Dramatic video shows a woman confronting a harasser at the gym
That's how you do it.
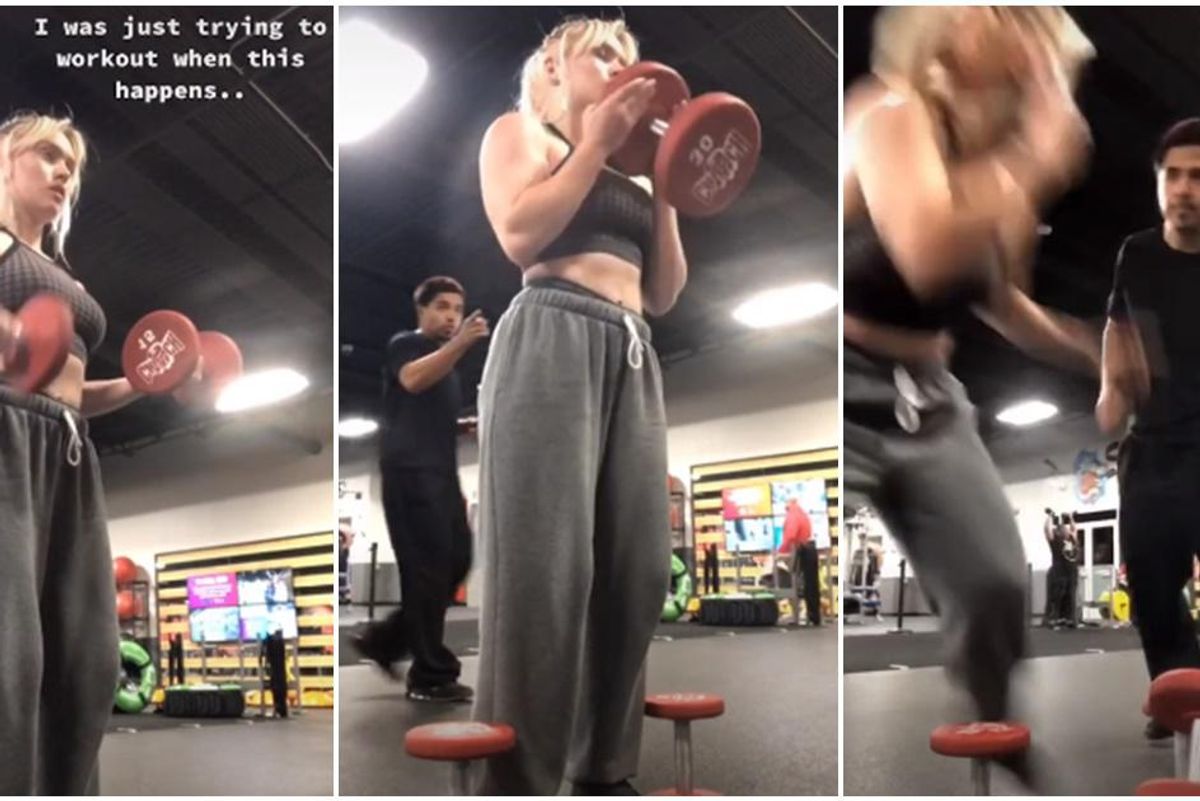

Chelsie Gleason confronts a man who was harassing her.
A video on TikTok posted by Chelsie Gleason has more than 12 million views because of the way she assertively told a man who who was harassing her to get away. Gleason was filming herself lifting weights when a man approached her attempting to strike up a conversation. She ignored him and was wearing earbuds, but the man didn't get the point.
"I was just trying to work out when this happens," a voiceover says in the video taken at a Crunch Fitness gym. "I've never met this guy and he's been harassing me for months." Finally, Gleason had enough and snapped at the man. "Don't come near me," she said confidently as she dropped her weights and took a step back. The man immediately turned and briskly walked away. You can tell she got her point across because he looked like he wanted to get out of there fast.
@justchesslee being a female is fun(:
Registered dietitian Carrie Taylor says that Gleason did the right thing by telling the man to stop while he was harassing her. She says that if you tell someone to stop harassing you at the gym and they persist, to immediately talk to the manager and threaten to call the police if swift action isn't taken.
She says you should also get a restraining order if necessary. Anything to stop the harassment because it could intensify. Gyms should also prominently post signs that warn people about sexual harassment so that these situations don't happen in the first place.
After the video went viral, Crunch Fitness announced it had found the man and banned him from its facilities.
"Our philosophy at Crunch is 'no judgments,' where we promote positive self-esteem and respect all races, cultures and nationalities in a fun atmosphere," a spokesperson for Crunch Fitness told Newsweek. "All of our gyms are committed to creating a safe and welcoming environment for all members."
"He's been found and as been banned! Thank you @CrunchFitness," Gleason wrote in the comment section.
One person in the comments made an important point about why this type of harassment is so dangerous. "Imagine if a shyer girl is walking to her car at night and he's out there...he needs to be kicked out," a TikTok viewer wrote. Who knows what the man's intentions were and whether he was grooming her for something truly terrible?
This isn't the first time Gleason has faced harassment in the gym. She's tweeted about it several times in the past. It's clear from the video that she's hit a breaking point.
Gleason's brave decision to confront the man put an end to his creepy, threatening behavior in the moment. But the video may serve a greater purpose by showing women how to react to men who harass them. Further, it could also deter men from harassing women in the first place by showing them there are serious consequences for being a creep.
This article originally appeared three years ago.
- Why the sexual harassment of fat people reaches a different level of ... ›
- 'I felt ill': Brendan Fraser describes sexual assault that nearly made ... ›
- These powerful sexual harassment PSAs by David Schwimmer are ... ›
- This 'creepy' guy wouldn't stop staring at her at the gym. She knew exactly what to do next. - Upworthy ›
- Woman captures video of man not being a creep at the gym ›
- Woman captures video of man not being a creep at the gym - Upworthy ›
- 'I felt ill': Brendan Fraser describes sexual assault that nearly made him quit acting - Upworthy ›
- Don't get mad when people walk through your video at the gym - Upworthy ›
- Woman pulls out phone to record a man following her - Upworthy ›
- Woman shares how man's gym encouragement made an impact - Upworthy ›
- 6 infuriating types of harassment women put up with at the gym - Upworthy ›






 A woman is getting angry at her coworker.via
A woman is getting angry at her coworker.via  A man with tape over his mouth.via
A man with tape over his mouth.via  A husband is angry with his wife. via
A husband is angry with his wife. via 
 Austin Powers impersonator arrives at Chase Hofer's apartment.Photo Credit: Kenneth Webb, TikTok
Austin Powers impersonator arrives at Chase Hofer's apartment.Photo Credit: Kenneth Webb, TikTok
 Mom hugging crying daughter
Mom hugging crying daughter Dad kissing child on cheek
Dad kissing child on cheek Mom comforting daughter
Mom comforting daughter

 A blue light painting of an infinity symbol. Photo by
A blue light painting of an infinity symbol. Photo by