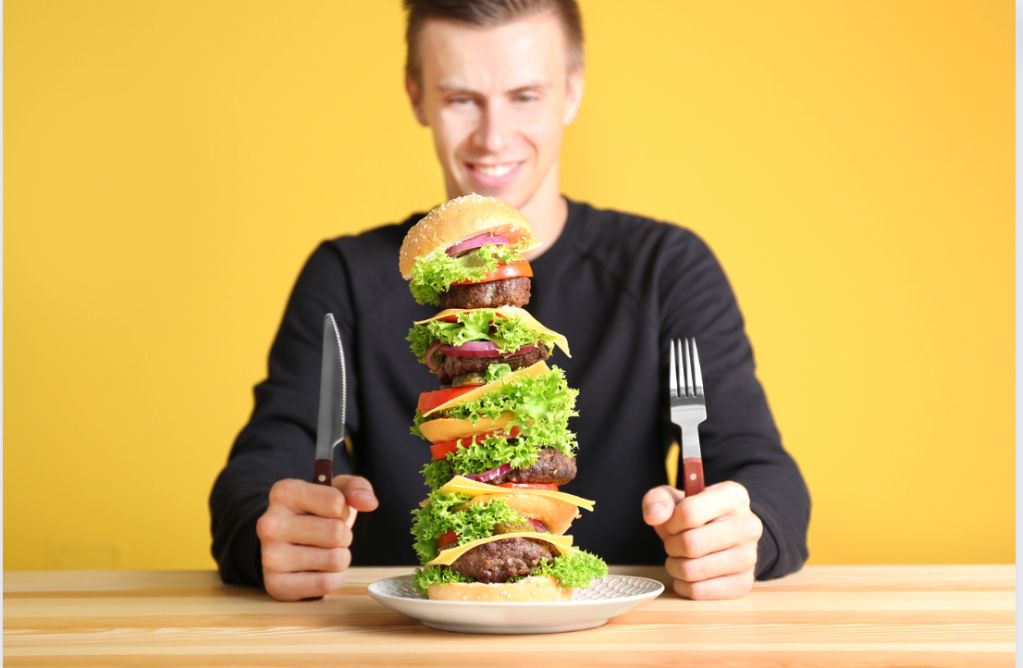
It’s something so simple, yet something so good — two tasty buns around mouthwatering meat.
Yes, it’s true: Hamburgers are wonderful. But what exactly makes them so wonderful? With so many parts and so many variations, it’s hard to know precisely why this dietary delight has become such an iconic part of our culture.
Over the centuries — yes, centuries — the hamburger has evolved from an umami underdog to a ubiquitous food staple all across the globe. And at the center of that strange journey is some surprising insight into humanity itself (and also a tasty meat patty).
Here are seven fascinating facts from across the years and continents that will make you appreciate the burger for more than just its taste.
1. The hamburger was invented in New Haven, Connecticut.
It was 1900 when Danish immigrant Louis Lassen first took the trimmings from his trademark steak sandwiches (which he also helped pioneer), packed them into patties, and placed them between two slices of toast from his sandwich wagon. The family still runs Louis’ Lunch Shop on Crown Street today and still serves the sandwiches on toast with no option for ketchup.
As someone who was born and raised in New Haven, I can assure you that this is 100% unequivocal truth. Even the U.S. Library of Congress has it on record!

2. Unless it was not invented in New Haven at all.
Perhaps it was Fletcher Davis of Athens, Texas, that actually invented it. He supposedly started cookin’ up those patties in the late 1880s, then brought his treat to the 1904 World’s Fair in St. Louis, where it gained global attention.
Or it could have been Charles and Frank Menches of Hamburg, New York, who ran out of sausage at a fair in 1885, so they packed together ground beef with coffee, brown sugar, and other brown spices to mask what was otherwise considered “lower class” meat.
Some people even give credit to Charlie Nagreen of Seymour, Wisconsin, who began serving flattened meatballs on bread in 1885, even though that’s pretty clearly a “meatball sandwich” and not a “hamburger.”
Maybe it all began at root beer-maker Oscar Weber Bilby’s Fourth of July party in 1891, right in Oklahoma — the heartland of America.
As you can see, there’s some question as to which of the 50 states can actually claim credit for this distinctly American delicacy. Unfortunately, people didn’t keep very clear records of these things back then, so it’s kind of hard to determine which one was the real pioneer.

3. But we do know that the first record of a hamburger-like recipe was from 1758.
“The Art of Cookery made Plain and Easy” by Hannah Glasse — the most popular cookbook in England for more than a century — was well-known in the American colonies too.
The cookbook was updated many times after its initial publication in 1747, but it was the 1758 edition that first made mention of a “hamburg sausage” — a combination of ground beef and spices that was cured and then served roasted on a single piece of toast.

4. The hamburg sausage wan’t quite a sandwich. But neither was the “hamburg steak,” another cousin of the burger.
Obviously, the question of “what defines a sandwich” has resulted in much debate. But one thing we can all agree on is that it requires some kind of casing in order to qualify as a “sandwich” … right?
While Glasse’s hamburg sausage could have arguably been an open-faced sandwich, the popular hamburg steak was definitely not a sandwich. The German dish gained popularity in the 18th century and comprised of, um, well, a patty of ground beef packed together — sometimes with spices or onions or egg — and then cooked and served. Which, come to think of it, does sound a lot like a hamburger without the bun.
(Some would argue that a hamburger without a bun is not technically a hamburger, but that’s a philosophical discussion for another time.)

5. Come to think of it, no one’s really sure who invented the sandwich either.
This may not sound like an important part of hamburger history, but bear with me. You’ll see how it connects.
Credit often goes to John Montagu, the fourth Earl of Sandwich, who allegedly needed some way to contain his food so that he could continue playing cards with his friends without making a mess or needing utensils.
But he was hardly the first to think of such a thing — Hillel the Elder was known for eating flatbread sandwiches as far back as the first century, and of course, many Middle Eastern and Eurasian cultures made use of the pita to contain all kinds of tasty treats, including — wait for it — minced meats.
Now do you see where this is going?

6. That’s right: The hamburger goes all the way back to Genghis Khan. (Sort of.)
Look, there’s a lot of world to conquer, OK? And when you were part of Khan’s Golden Horde, you didn’t have a lot of time to stop and eat between invading 2/3 of the planet. Khan’s soldiers would sometimes stay on horseback for days at a time, which wasn’t really conducive to eating soup either.
They found a way around the problem by thinly slicing meat and packing it together into portable patties that could be taken on the road and eaten as needed. Sometimes they were boiled, sometimes cured ahead of time, and more often than not, they were just eaten raw (but, contrary to popular belief, they were not placed under their saddles and cooked by butt-heat friction).

In one part of the world, this minced meat may have evolved into kebabs, which of course were then contained in the aforementioned pitas. Genghis’s grandson Kublai Khan is believed to have passed this raw meaty snack on to the Russians, who called it “steak tartare,” reportedly after their name for the Turco-Mongol peoples.
It would only be a matter of time before Russians shared the recipe with Germans, who gave it a twist of their own and turned it into hamburg steaks.
7. But the absolute oldest reference to a burger-like food comes from fourth-century Rome.
The ancient Roman Empire contributed a great many things to the modern world — including, believe it or not, fast food in the form of the ready-to-go thermopholia markets (literally “a place where something hot is sold”). According to a fourth-century cookbook, some of these thermopholia sold a packed patty known as Isica Omentata, which was made from minced meat, pine nuts, fish sauce, wine, and other spices. You can even find some modernized recipes and make your own Roman patties the next time you’re in the mood for a gladiator match!

The hamburger’s globe-trotting history shows us exactly why people around the world love those meaty buns.
(Besides the fact they’re delicious, I mean.)
The real power of the burger is much more primal than that. Bread and meat are dietary staples of every culture since pretty much the dawn of civilization as we know it. It only makes sense to bring them together in such a simple way. And as technologies continued to evolve, of course we’d use them to perfect this quintessential combination, which would, in turn, give rise to the modern burger as we know it.

That’s why the hamburger’s winding journey from Rome to Mongolia to Russia to Germany and, finally, to the United States is such a telling story: It shows how separate cultures have so much in common across time and space. In that regard, it almost doesn’t matter who was first to slap that patty on a bun or what inspired them do it — because the impulse was intrinsically human. Which means, yes, the hamburger has the power to unite us all, no matter where we come from, like one big global barbecue.
But also, they’re delicious.
This article originally appeared on 03.22.18