Ancient Hawaiian land system could transform sustainability's future—and it’s going viral
Welcome to the world of Ahupua’a.
Ancient Hawaiians were agricultural masters.
Switch to electric, use less water, recycle everything: in a time when fighting climate change seems insurmountable, an incredible solution is re-emerging from the ancient past—and it’s making major waves on TikTok. The ahupuaʻa system, Hawai’i’s approach to land management before the once-sovereign nation was colonized, is shocking the world as people discover its incredible potential to revolutionize sustainability—and potentially solve our modern climate crisis.
@ben_jamin_witu You cannot convince me we are more technologically advanced when ancient societies used nature as their technology and balanced themselves for thousands of years. VC: Hyperspective on IG. #landback #foodsoverignty #indigenous #wisdom #tiktok #fyp ♬ Lights Are On - Instrumental - Edith Whiskers
Meet Benjamin Kaimipono (@ben_jamin_witu), a Native Hawaiian (Kanaka ‘Ōiwi) TikTok creator whose videos—some original, some reposts—about Native Hawaiian life, practices, and history are creating a vitally important tapestry of a culture erased. One of the videos, a repost from @hyperspective on Instagram, (a boutique creative agency in Honolulu) depicts a simulated version of the Hawaiian ahupua’a system with the caption: “You cannot convince me we are more technologically advanced when ancient societies used nature as their technology and balanced themselves for thousands of years.”
The responses are filled with pride, respect, and wonder. One commenter wrote, “This is why land back is crucial today with global warming at an all-time high! Indigenous peoples are in tune with the land and know better than anyone else how to take care of it ✊🏽.” Others appreciated Kaimipono's sharing of Native Hawaiian knowledge, with one person writing: “This... is the proper use of the 'āina. live and learn and always Aloha 'Āina. Proud to be Hawaiian. Ha'aheo au. 😎🤙🏾” (According to Lāna'i Culture & Heritage Center, “'āina” is generally translated as “land” but directly means “that which feeds”; “Ha'aheo au” means “I am proud.”)
Another wrote:
“Hawaiians understood what it meant to live righteously off the land, and we're centuries ahead of their time with resource management. There's connection to the land is a key value. That's why native cultures always knew how to be sustainable with the resources they had, and didn't overuse or destroy it.”
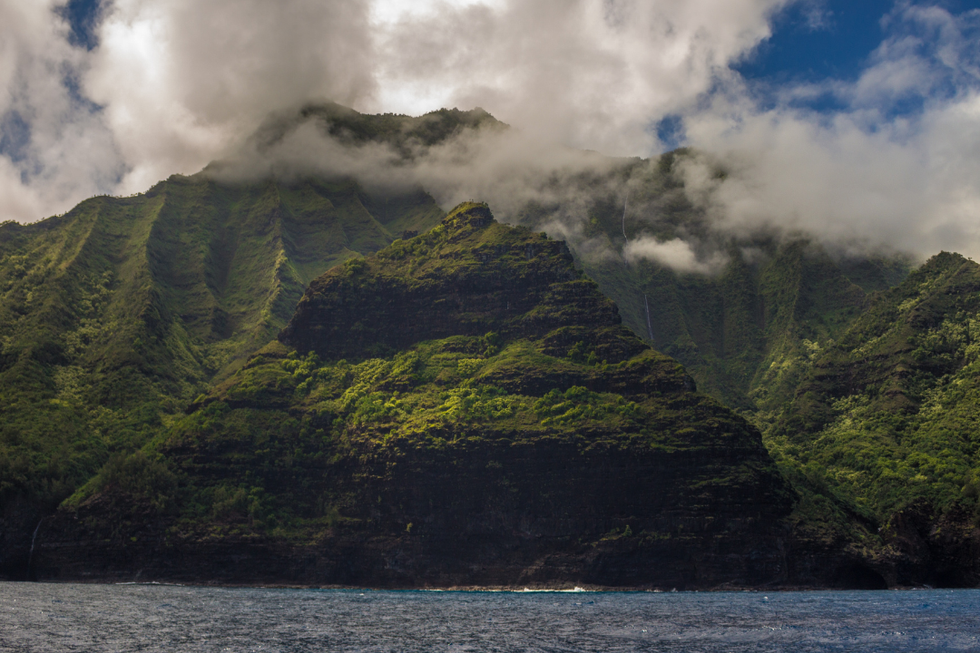

Why this ancient system works
The ahupua’a system, which thrived in Hawai’i for nearly a millennium between 1000 CE to 1848, wasn’t just smart—it was mathematic, geologic, and climatic genius. Picture this: 725 perfectly organized sections across eight islands. Each land parcel averages 5,678 and works in perfect harmony with nature. It was symbiosis at its finest: each ahupua’a operated like a self-contained utopia, combining forests, crops, and fishing zones, demonstrating a master class in resource management. This way, Hawaiians were able harness the power of the ecosystems around them while both supporting the 800,000 people living on the islands (and growing) and maintaining the land’s integrity.
In their seminal paper, “The Ahupua’a as a Traditional Hawaiian Resource Management Model for a Sustainable Coastal Environment,” researchers David W. Blane and Christopher Chung describe the ahupua’a as “a practical and rational approach to resources management that conforms with the existing geography and its resources rather than altering them for human convenience,” adding:
“…as you may already have surmised, the ahupua‘a means much more. The ahupua‘a embodies a unique relationship between the Hawaiian people and the land as well as the practical and rational approaches applied to insure the sustainability of the natural environment from overexploitation, pollution, and extinction.”
Land management magic
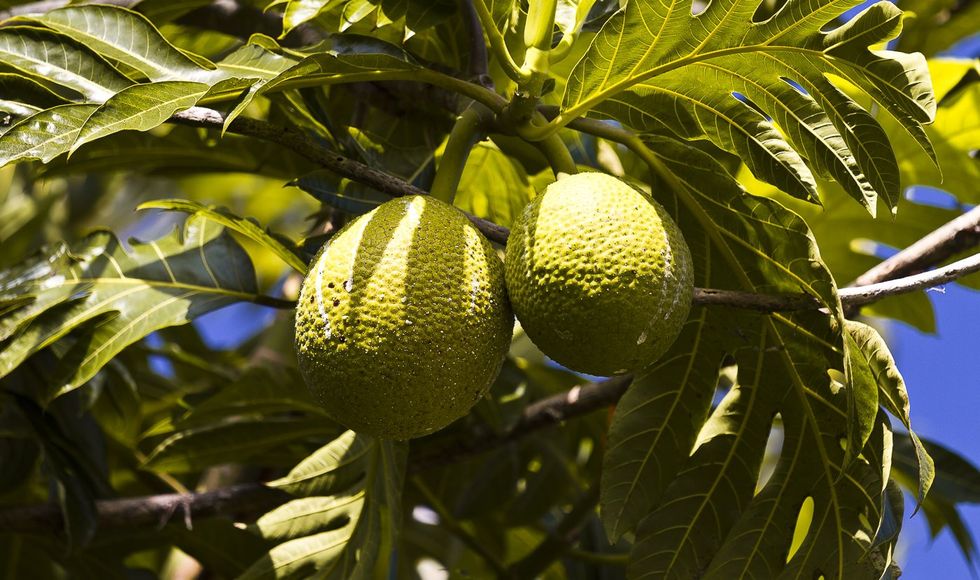
This could get very scientific very fast, but here’s the simple version: ahupua’a were wedge-shaped land units that spanned from the mountains (mauka) down through the cultivated lowlands (mala) to the sea (makai). This way, each unit, each slice, had everything they needed to survive: forests to harvest wood from and collect bird feathers; irrigated agricultural terraces (lo’i) where they mostly grew taro, and dryland farms used to cultivate sweet potato (’uala), coconuts (niu), breadfruit (’ulu), and bananas (mai’a), just to name a few. Each ahupua’a also contained a coastal and marine area, where Hawaiians could fish and produce salt.
The leadership structure was also pure brilliance: each ahupua’a had its own chief (ali’i), overseer (konohiki), and priests (kahuna) who worked together, overseeing the administration of their land and ensuring that resources were used efficiently and sustainably. But perfection on this scale takes more than just good delegation; the ahupua’a leadership also incorporated important Native Hawaiian values like respect (aloha), cooperation (laulima), and stewardship (mālama) to ensure that everything remained balanced (pono). According to the North Shore Sustainable Communities Plan, here’s what made it all work:
- When resources ran low, they immediately stopped harvesting to preserve resources.
- They closed certain fishing areas seasonally so fish populations could bounce back.
- Inter-ahupua’a trade was commonplace, so residents felt connected, and the system kept strong.

"The Hawaiians believed that the land, the sea, the clouds and all of nature had a certain interconnectedness, which is why they used all of the resources around them to reach the desired balance in life." - Nation of Hawaii
As we watch our food systems fall apart, coastlines disappear, and farmlands struggle, remember: it doesn’t have to be this way. Modern urban planners could take a page out of the ancient Native Hawaiian’s book, as they construct our future cities, structures, and systems. No one is asking for a 180 total rehaul or a return to 1848. But there are small things we can do. In Hawai’i, they’ve already brought a few of these principles back to life. They’re restoring traditional fishponds, reconnecting forests with their corresponding coastal areas, and empowering local communities to steward their own resources. This is a real, sustainable way forward. Or, as the BBC said: “The ahupuaʻa system of land development, in practice for more than 1,000 years, has the potential to show the world a new path to sustainability." Are you ready to be a part of that change?
- Researchers dumped tons of coffee waste into a forest. This is what it looks like now. ›
- Students brilliantly pranked the school yearbook with the most obnoxious Hawaiian shirt ›
- Hawaiian eco-entrepreneur unites people to fix the Big Island’s massive cardboard problem ›
- Vet techs in Hawaii break out the dance moves to distract a nervous dog during a blood draw ›





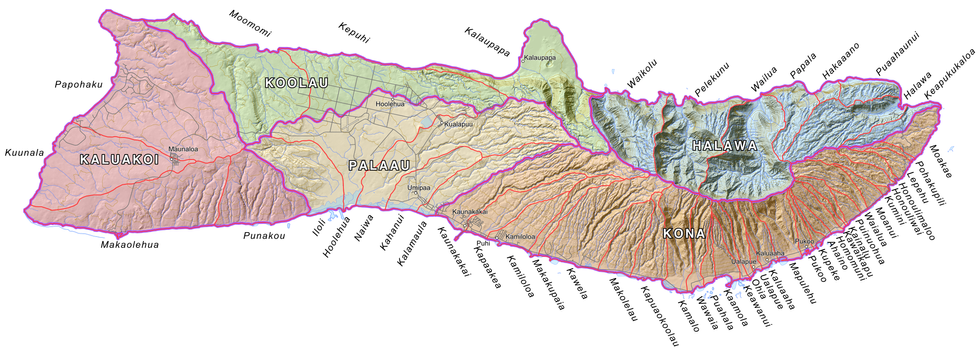 An ahupua'a
An ahupua'a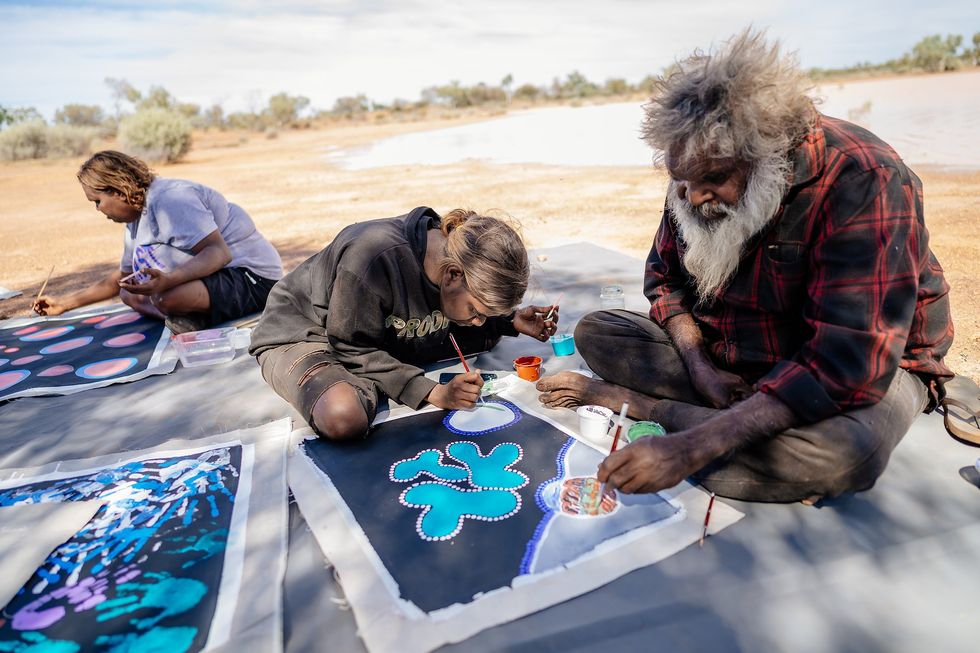  James Roh
James Roh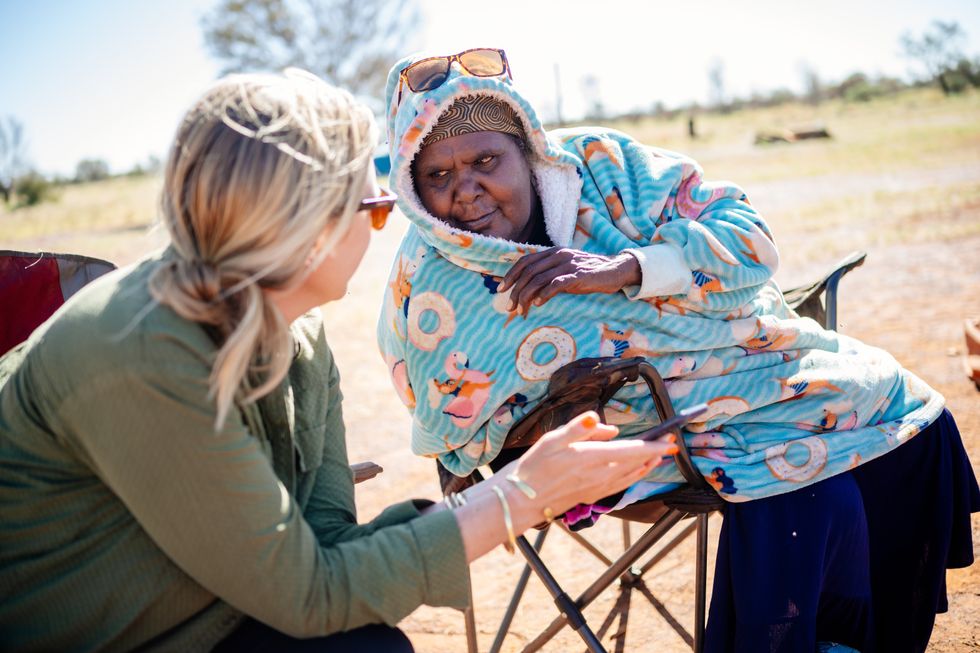 James Roh
James Roh
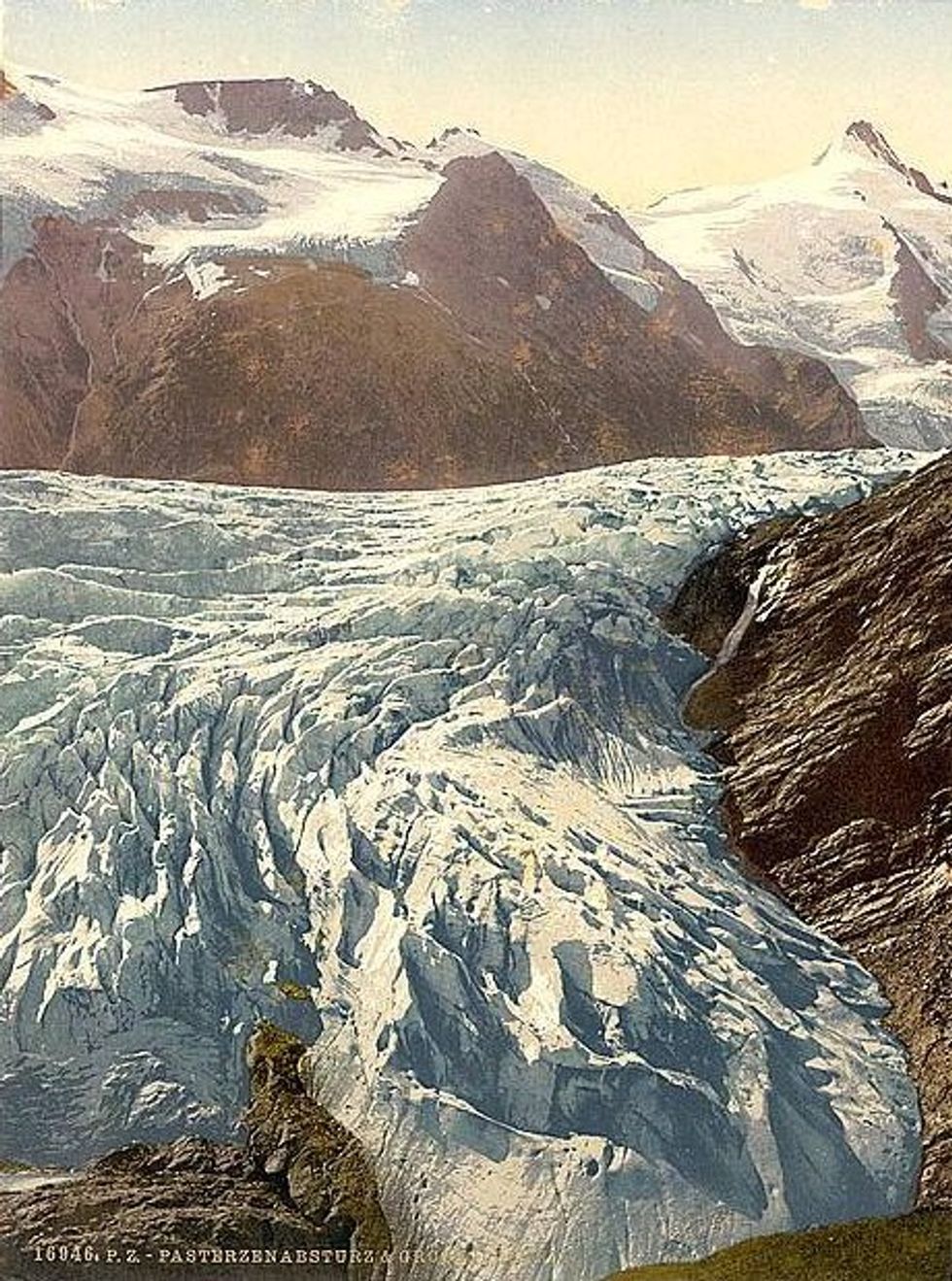
 The Pasterze Glacier in a 1900 postcardImage via Wikicommons
The Pasterze Glacier in a 1900 postcardImage via Wikicommons What's left of the Pasterze GlacierEuropean Union, Copernicus Sentinel-2 imagery
What's left of the Pasterze GlacierEuropean Union, Copernicus Sentinel-2 imagery Serratia marcescens up close.via
Serratia marcescens up close.via