will continue to change, it's important to remain aware of how we affect the Earth — and how the Earth affects us.
This article originally appeared on 01.23.17
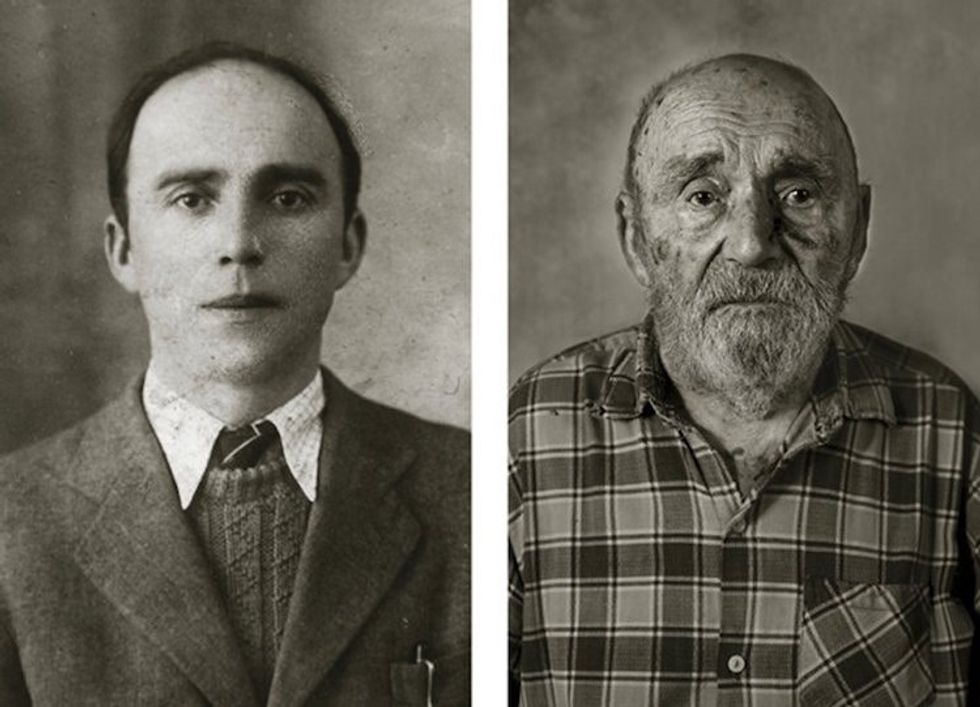
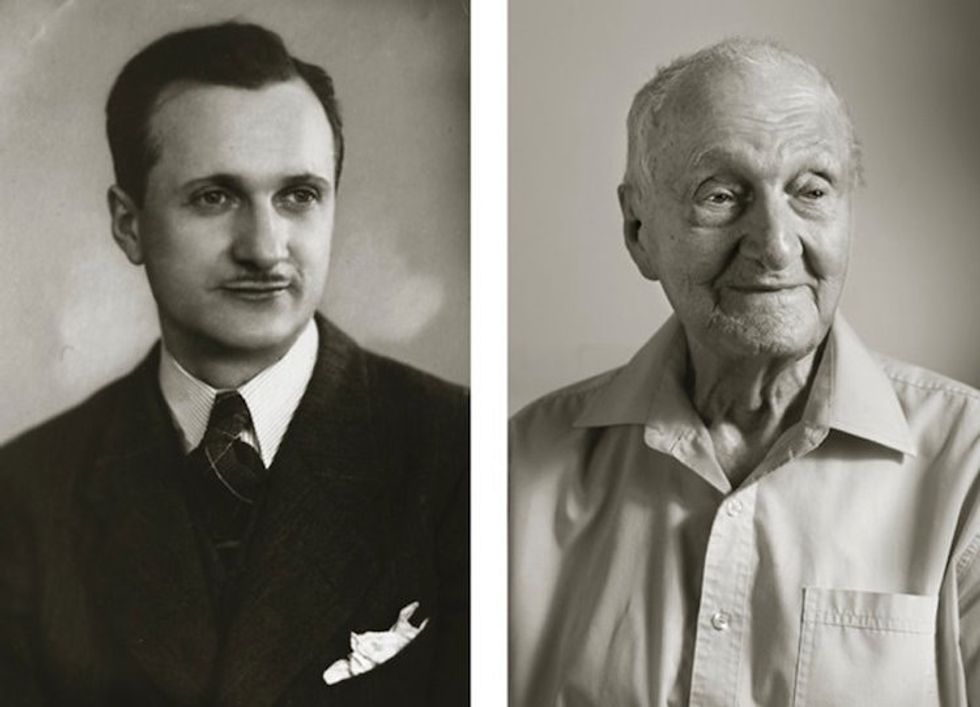
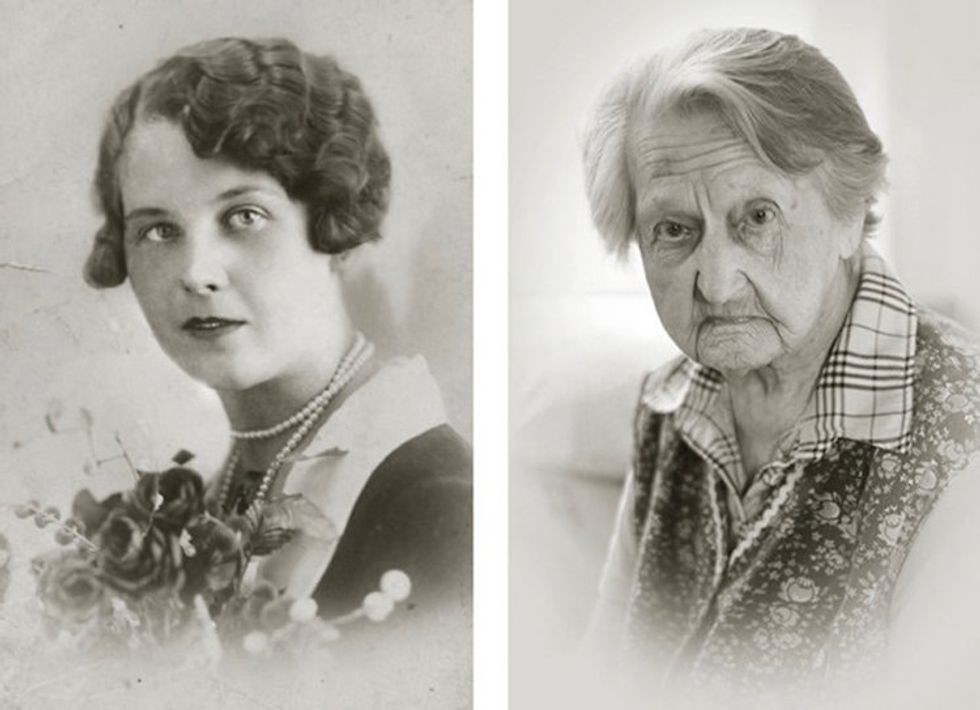
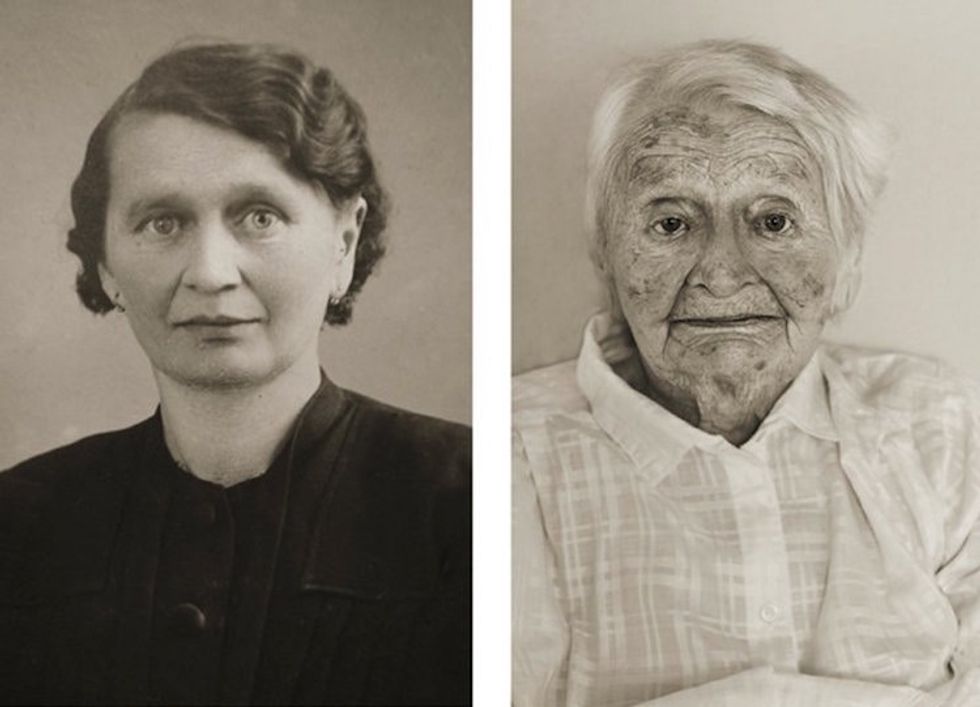
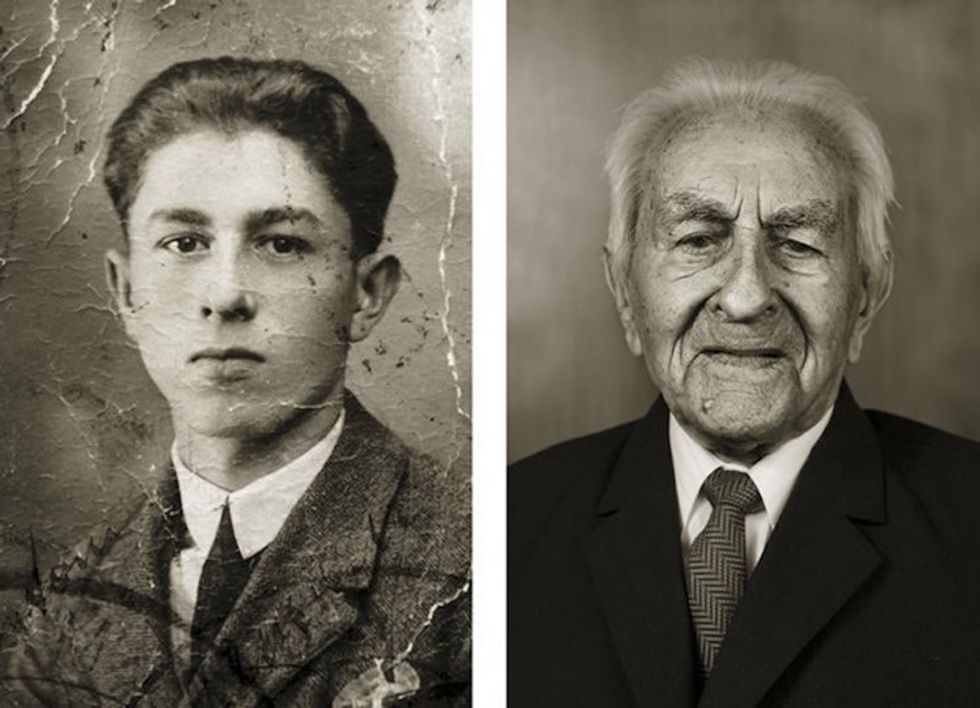
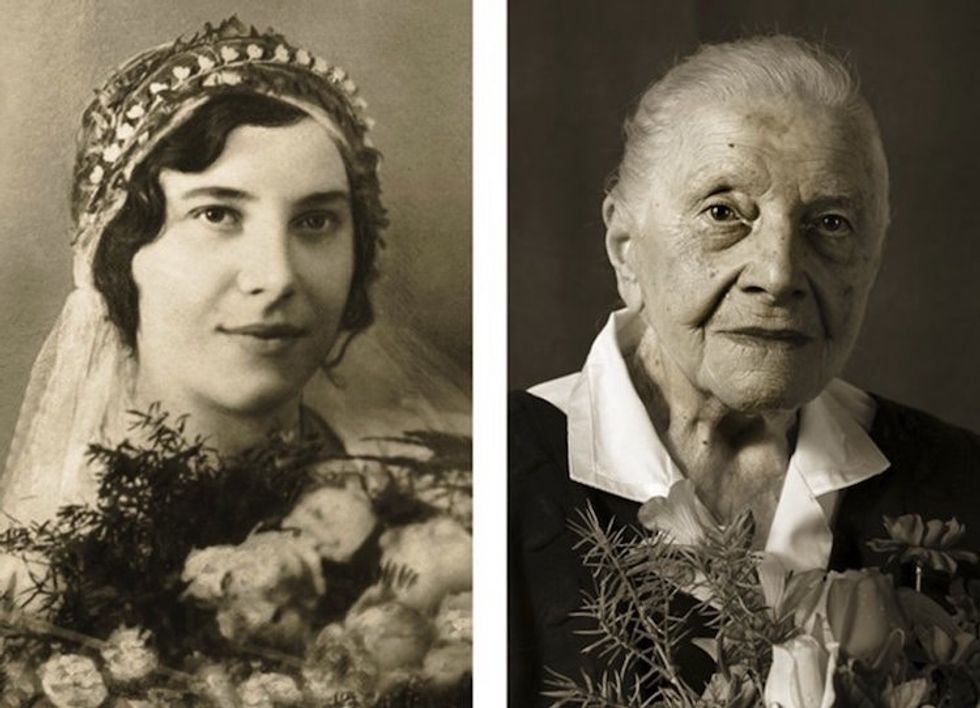
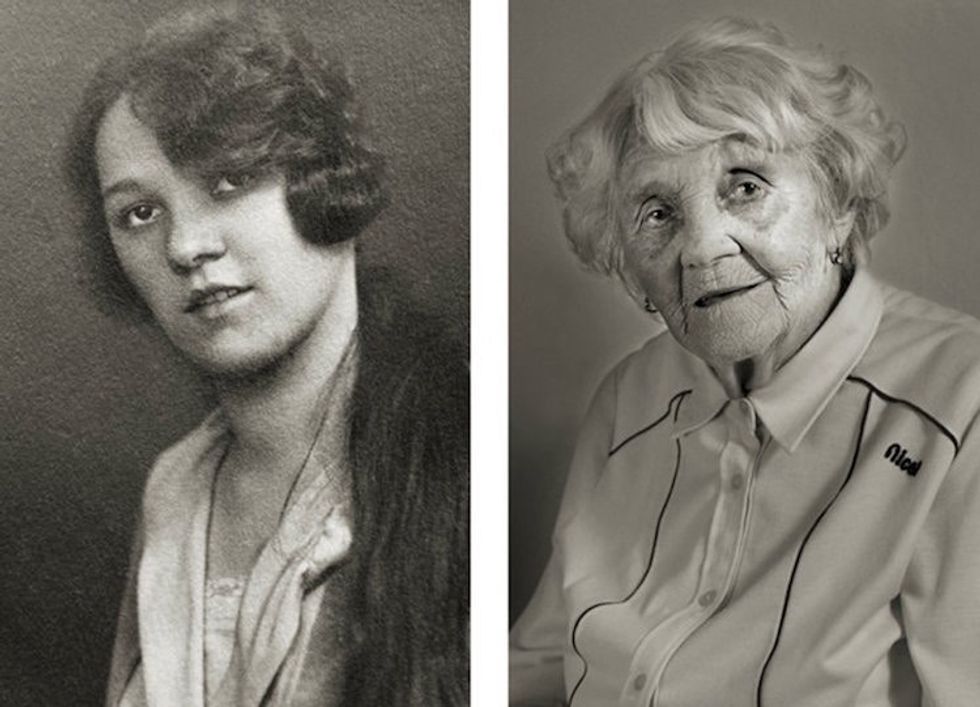
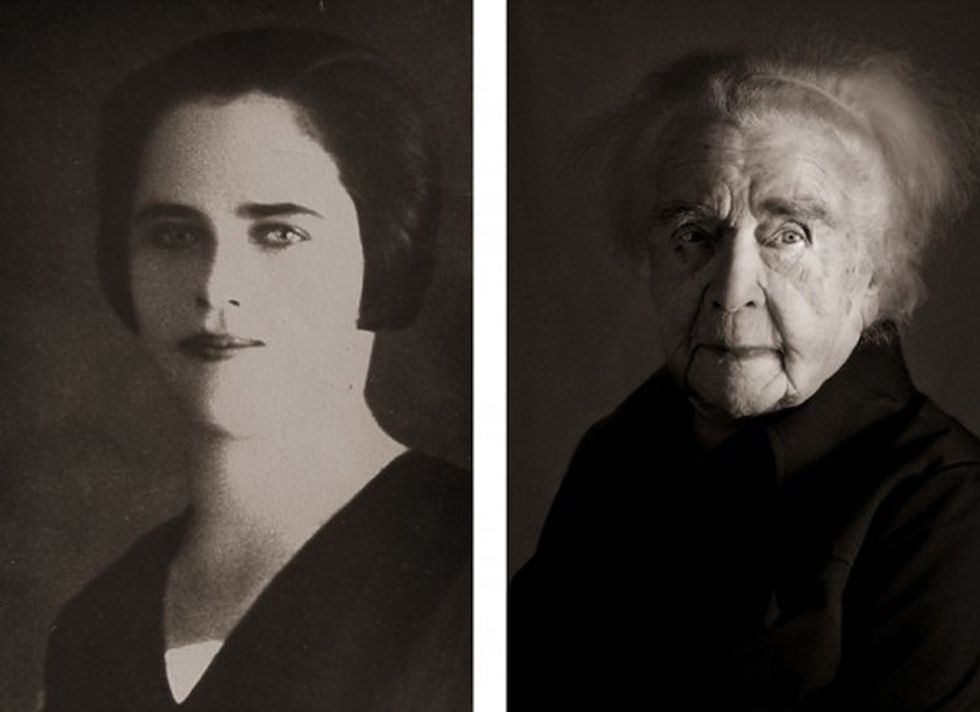
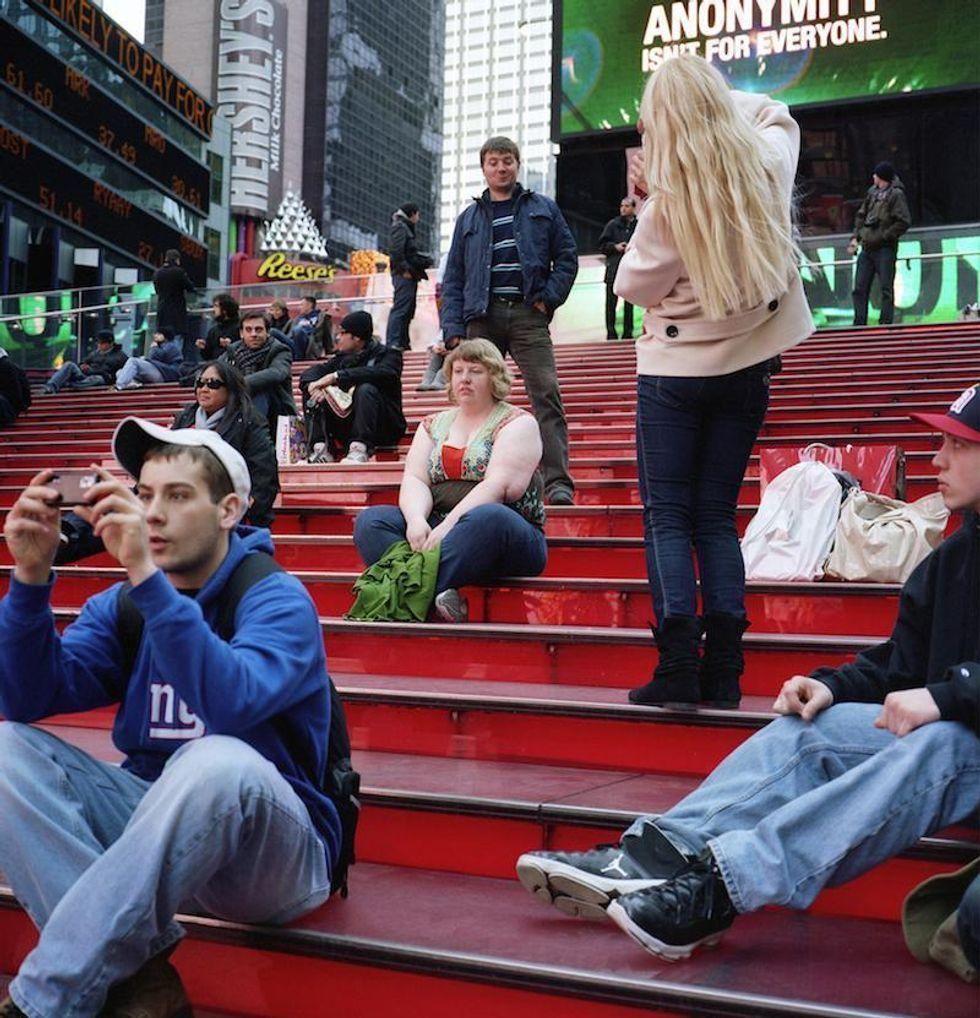
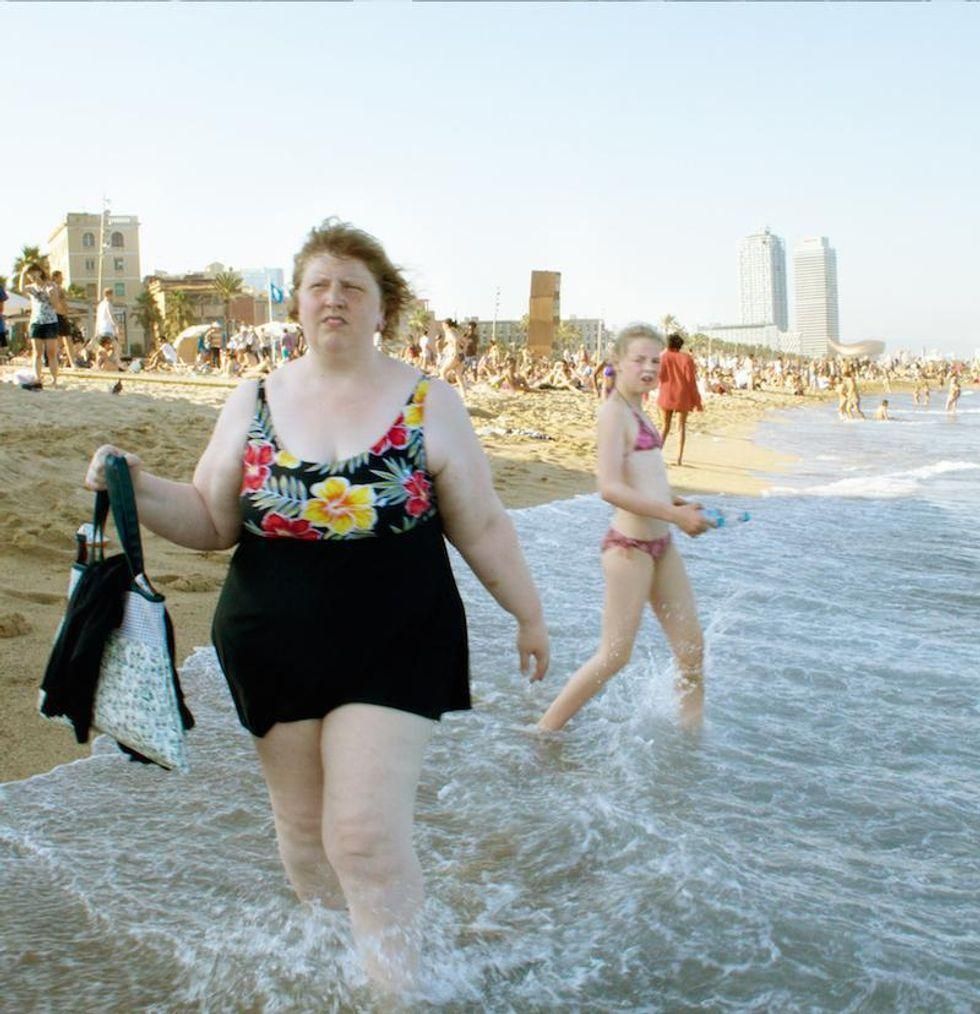
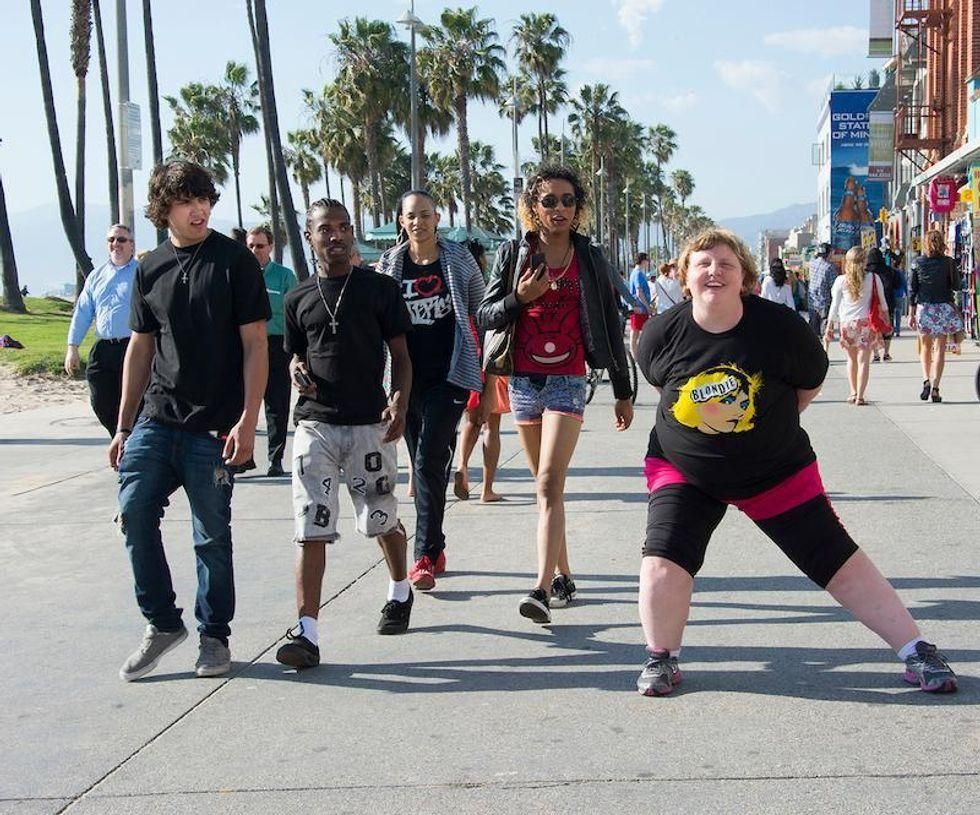
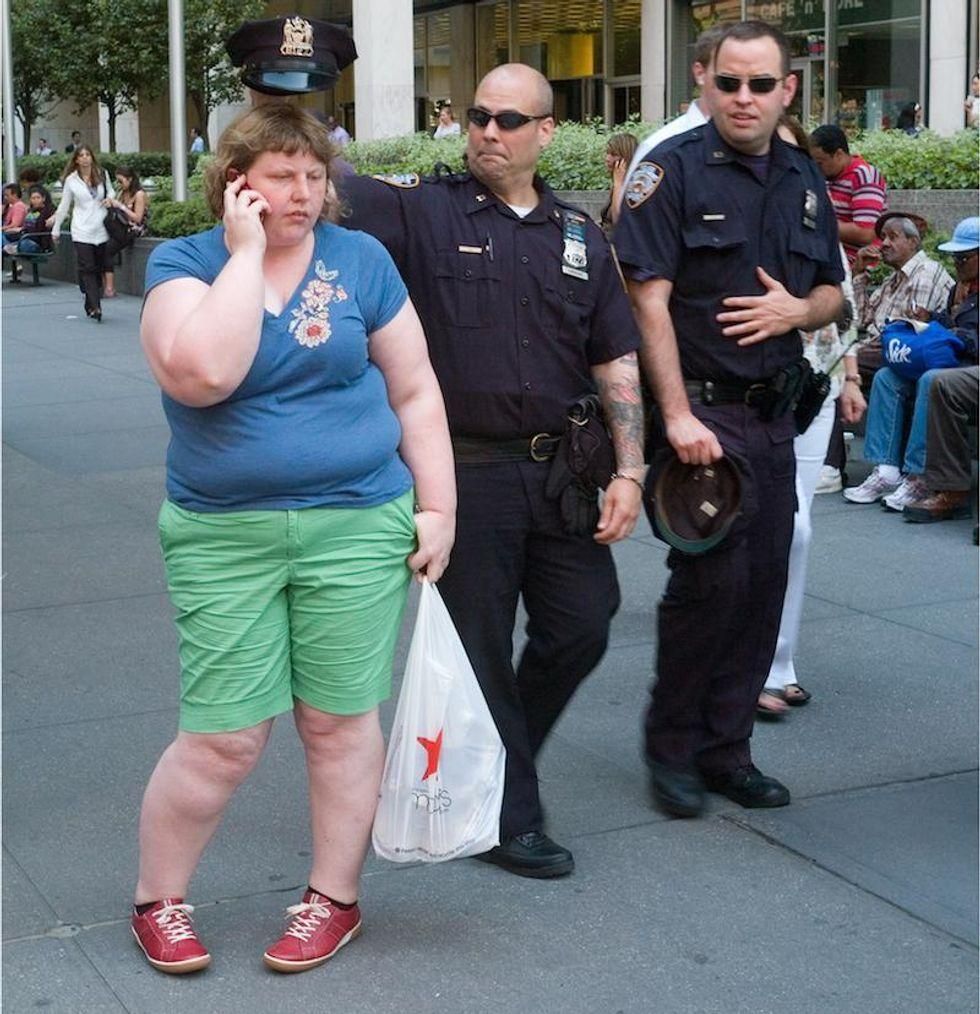



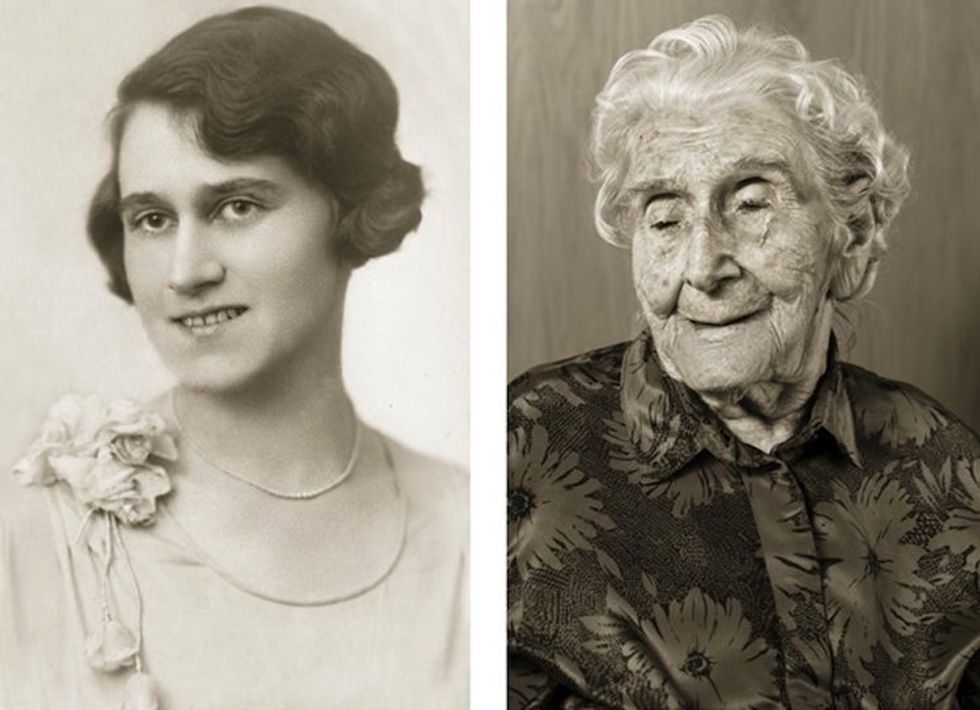



















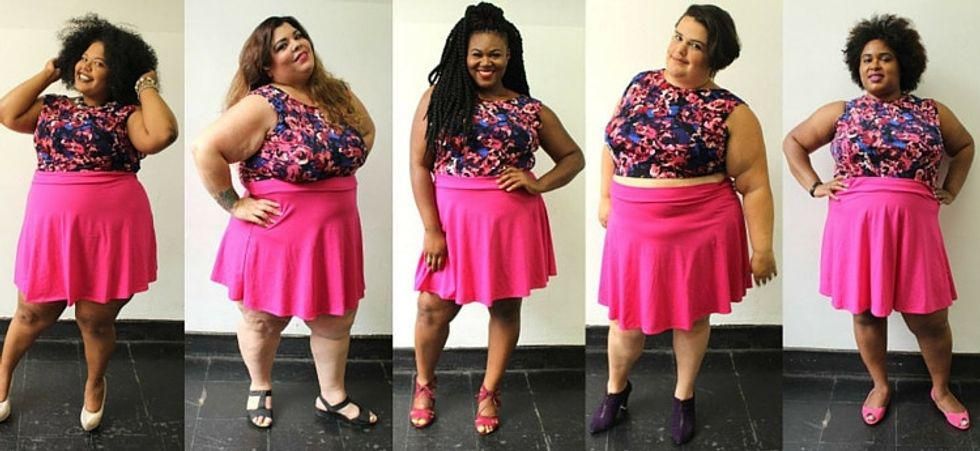
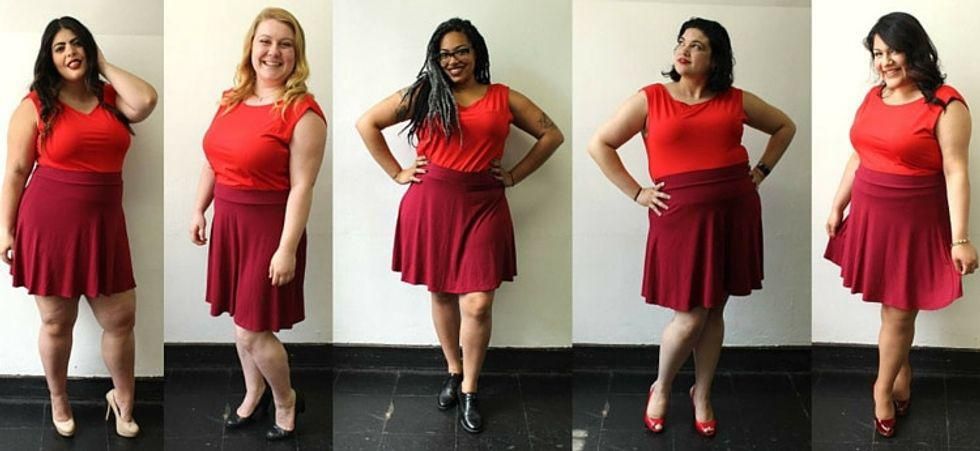
 Image via
Image via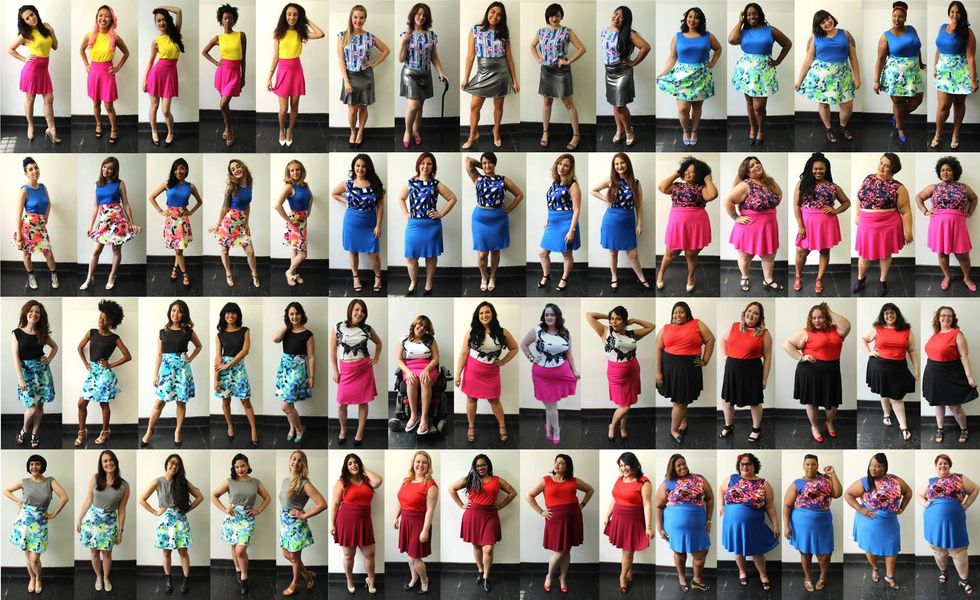  All images via Smart Glamor, used with permission.
All images via Smart Glamor, used with permission.