Who ever thought you could fight the effects of drought just by mixing fruits together?
A 16-year-old from Johannesburg, that's who!
Photo by Andrew Weeks, used with permission.
Science whiz Kiara Nirghin, a grade 11 student at St. Martin's School in Johannesburg, came up with an idea that could make a big difference in drought-stricken regions.
"Currently, South Africa is experiencing one of the worst droughts in its history," said Nirghin. "I started looking at it, and not only is it affecting my community, it's a worldwide problem. From there, I started looking at, 'OK. What could I do to lessen the impact that the drought had on South Africa's food supply?' — which is one of the main things that it is affecting."
Photo by unserekleinemaus/Pixabay.
With temperatures rising to blistering levels and South Africa declaring a state of disaster due to drought in eight provinces, Nirghin's game-changing invention couldn't have come at a better time.
Using orange peels and avocado skins, Nirghin created her own superabsorbent polymer (SAP) to nourish crops in desperate need of water.
An SAP is a powder-like material that can take in large amounts of liquid without taking up a lot of space. In fact, it's known to absorb hundreds of times its own weight. SAPs are planted alongside crops to create mini reservoirs of water that keep soil moist longer and allow growing plants to survive with less rainfall or water.
A helpful slide from Nirghin's award-winning submission. Image via Google Science Fair.
According to Science Direct, the problem with many SAPs is they're made from some pretty harsh chemicals that can harm people as well as the environment. So Nirghin set out to create a more natural, biodegradable alternative.
"I started looking at what characterized a superabsorbent polymer and how I could emulate that characterization," she said. "And one of those things were the polysaccharide found in orange peels."
GIF via Google Science Fair.
Nirghin breaks down her process in a video for the Google Science Fair. First, she boiled the orange peels to extract pectin (more typically used as a gelling agent in jams and jellies). She then combined the pectin with sun-dried orange peels, baked the mixture, crushed it into a powder, and added more sun-dried orange peels and avocado skins.
The project, dubbed "No More Thirsty Crops," earned Nirghin the grand prize at this year's Google Science Fair.
GIF via Google Science Fair.
Not only is Nirghin's SAP biodegradable, it's also affordable — and creating it produces less pollution than regular SAPs.
"[Commercial SAPs are] not biodegradable and they’re extremely costly," said Nirghin. "And one of the important aspects that’s often overlooked is that the making of the superabsorbent polymers pollutes the environment. … The production is not only timely, it’s very difficult to reproduce in poorer areas … So I looked at basically minimizing all those negative aspects."
In Nirghin's research paper, she estimates her SAP would cost about $30 to $60 per metric ton to mass produce — whereas current commercial SAPs can go for a staggering $2,000 to $3,000 per metric ton. Even better? Nirghin found her method to be more effective at retaining water than commercial SAPs.
Nirghin now has her sights set on getting her SAP in as many hands as possible and affecting more positive change around the world.
"I would love for it to go into actual farms out there," Nirghin said. "I want it to actually be supplied to farmers all over the world that are currently experiencing a drought. I don’t want to keep it as an idea that I just came up with … I would really like for it to go out and help people out there."
On top of her Google Science Fair victory, Nirghin's invention also garnered her a spot on Time's 30 Most Influential Teens of 2016 — an honor that could help her spread even more good. For starters, she's already looking to expand her SAP to test water filtration as well as oil removal from water.
Nirghin also has an inspiring message for anyone looking to follow in her footsteps.
Nirghin (third from left) and her fellow finalists. Photo by the Nirghin family, used with permission.
She said, "One of the main things is looking at what your community is facing because it's great coming up with an idea, but unless it impacts your community and makes it better — like the Google Science Fair says, 'What will you make better?' — that should be one of the main driving forces to lessen the impact of the problems of your community."
From there, just think of that idea as a freshly planted crop. With a little nourishment and attention, it can grow into something even stronger and more essential than you ever imagined.
- Researchers have figured out why return trips always seem to go by more quickly - Upworthy ›
- Why you can't grow a Hass avocado from a Hass avocado seed - Upworthy ›
- How to store half an avocado without it turning brown ›
- How to store half an avocado without it turning brown - Upworthy ›
- Physicist delights with ruler-breaking science demonstration - Upworthy ›
- Why you can't grow a Hass avocado from a Hass avocado seed - Upworthy ›
- A juice company dumped orange peels in a national park. Here's what it looks like now. - Upworthy ›
- The mating habits of anglerfish are capturing the internet - Upworthy ›
- Scientists prove that coin tosses are not 50/50 - Upworthy ›
- Woman brings her own avocado to a restaurant - Upworthy ›
- A juice company dumped orange peels in a national park. This is what it looks like today. - Upworthy ›
- The world's slowest experiment has been going nearly 100 years - Upworthy ›
- Meghan Markle delivers powerful speech in South Africa - Upworthy ›
- Kid shares unhinged Rice Krispies Treat science experiment - Upworthy ›
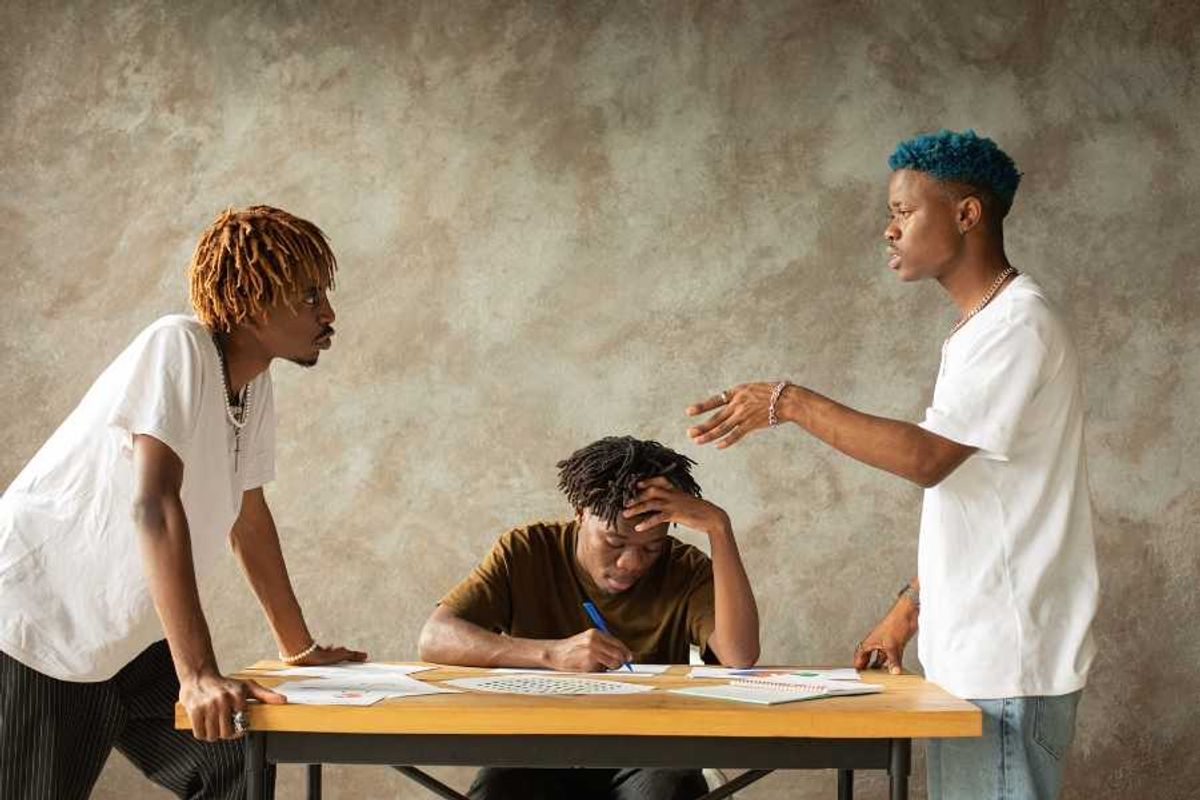
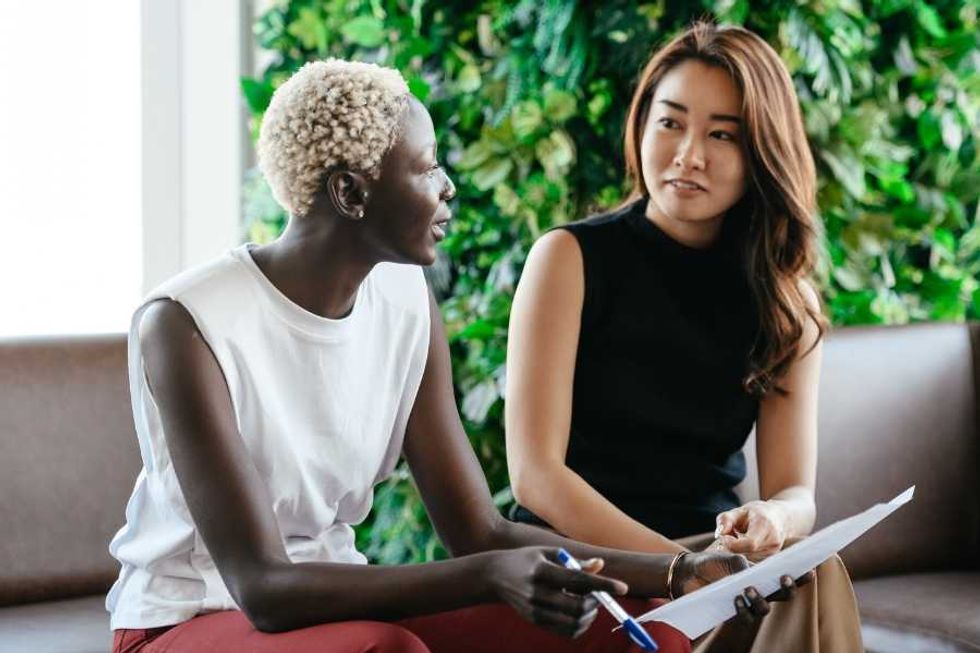


 Questions are more effective than facts when it comes to disagreements.
Questions are more effective than facts when it comes to disagreements.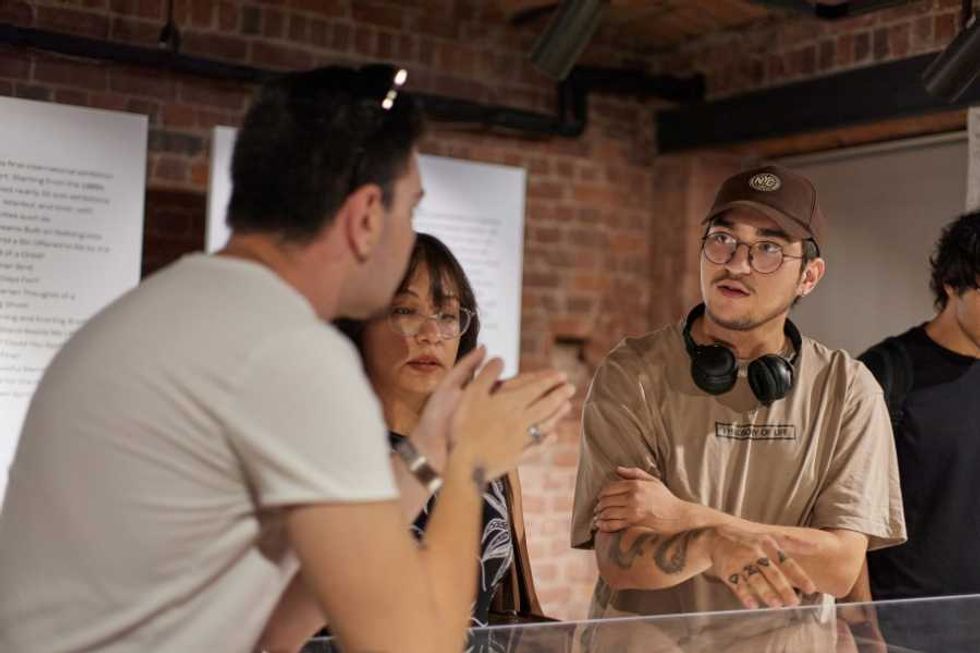 Asking people to elaborate leads to more open-mindedness.
Asking people to elaborate leads to more open-mindedness.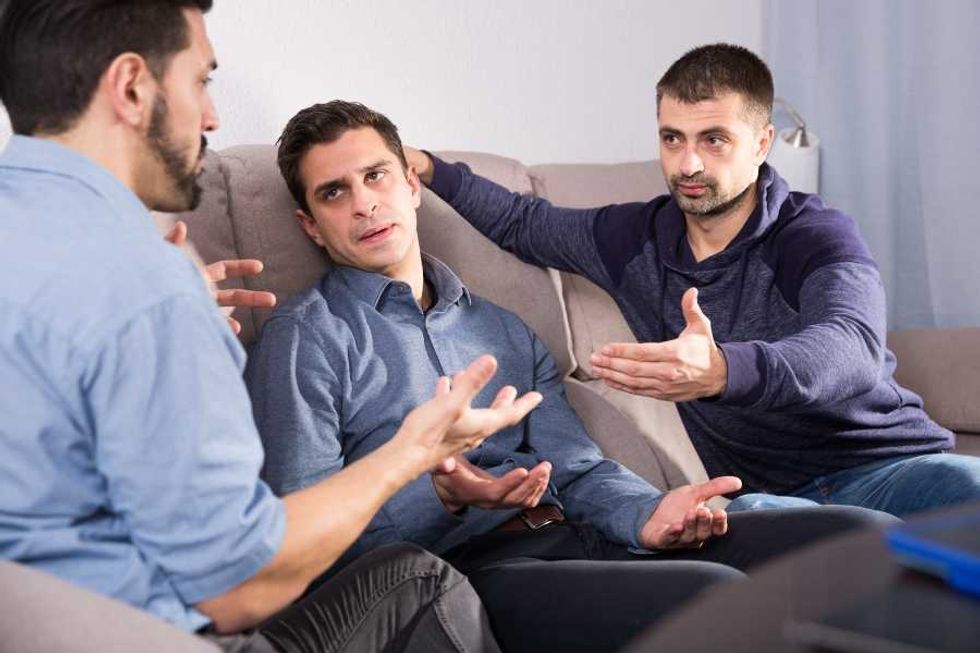 Curiosity can help people get closer to consensus.
Curiosity can help people get closer to consensus. 
 A young girl has a tantrum. Photo credit:
A young girl has a tantrum. Photo credit: 
 Individual impact isn't as inspiring to Gen Z as it was to
Individual impact isn't as inspiring to Gen Z as it was to  Gen Z is much more black and white about behaviors than previous generations.
Gen Z is much more black and white about behaviors than previous generations. 
 Jimmy Carr became a dad in 2019.Albin Olsson/
Jimmy Carr became a dad in 2019.Albin Olsson/
 A teen girl getting a hug.
A teen girl getting a hug. A teen boy wearing headphones while looking at his phone.
A teen boy wearing headphones while looking at his phone.