How to be an ally to someone dealing with PTSD
An estimated 8 percent of the population will experience post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in their lifetime.

Helping those affected by PTSD.
Up to 8% of the American population will experience post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in their lifetime, according to the National Center for PTSD.
As much as people might not want to discuss it, traumatic experiences are not rare. In fact, recent data suggests that 60% of men and 50% of women will experience at least one traumatic event in their lifetime.
For a long time, it was believed that only those who had served in the military could develop PTSD, but that's simply not true.
The reality is that, while it may be more prevalent among certain groups, PTSD can affect anyone who's experienced a traumatic event. It's important to be able to speak about it clearly and openly, without fear or condemnation, in order to promote understanding and healing.

Cognitive behavioral therapy is one piece of the puzzle.
Photo by Lucrezia Carnelos on UnsplashToday, more treatments exist for PTSD than ever before.
The medical and psychological communities are finding new and effective ways of treating the disorder. For example, therapies involving virtual reality and paintball have shown to be promising in treating veterans. Both are methods where an individual is exposed to the triggers of their symptoms in a safe and controllable way.
Cognitive behavioral therapy (where one learns to think more realistically and logically) and eye movement desensitization reprocessing (in which an individual relives the traumatic experience in small doses and while remaining firmly in reality) can also be effective in treating the disorder. But therapy, no matter how effective, is only one piece of the puzzle.
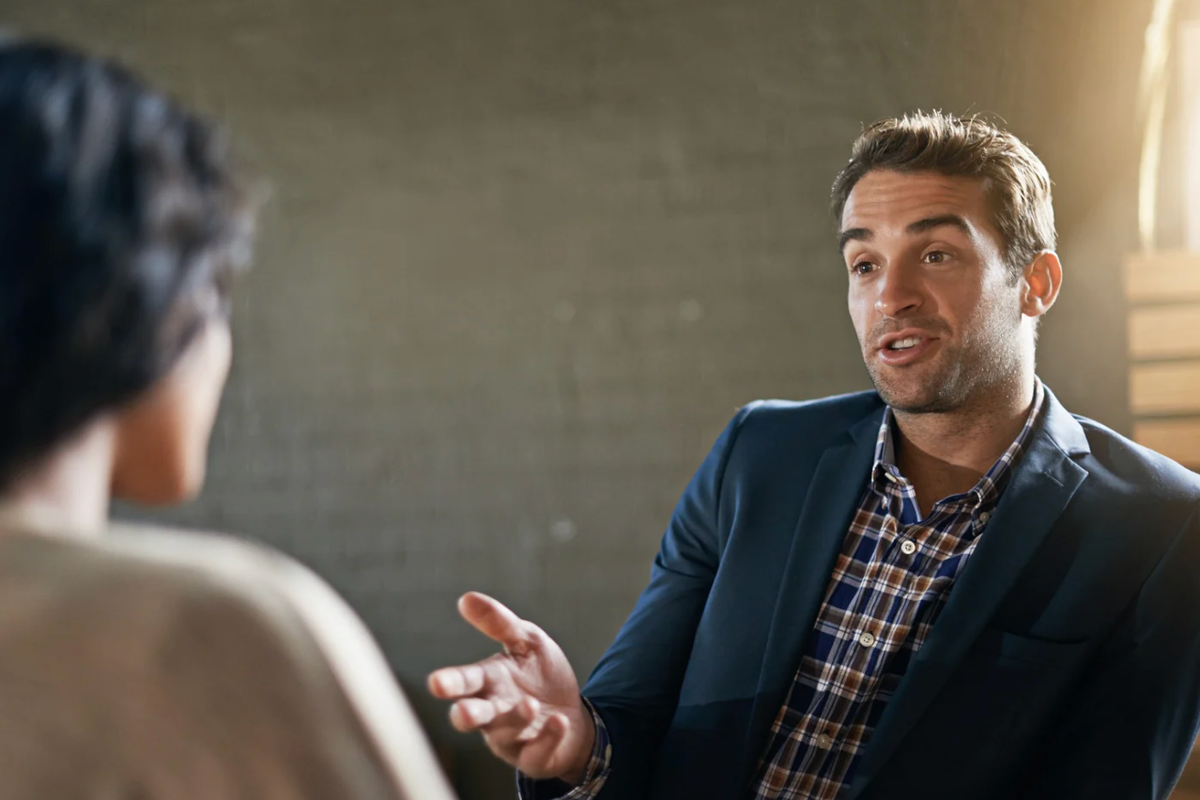
Helping those with PTSD must also include compassion. Here's how to be an ally.
It's likely that you know someone who's experienced PTSD. It's also likely that you didn't know how to think or react to the disorder.
Confusion (and even judgment) are normal responses. After all, most of us aren't trained therapists. But you don't have to be a mental health professional to help a friend or loved one who's experiencing PTSD.
There's no one right thing to say to someone who's experiencing the disorder. The best thing you can do is just be there. While it may seem helpful to offer wisdom or offer suggestions for how your loved ones can "move on" or "get over it," that's actually counter-intuitive.

Helpful therapy is important.
Photo by Omar Lopez on UnsplashThose living with PTSD are already under a great deal of pressure. Suggesting therapy is helpful, but trying to make your loved one see "the good side of things" or "remember that this is all part of a bigger plan" is likely to create even more guilt and stress rather than prompt action. PTSD is painful and it's serious, but it's never a sign of weakness.
Respecting boundaries is also important. It's up to the individual when they choose to talk about their trauma. Nobody should force it or take it personally if they don't.
Show up, listen, care. These things are enough. More importantly, they're important steps toward ending stigma and helping our loved ones heal.
This article originally appeared on 06.27.18


 A woman reading a book.via
A woman reading a book.via A woman tending to her garden.via
A woman tending to her garden.via
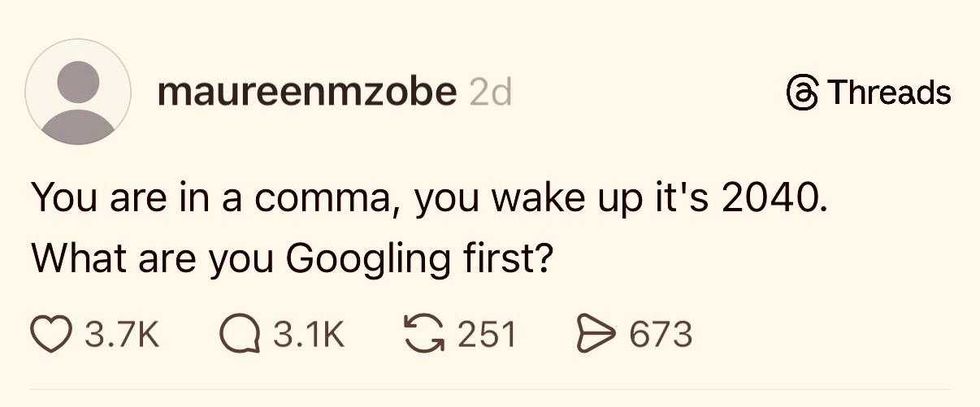 A person on Threads makes a typo.Photo credit: Threads/@maureenmzobe
A person on Threads makes a typo.Photo credit: Threads/@maureenmzobe
 Individual impact isn't as inspiring to Gen Z as it was to
Individual impact isn't as inspiring to Gen Z as it was to  Gen Z is much more black and white about behaviors than previous generations.
Gen Z is much more black and white about behaviors than previous generations. 
 Young man holds up his hand to show five.
Young man holds up his hand to show five.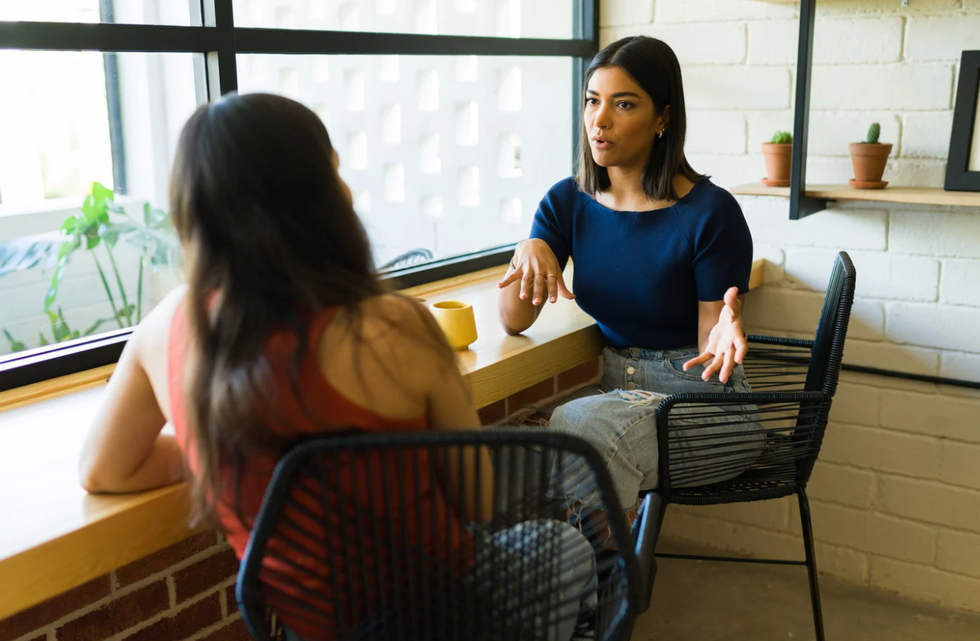 Two women having a conversation at a coffee shop.
Two women having a conversation at a coffee shop.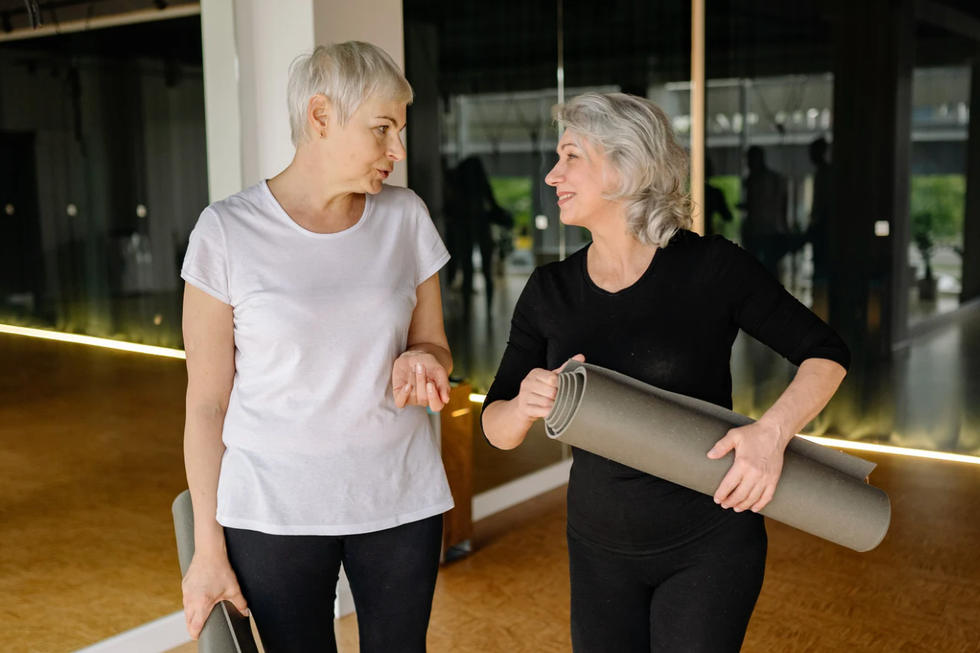  Two women talking as the leave a yoga class
Two women talking as the leave a yoga class