In March 2023, after months of preparation and paperwork, Anita Omary arrived in the United States from her native Afghanistan to build a better life. Once she arrived in Connecticut, however, the experience was anything but easy.
“When I first arrived, everything felt so strange—the weather, the environment, the people,” Omary recalled. Omary had not only left behind her extended family and friends in Afghanistan, she left her career managing child protective cases and supporting refugee communities behind as well. Even more challenging, Anita was five months pregnant at the time, and because her husband was unable to obtain a travel visa, she found herself having to navigate a new language, a different culture, and an unfamiliar country entirely on her own.
“I went through a period of deep disappointment and depression, where I wasn’t able to do much for myself,” Omary said.
Then something incredible happened: Omary met a woman who would become her close friend, offering support that would change her experience as a refugee—and ultimately the trajectory of her entire life.
Understanding the journey
Like Anita Omary, tens of thousands of people come to the United States each year seeking safety from war, political violence, religious persecution, and other threats. Yet escaping danger, unfortunately, is only the first challenge. Once here, immigrant and refugee families must deal with the loss of displacement, while at the same time facing language barriers, adapting to a new culture, and sometimes even facing social stigma and anti-immigrant biases.
Welcoming immigrant and refugee neighbors strengthens the nation and benefits everyone—and according to Anita Omary, small, simple acts of human kindness can make the greatest difference in helping them feel safe, valued, and truly at home.
A warm welcome
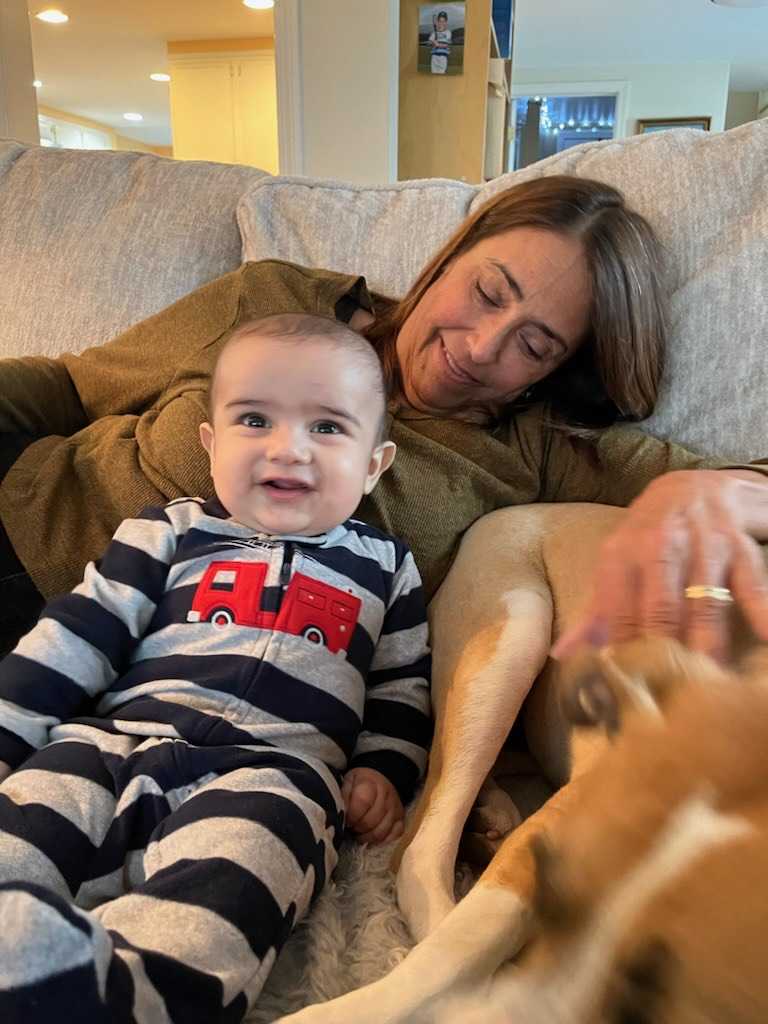

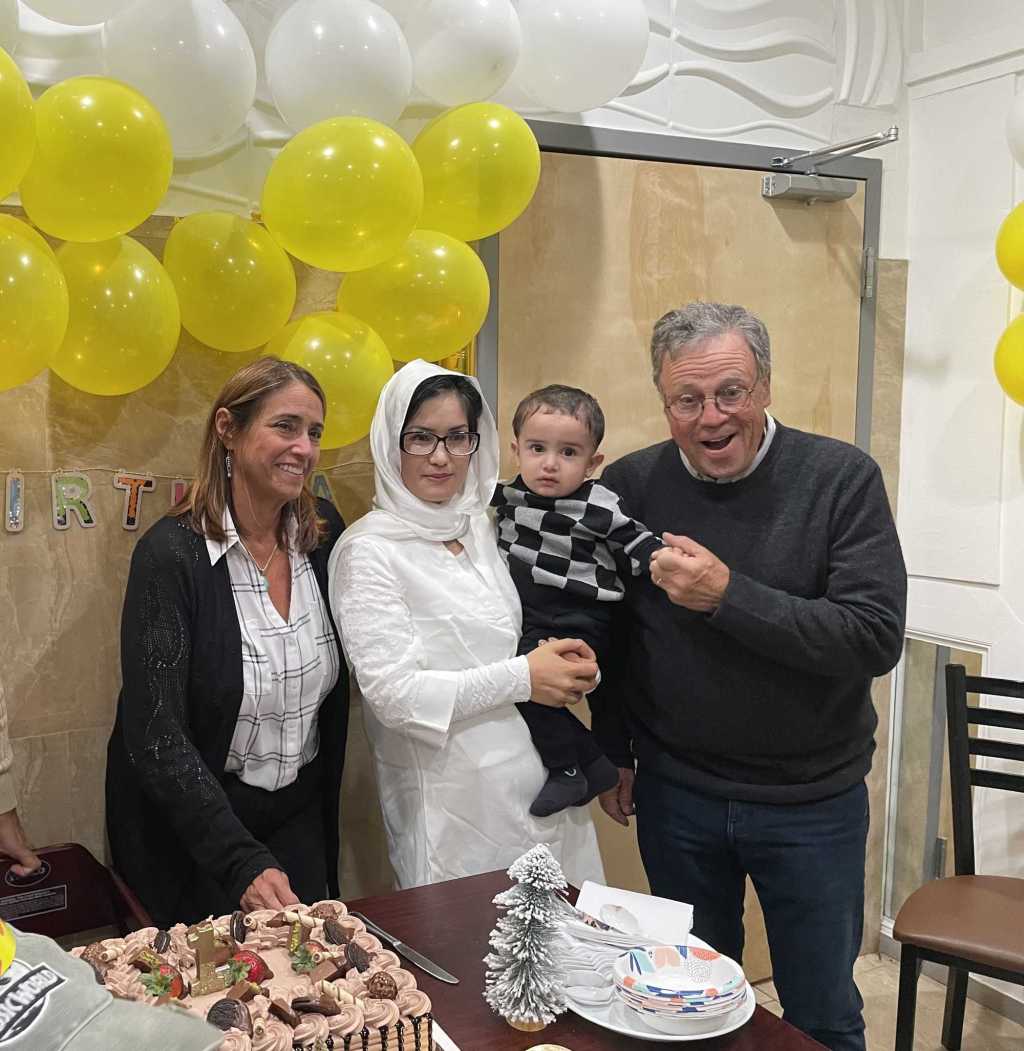
Anita Omary was receiving prenatal checkups at a woman’s health center in West Haven when she met Dee, a nurse.
“She immediately recognized that I was new, and that I was struggling,” Omary said. “From that moment on, she became my support system.”
Dee started checking in on Omary throughout her pregnancy, both inside the clinic and out.
“She would call me and ask am I okay, am I eating, am I healthy,” Omary said. “She helped me with things I didn’t even realize I needed, like getting an air conditioner for my small, hot room.”
Soon, Dee was helping Omary apply for jobs and taking her on driving lessons every weekend. With her help, Omary landed a job, passed her road test on the first attempt, and even enrolled at the University of New Haven to pursue her master’s degree. Dee and Omary became like family. After Omary’s son, Osman, was born, Dee spent five days in the hospital at her side, bringing her halal food and brushing her hair in the same way Omary’s mother used to. When Omary’s postpartum pain became too great for her to lift Osman’s car seat, Dee accompanied her to his doctor’s appointments and carried the baby for her.
“Her support truly changed my life,” Omary said. “Her motivation, compassion, and support gave me hope. It gave me a sense of stability and confidence. I didn’t feel alone, because of her.”
More than that, the experience gave Omary a new resolve to help other people.
“That experience has deeply shaped the way I give back,” she said. “I want to be that source of encouragement and support for others that my friend was for me.”
Extending the welcome
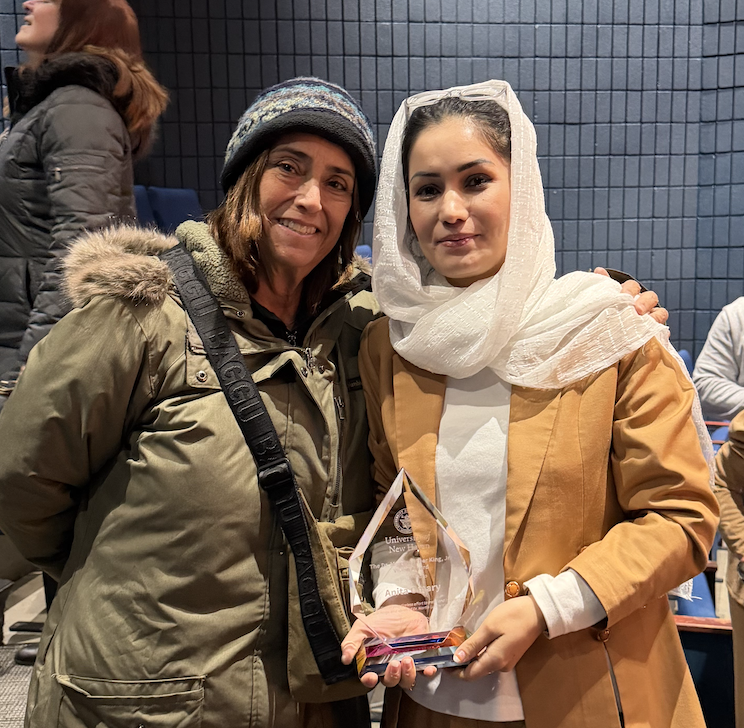

Omary is now flourishing. She currently works as a career development specialist as she continues her Master’s degree. She also, as a member of the Refugee Storytellers Collective, helps advocate for refugee and immigrant families by connecting them with resources—and teaches local communities how to best welcome newcomers.
“Welcoming new families today has many challenges,” Omary said. “One major barrier is access to English classes. Many newcomers, especially those who have just arrived, often put their names on long wait lists and for months there are no available spots.” For women with children, the lack of available childcare makes attending English classes, or working outside the home, especially difficult.
Omary stresses that sometimes small, everyday acts of kindness can make the biggest difference to immigrant and refugee families.
“Welcome is not about big gestures, but about small, consistent acts of care that remind you that you belong,” Omary said. Receiving a compliment on her dress or her son from a stranger in the grocery store was incredibly uplifting during her early days as a newcomer, and Omary remembers how even the smallest gestures of kindness gave her hope that she could thrive and build a new life here.
“I built my new life, but I didn’t do it alone,” Omary said. “Community and kindness were my greatest strengths.”
Are you in? Click here to join the Refugee Advocacy Lab and sign the #WeWillWelcome pledge and complete one small act of welcome in your community. Together, with small, meaningful steps, we can build communities where everyone feels safe.
This article is part of Upworthy’s “The Threads Between U.S.” series that highlights what we have in common thanks to the generous support from the Levi Strauss Foundation, whose grantmaking is committed to creating a culture of belonging.