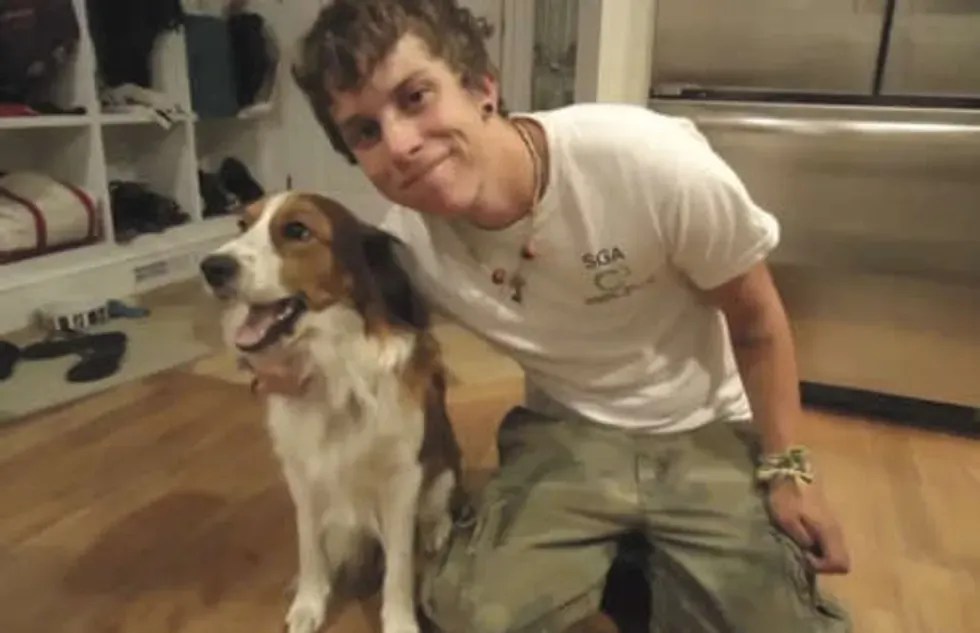
Recently, my wife and I went through one of the more excruciating experiences of our lives – the euthanasia of our beloved dog, Murphy.
I remember making eye contact with Murphy moments before she took her last breath – she flashed me a look that was an endearing blend of confusion and the reassurance that everyone was OK because we were both by her side.
When people who have never had a dog see their dog-owning friends mourn the loss of a pet, they probably think it’s all a bit of an overreaction; after all, it’s “just a dog.”
However, those who have loved a dog know the truth: Your own pet is never “just a dog.”
Many times, I’ve had friends guiltily confide to me that they grieved more over the loss of a dog than over the loss of friends or relatives.
Research has confirmed that for most people, the loss of a dog is in almost every way comparable to the loss of a human loved one.
Unfortunately, there’s little in our cultural playbook — no grief rituals, no obituary in the local newspaper, no religious service – to help us get through the loss of a pet, which can make us feel more than a bit embarrassed to show too much public grief over our dead dogs.
Perhaps if people realized just how strong and intense the bond is between people and their dogs, such grief would become more widely accepted. This would greatly help dog owners to integrate the death into their lives and help them move forward.
What is it about dogs, exactly, that make humans bond so closely with them?
For starters, dogs have had to adapt to living with humans over the past 10,000 years. And they’ve done it very well: They’re the only animal to have evolved specifically to be our companions and friends.
Anthropologist Brian Hare has developed the “Domestication Hypothesis” to explain how dogs morphed from their grey wolf ancestors into the socially skilled animals that we now interact with in very much the same way as we interact with other people.
Perhaps one reason our relationships with dogs can be even more satisfying than our human relationships is that dogs provide us with such unconditional, uncritical positive feedback. (As the old saying goes, “May I become the kind of person that my dog thinks I already am.”)
This is no accident. They have been selectively bred through generations to pay attention to people, and MRI scans show that dog brains respond to praise from their owners just as strongly as they do to food (and for some dogs, praise is an even more effective incentive than food). Dogs recognize people and can learn to interpret human emotional states from facial expression alone. Scientific studies also indicate that dogs can understand human intentions, try to help their owners, and even avoid people who don’t cooperate with their owners or treat them well.
Not surprisingly, humans respond positively to such unrequited affection, assistance, and loyalty.
Just looking at dogs can make people smile. Dog owners score higher on measures of well-being, and they are happier, on average, than people who own cats or no pets at all.
Our strong attachment to dogs was subtly revealed in a recent study of “misnaming.” Misnaming happens when you call someone by the wrong name, like when parents mistakenly calls one of their kids by a sibling’s name. It turns out that the name of the family dog also gets confused with human family members, indicating that the dog’s name is being pulled from the same cognitive pool that contains other members of the family. (Curiously, the same thing rarely happens with cat names.)
It’s no wonder dog owners miss them so much when they’re gone.
Psychologist Julie Axelrod has pointed out that the loss of a dog is so painful because owners aren’t just losing the pet. It could mean the loss of a source of unconditional love, a primary companion who provides security and comfort, and maybe even a protégé that’s been mentored like a child.
The loss of a dog can also seriously disrupt an owner’s daily routine more profoundly than the loss of most friends and relatives. For owners, their daily schedules — even their vacation plans — can revolve around the needs of their pets. Changes in lifestyle and routine are some of the primary sources of stress.
According to a recent survey, many bereaved pet owners will even mistakenly interpret ambiguous sights and sounds as the movements, pants, and whimpers of the deceased pet. This is most likely to happen shortly after the death of the pet, especially among owners who had very high levels of attachment to their pets.
While the death of a dog is horrible, dog owners have become so accustomed to the reassuring and nonjudgmental presence of their canine companions that, more often than not, they’ll eventually get a new one.
So yes, I miss my dog.
But I’m sure that I’ll be putting myself through this ordeal again in the years to come.
This story originally appeared on The Conversation and is printed here with permission.
![]()