People are dumbfounded when they learn this little known secret to burning candles correctly
There's an art to avoiding the "memory ring" that makes a candle tunnel around the wick.
The evolution of candles from lighting necessity to scented ambience creator is kind of funny. For thousands of years, people relied on candles and oil lamps for light, but with the invention of the light bulb in 1879, fire was no longer needed for light. At that time, people were probably relieved to not have to set something on fire every time they wanted to see in the dark, and now here we are spending tons of money to do it just for funsies.
We love lighting candles for coziness and romance, relishing their warm, soft light as we shrink from the fluorescent bulb craze of the early 2000s. Many people use candles for adding scent to a room, and there are entire candle companies just for this purpose (Yankee Candles, anyone?). As of 2022, candles were an $11 billion business. Michael Scott once said they're the number one fastest growing product in the scent aroma market.

With their widespread use, you'd think we'd know a thing or two about candles, but as it turns out, a whole bunch of us have been burning candles wrong our entire lives without knowing it.
A recent post on Twitter X started the education session:
"Just learned that my fiancé, who buys candles all the time and we literally always have candles burning, did not actually know how they work and blew out a medium first burn candle 30 minutes after I lit it when I wasn’t paying attention and ruined it," the user wrote.
Many people had no idea what she was talking about. In fact, the original since-deleted post went viral with hundreds of people asking: Huh? So the OP explained.
"If a candle is not burned for long enough on first burn to melt edge to edge it will create a 'memory ring.' Once a candle has a memory ring, it will continue to tunnel and never burn all the way across."
Now THAT'S something almost everyone has experienced. Candles are pretty expensive, so it's frustrating when all that delicious-smelling wax gets left behind. Apparently, a short first burn (in this case, just 30 minutes) is one of the main culprits of a ruined candle.
Tunneling is the name of the phenomenon where a narrow tube-shaped area of candle continues to burn deeper and deeper, leaving lots of "waste" wax around its edges. Experts agree that the first burn should last 2-4 hours at least to avoid an uneven or narrow memory ring. (But don't burn a candle for over 10 hours at a time or you risk too much carbon buildup on your wicks.)
"If a candle is not burned for long enough on first burn to melt edge to edge it will create a 'memory ring.' Once a candle has a memory ring, it will continue to tunnel and never burn all the way across."
"This is why you should not light a large candle at night, which is unlikely to burn all the way across before you need to blow out to go to bed. Allow at least one hour per inch of candle width," she went on.
So that's why candles always end up with a hole in the middle, making us think the candle companies are just running a scam to make us go through candles faster. Nope. It's user error, and many people were flabbergasted by this realization.
"This is the most useful information I’ve been given my entire adult life," wrote one person.
"This skill should be taught in schools," shared another. "The amount I’ve wasted on half burnt candles is outrageous, the amount of times I’ve used Algebra since leaving school = 0."
"When I worked at Pier 1 in the 90s I got to go to some candle workshop that taught us the correct way to use (and therefore sell) candles and that is probably some of the most useful knowledge I've carried in my head this long life," shared another.
Well, never say 'never,' because here's the good news: a tunneled candle can be fixed!
Probably the easiest way is to avoid tunneling your candles in the first place by burning them long enough upon first burn to liquify the entire top layer of wax. Again, that's usually 2-4 hours.
It also helps to care for the wicks regularly! Good wicks allow for a clean, even burn. Trim the burnt ends before lighting the candle and, if possible, use a snuffer instead of blowing out the flames with your mouth. Using a candle warmer is another way to get an even melt; with the added perk of making the scented wax last much, much longer.
But even if you do accidentally "ruin" a candle, it can be recovered. Placing a ring of foil around the candle with just a small opening at the top for the flame will help trap heat and help the edges of the wax melt on the next burn. Once the memory ring evens out, you can burn the candle like normal again.
(In fact, you can even use a candle warmer to melt the wax back to even and then resume burning. Some clever candlers even put candles on the hot pad of their coffee makers as a DIY hack.)
- YouTube www.youtube.com
The candle posts also prompted a separate discussion about candles and indoor air quality and the volatile organic compounds that are released when they are burned.
Some people equated burning candles with having a small engine running in your living room, though according to the Cleveland Clinic, there's scant evidence that the amount of toxins released by burning candles is actually hazardous to your health, especially if you use high quality candles in a well-ventilated area.
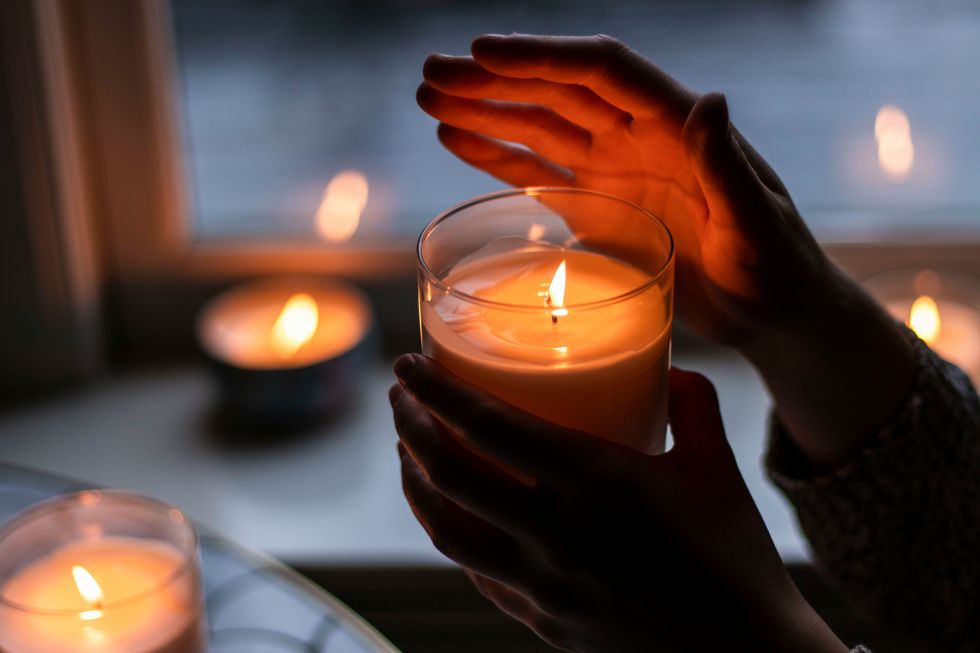

How do you know if a candle is "high quality"? First, check the wick for metal. Lead in wicks is not nearly as common as it used to be, but best not to risk it if you find metal in the wick. Second, choose soy, beeswax, palm or coconut wax candles instead of paraffin, which is petroleum-based product and more likely to put off soot and smoke particles. Everyone reacts differently to different amounts of particulates in the air, so if you find yourself getting headaches or respiratory symptoms when using candles, it's probably best to avoid them.
But if you tolerate them, feel free to enjoy as recommended,—just make sure that first burn melts the wax all the way to the edges to avoid the dreaded tunneling.
This article originally appeared last year. It has been updated.




 Every child should get to experience this.
Every child should get to experience this.  live coralsPhoto by
live coralsPhoto by  Photo by
Photo by 
 a couple of animals that are in some waterPhoto by
a couple of animals that are in some waterPhoto by  green algae underwater photographyPhoto by
green algae underwater photographyPhoto by  James Roh
James Roh James Roh
James Roh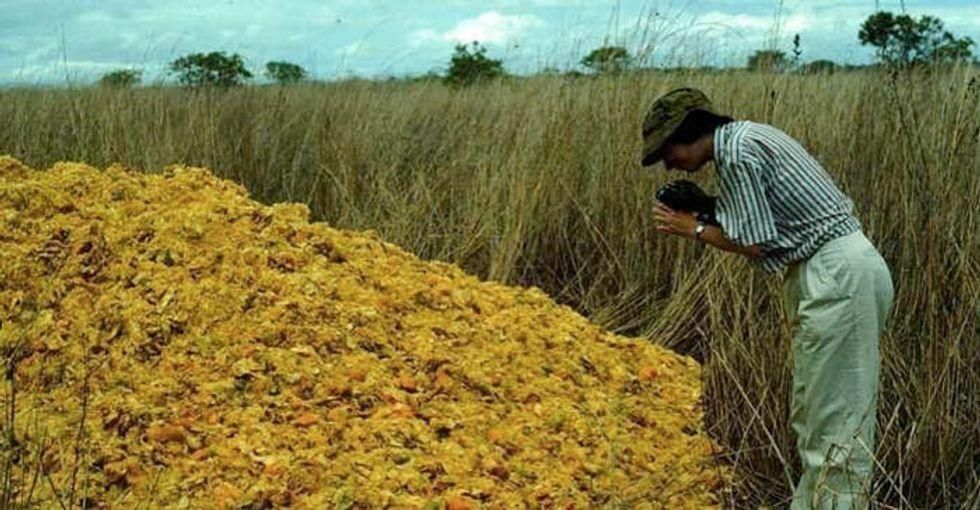 The first deposit of orange peels in 1996.
The first deposit of orange peels in 1996.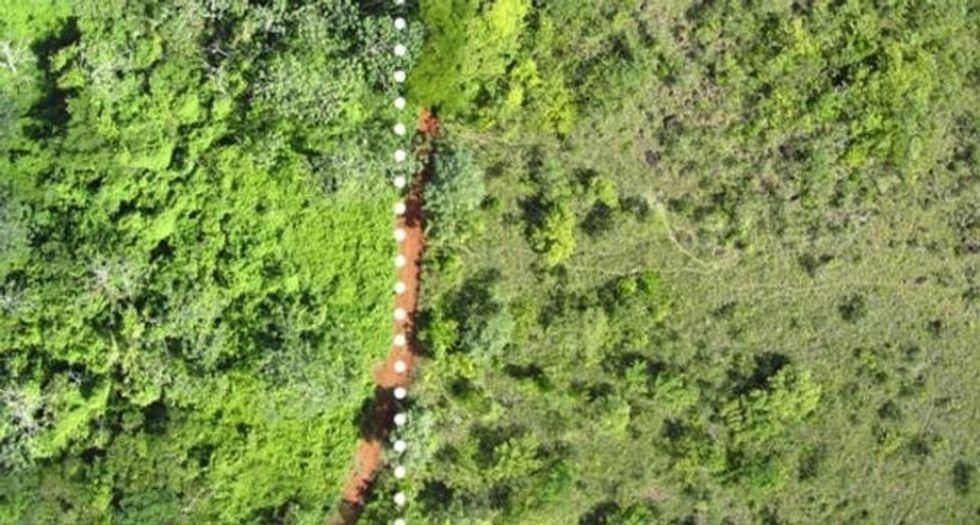 The site of the orange peel deposit (L) and adjacent pastureland (R).
The site of the orange peel deposit (L) and adjacent pastureland (R). Lab technician Erik Schilling explores the newly overgrown orange peel plot.
Lab technician Erik Schilling explores the newly overgrown orange peel plot.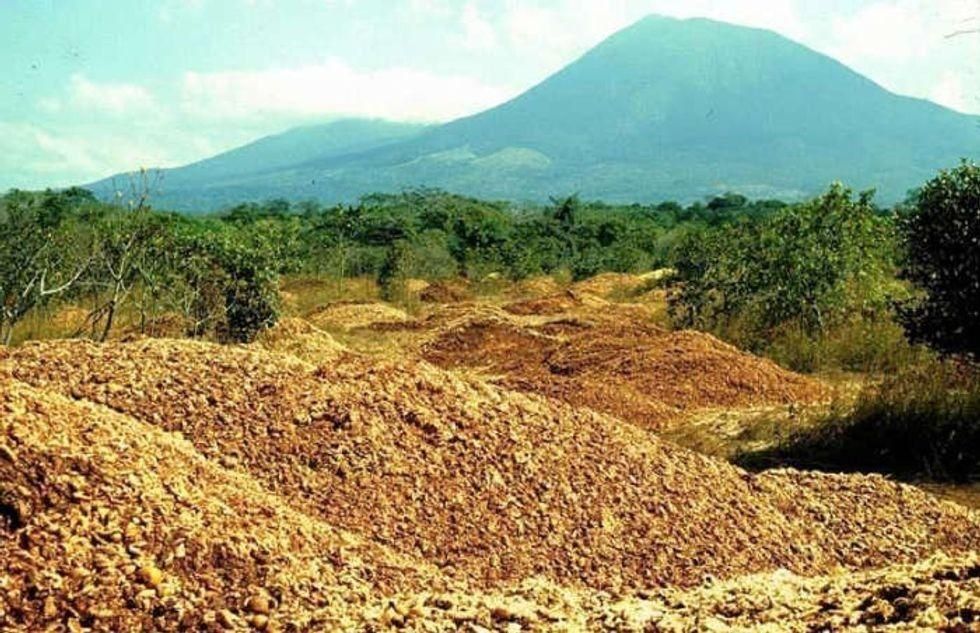 The site after a deposit of orange peels in 1998.
The site after a deposit of orange peels in 1998. The sign after clearing away the vines.
The sign after clearing away the vines. The beautiful, brutal Great Blasket IslandGreat Blasket Island
The beautiful, brutal Great Blasket IslandGreat Blasket Island Hello, seals
Hello, seals  Meet your new stewardsCamille Rosenfeld
Meet your new stewardsCamille Rosenfeld
There's a reason why some people can perfectly copy accents, and others can't