Study discovers people don't age steadily, but in dramatic bursts at two specific ages
This explains SO much about your 40s.
If you feel "old" practically overnight, there may be a good reason for that.
Aging is weird. You're trucking along, enjoying your middle-aged life, finally feeling like a real adult, when you look in the mirror one day and gasp. "Where did those wrinkles come from?" "Is that skin on my arm…crepey?!?" "Why am I aching like that?"
Somewhere in your mid-40s, you start noticing obvious signs of aging that seem to arrive overnight. You assumed it was a gradual process that you just hadn't noticed, but it sure as heck felt like it happened really fast.
New research indicates that may very well be the case. A 2024 study from researchers at Stanford tracked thousands of different molecules in people age 25 to 75 and found that people tend to make two big leaps in aging—one around age 44 and another around age 60. These findings indicate that aging can actually happen in bursts.

“We’re not just changing gradually over time. There are some really dramatic changes,” said senior study author Michael Snyder, Ph.D., a geneticist and director of the Center for Genomics and Personalized Medicine at Stanford University. “It turns out the mid-40s is a time of dramatic change, as is the early 60s. And that’s true no matter what class of molecules you look at.” The researchers assumed the mid-40s changes would be attributed to menopausal or perimenopausal changes in women influencing the overall numbers, but when they separated the results by sex they saw similar changes in men in their 40s.
@suddenly_susan_ The accuracy 🤣 #40s #genxtiktok #womenover40 #relatable
"“This suggests that while menopause or perimenopause may contribute to the changes observed in women in their mid-40s, there are likely other, more significant factors influencing these changes in both men and women. Identifying and studying these factors should be a priority for future research,” said study author Xiaotao Shen, PhD, a former Stanford Medicine postdoctoral scholar who now teaches at Nanyang Technological University in Singapore.

The study included 108 participants who submitted blood and other samples every few months for several years. The scientists tracked age-related changes in 135,000 different molecules—nearly 250 billion distinct data points—to see how aging occurs.
The study may shed light on the reasons for jumps in certain diseases and maladies at certain ages. For the 40-somethings, scientists found significant changes in molecules related to alcohol, caffeine, and lipid metabolism, cardiovascular disease, and skin and muscle. For those in their 60s, changes related to carbohydrate and caffeine metabolism, immune regulation, kidney function, cardiovascular disease, and skin and muscle were found.

The study authors did note that lifestyle might play a role in some of these changes. For instance, alcohol metabolism may be influenced by people drinking more heavily in their 40s, which tends to be a period of higher stress for many people. However, the researchers added that these bursts of aging in the mid-40s and early 60s indicate that people may want to pay closer attention to their health around those ages and make lifestyle changes that support greater overall health, such as increasing exercise or limiting alcohol.
The research team plans to study the drivers of these aging bursts to find out why they happen at these ages, but whatever the reasons, it's nice to know that the seemingly sudden onset of age-related woes isn't just in our imaginations.
It's understandable that we worry about aging, as physical signs of aging remind us of our own mortality. We also have all kinds of social messaging that tells us youth is ideal and beautiful and old is bad and ugly, so of course we give aging the side-eye. But none of us can avoid aging altogether, so the more positive and healthy we are in our approach to aging, the better off we'll be, no matter when and to what degree aging hits us.
This story originally appeared last year. It has been updated.
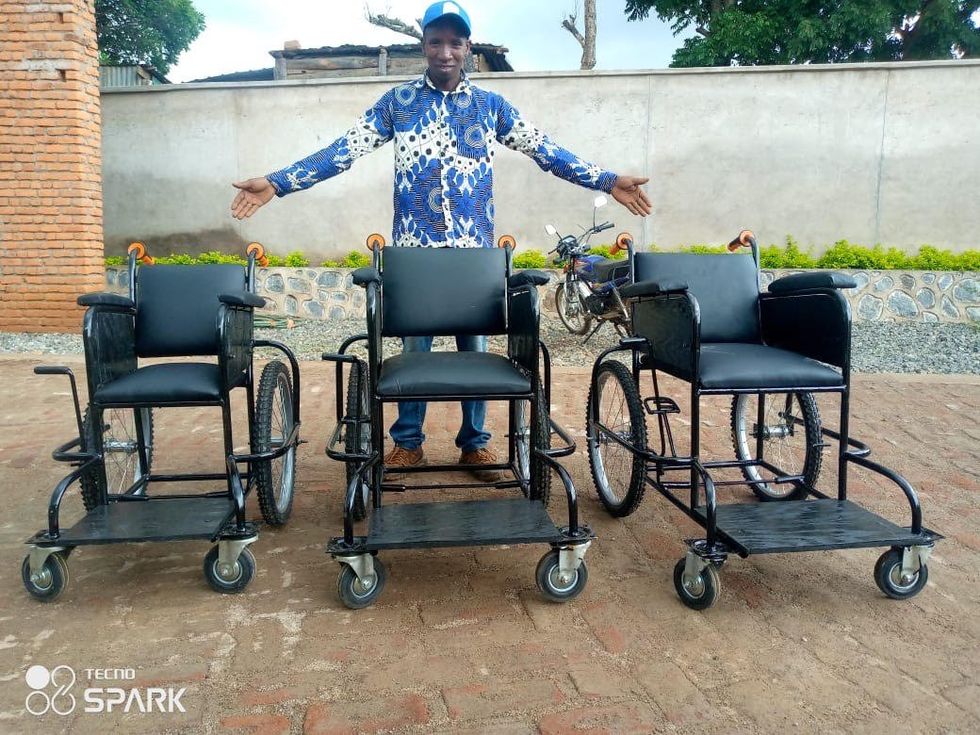




 Malawi Wheels Country Coordinator Gelson Mtinga poses with three new wheelchairs.Courtesy of Malawi Wheels
Malawi Wheels Country Coordinator Gelson Mtinga poses with three new wheelchairs.Courtesy of Malawi Wheels Justin may not be able to walk, but he loves to play soccer.Courtesy of Malawi Wheels
Justin may not be able to walk, but he loves to play soccer.Courtesy of Malawi Wheels Justin in his chair with his brother and a friend.Courtesy of Malawi Wheels
Justin in his chair with his brother and a friend.Courtesy of Malawi Wheels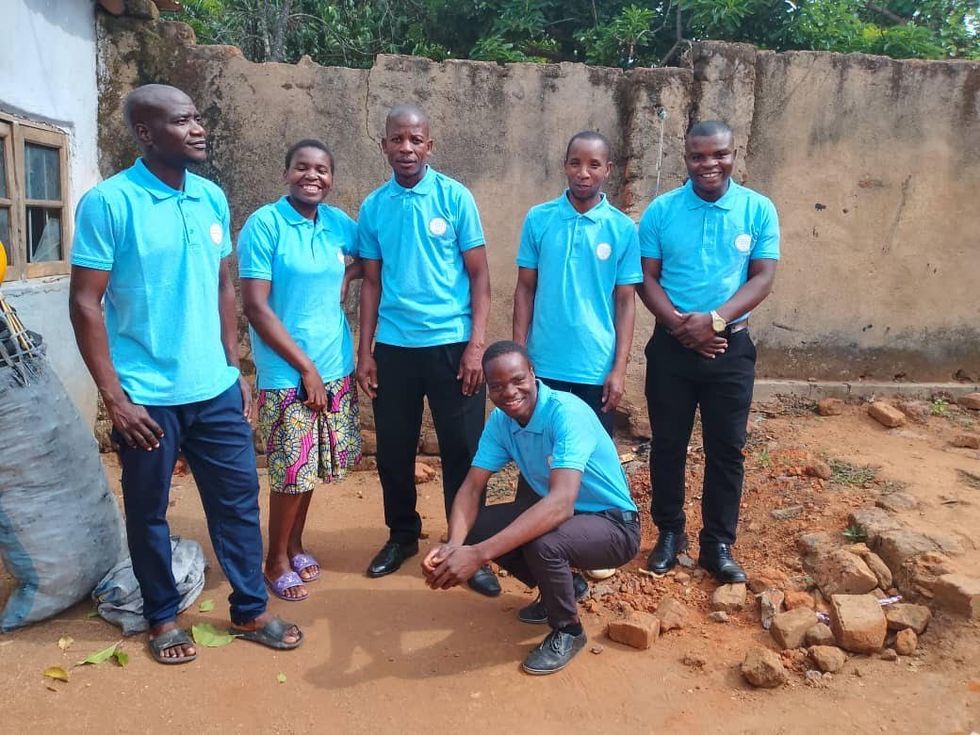 The Malawi Wheels team, left to right: Samuel George (wheelchair engineer) Esther Anthony (office manager), Emmanuel Fred (wheelchair engineer), Stevie Wilson (fieldwork manager), Gelson Mtinga (country director) , Oscar Tamatha (wheelchair engineer) Courtesy of Malawi Wheels
The Malawi Wheels team, left to right: Samuel George (wheelchair engineer) Esther Anthony (office manager), Emmanuel Fred (wheelchair engineer), Stevie Wilson (fieldwork manager), Gelson Mtinga (country director) , Oscar Tamatha (wheelchair engineer) Courtesy of Malawi Wheels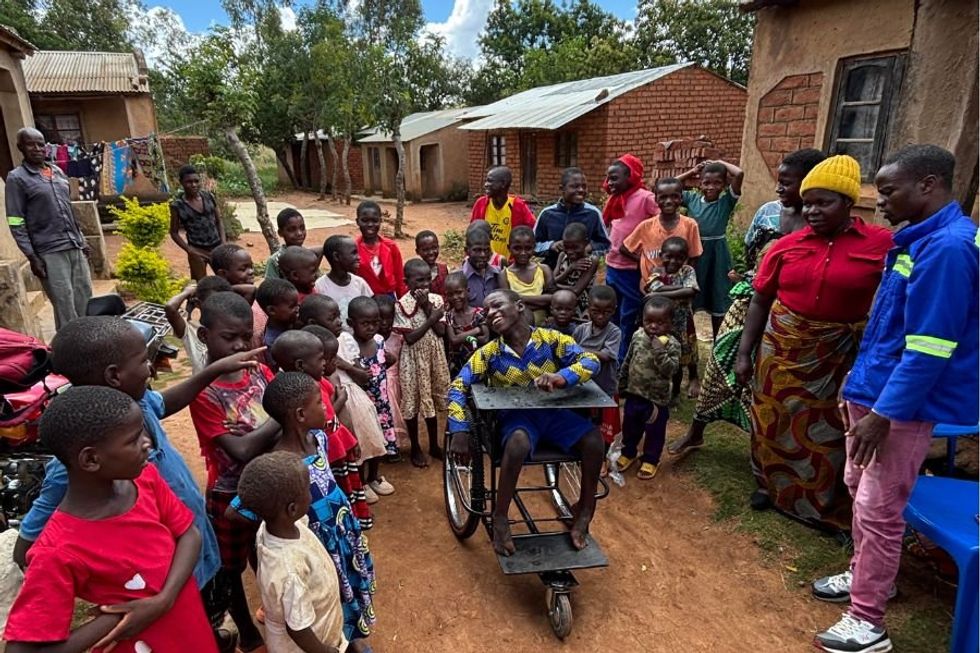 Miracle and his community the day he got his wheelchairCourtesy of Malawi Wheels
Miracle and his community the day he got his wheelchairCourtesy of Malawi Wheels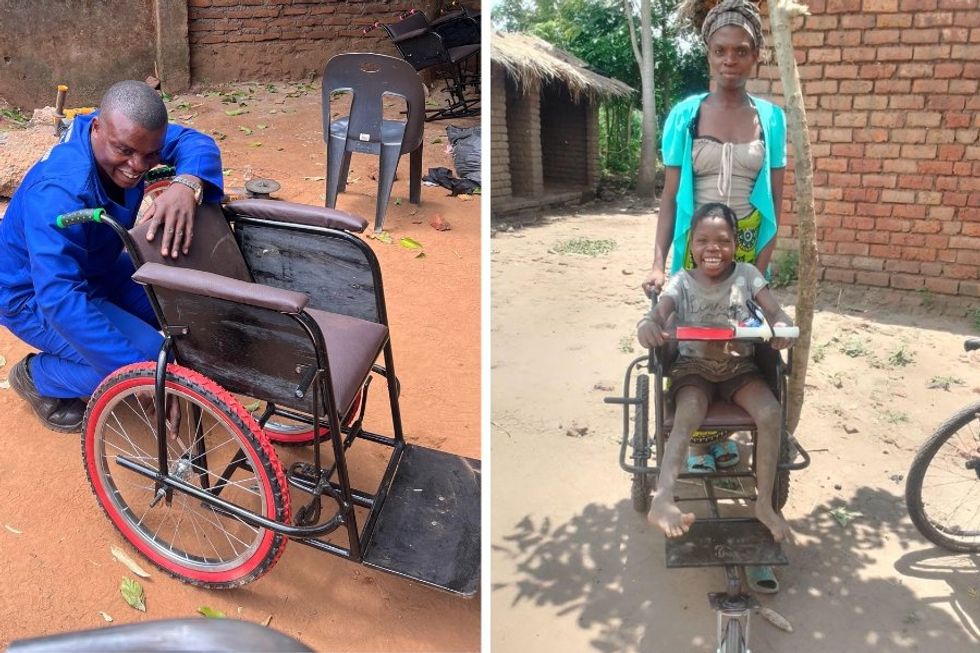 Oscar puts finishing touches on a wheelchair (left), Rose with her mom after getting into her Malawi Wheels chair for the first time (right)Courtesy of Malawi Wheels
Oscar puts finishing touches on a wheelchair (left), Rose with her mom after getting into her Malawi Wheels chair for the first time (right)Courtesy of Malawi Wheels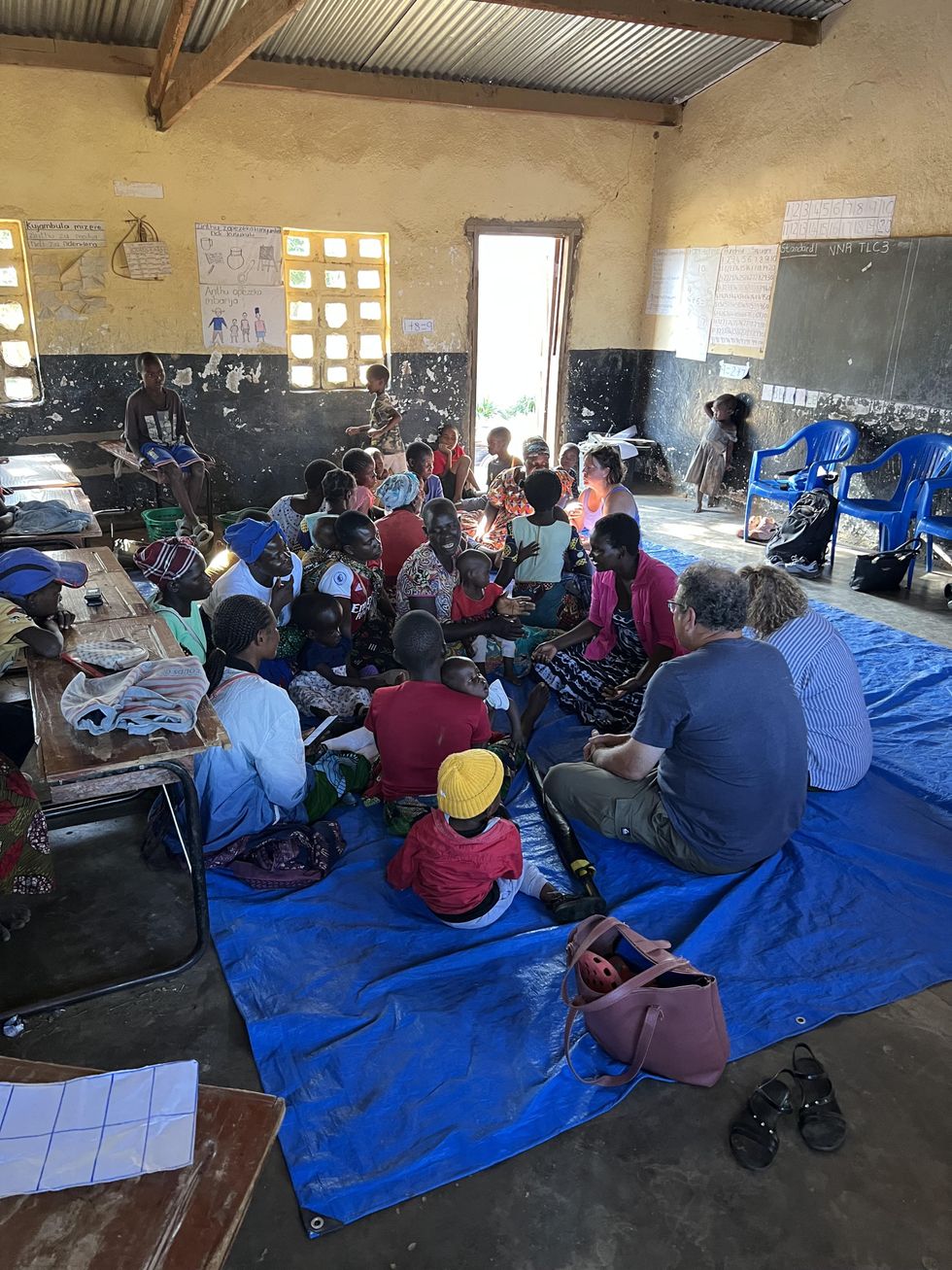 Parent groups provide emotional and spiritual support as well as physical therapy education for parents of kids with disabilities.Courtesy of Malawi Wheels
Parent groups provide emotional and spiritual support as well as physical therapy education for parents of kids with disabilities.Courtesy of Malawi Wheels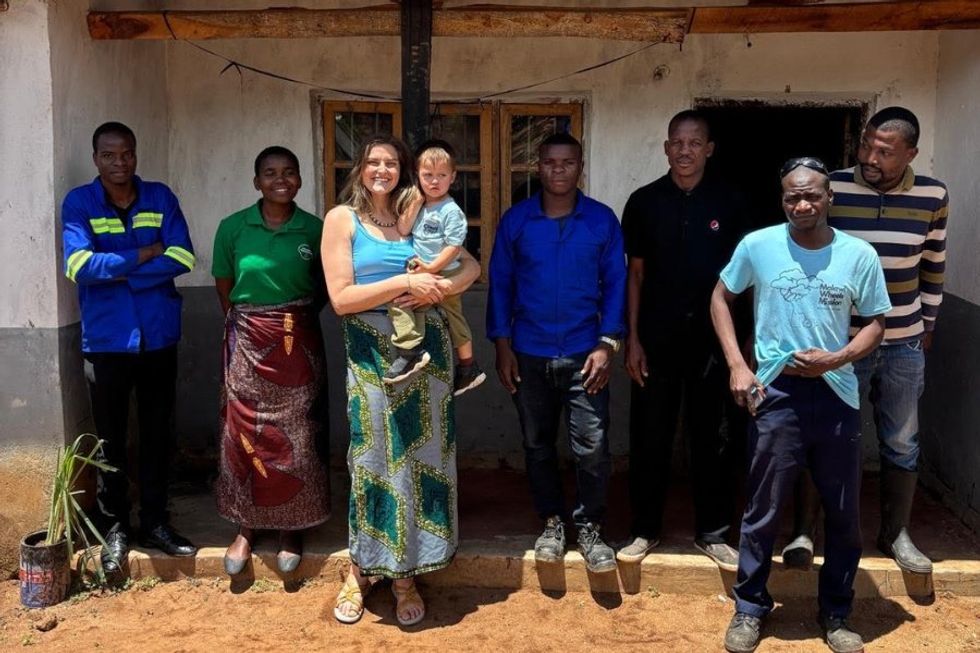 Danielle and her son with the Malawi Wheels team.Courtesy of Malawi Wheels
Danielle and her son with the Malawi Wheels team.Courtesy of Malawi Wheels A day at the park turned hateful and confrontation for Roobie Pierce and his son.Dakota Lim/Unsplash
A day at the park turned hateful and confrontation for Roobie Pierce and his son.Dakota Lim/Unsplash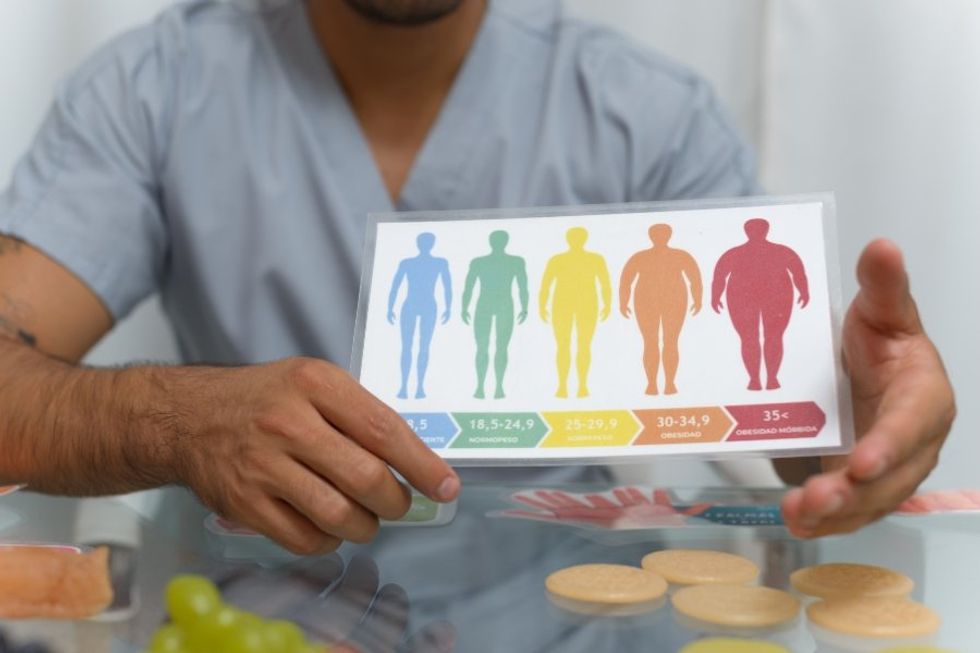 BMI is not always an accurate measure of health.
BMI is not always an accurate measure of health.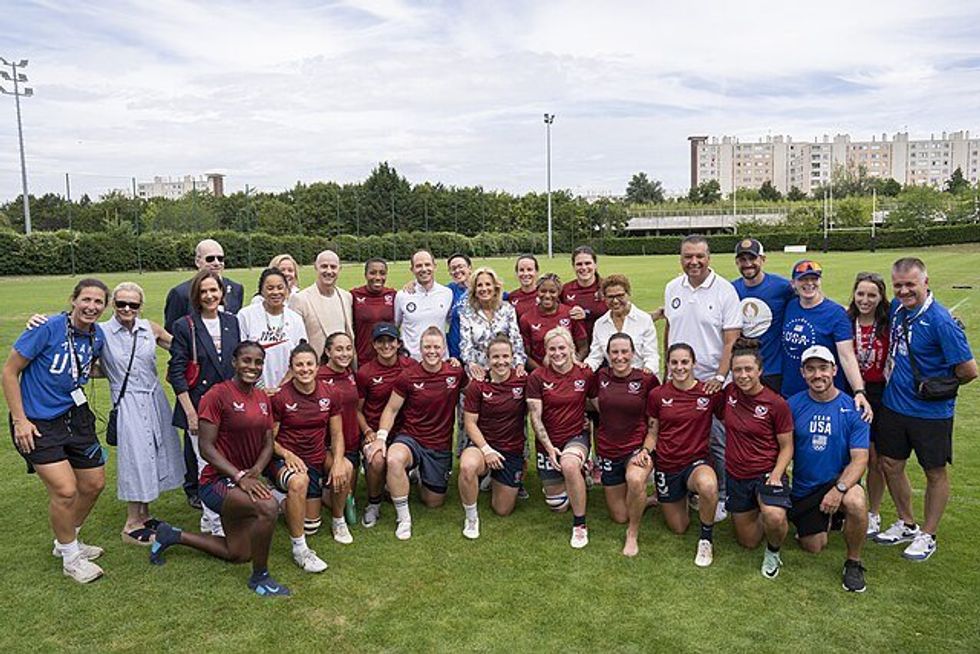 The U.S. women's rugby team with First Lady Jill Biden and members of the U.S. delegation to the 2024 Summer Olympic Games
The U.S. women's rugby team with First Lady Jill Biden and members of the U.S. delegation to the 2024 Summer Olympic Games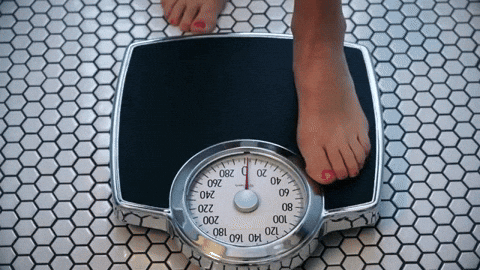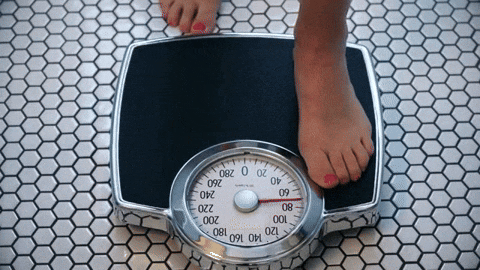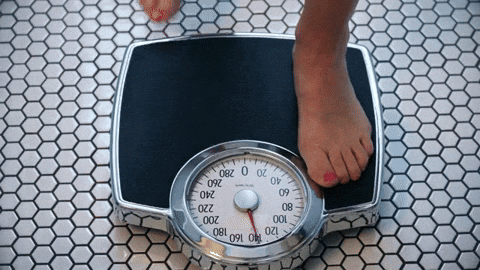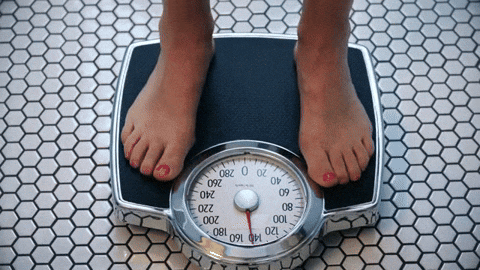 Weight and BMI can't say what we can do.
Weight and BMI can't say what we can do.