Tags
More for You
-
The next generation of female leaders has arrived. Here’s how they’re making sure they (and every girl) get a chance to learn.
Malala Fund and their local partners, with support from Pura, help girls find their voice. The result: greater access to education and a better world.
Music, community and joy drive real change
In a small village in Pwani, a district on Tanzania’s coast, a massive dance party is coming to a close. For the past two hours, locals have paraded through the village streets, singing and beating ngombe drums; now, in a large clearing, a woman named Sheilla motions for everyone to sit facing a large projector screen. A film premiere is about to begin.
It’s an unusual way to kick off a film about gender bias, inequality, early marriage, and other barriers that prevent girls from accessing education in Tanzania. But in Pwani and beyond, local organizations supported by Malala Fund and funded by Pura are finding creative, culturally relevant ways like this one to capture people’s interest.
The film ends and Sheilla, the Communications and Partnership Lead for Media for Development and Advocacy (MEDEA), stands in front of the crowd once again, asking the audience to reflect: What did you think about the film? How did it relate to your own experience? What can we learn?
Sheilla explains that, once the community sees the film, “It brings out conversations within themselves, reflective conversations.” The resonance and immediate action create a ripple effect of change.

MEDEA Screening Audience in Tanzania. Captured by James Roh for Pura Across Tanzania, gender-based violence often forces adolescent girls out of the classroom. This and other barriers — including child marriage, poverty, conflict, and discrimination — prevent girls from completing their education around the world.
Sheilla and her team are using film and radio programs to address the challenges girls face in their communities. MEDEA’s ultimate goal is to affirm education as a fundamental right for everyone, and to ensure that every member of a community understands how girls’ education contributes to a stronger whole and how to be an ally for their sisters, daughters, granddaughters, friends, nieces, and girlfriends.
Sheilla’s story is one of many that inspired Heart on Fire, a new fragrance from the Pura x Malala Fund Collection that blends the warm, earthy spices of Tanzania with a playful, joyful twist. Here’s how Pura is using scent as a tool to connect the world and inspire action.
A partnership focused on local impact, on a global mission
Pura, a fragrance company that recognizes education as both freedom and a human right, has partnered with Malala Fund since 2022. In order to defend every girl’s right to access and complete 12 years of education, Malala Fund partners with local organizations in countries where the educational barriers are the greatest. They invest in locally-led solutions because they know that those who are closest to the problems are best equipped to solve and build durable solutions, like MEDEA, which works with communities to challenge discrimination against girls and change beliefs about their education.
But local initiatives can thrive and scale more powerfully with global support, which is why Pura is using their own superpower, the power of scent, to connect people around the world with the women and girls in these local communities.
The Pura x Malala Fund Collection incorporates ingredients naturally found in Tanzania, Nigeria, Pakistan, and Brazil: countries where Malala Fund operates to address systemic education barriers. Eight percent of net revenue from the Pura x Malala Fund Collection will be donated to Malala Fund directly, but beyond financial support, the Collection is also a love letter to each unique community, blending notes like lemon, jasmine, cedarwood, and clove to transport people, ignite their senses, and help them draw inspiration and hope from the global movement for girls’ education. Through scent, people can connect to the courage, joy, and tenacity of girls and local leaders, all while uniting in a shared commitment to education: the belief that supporting girls’ rights in one community benefits all of us, everywhere.
You’ve already met Sheilla. Now see how Naiara and Mama Habiba are building unique solutions to ensure every girl can learn freely and dare to dream.
Naiara Leite is reimagining what’s possible in Brazil

Julia with Odara in Brazil. Captured by Luisa Dorr for Pura In Brazil, where pear trees and coconut plantations cover the Northeastern Coast, girls like ten-year-old Julia experience a different kind of educational barrier than girls in Tanzania. Too often, racial discrimination contributes to high dropout rates among Black, quilombola and Indigenous girls in the country.
“In the logic of Brazilian society, Black people don’t need to study,” says Naiara Leite, Executive Coordinator of Odara, a women-led organization and Malala Fund partner. Bahia, the state where Odara is based, was once one of the largest slave-receiving territories in the Americas, and because of that history, deeply-ingrained, anti-Black prejudice is still widespread. “Our role and the image constructed around us is one of manual labor,” Naiara says.
But education can change that. In 2020, with assistance from a Malala Fund grant, Odara launched its first initiative for improving school completion rates among Black, quilombola, and Indigenous girls: “Ayomidê Odara”. The young girls mentored under the program, including Julia, are known as the Ayomidês. And like the Pura x Malala Fund Collection’s Brazil: Breath of Courage scent, the Ayomidês are fierce, determined, and bursting with energy.

Ayomidês with Odara in Brazil. Captured by Luisa Dorr for Pura Ayomidês take part in weekly educational sessions where they explore subjects like education and ethnic-racial relations. The girls are encouraged to find their own voices by producing Instagram lives, social media videos, and by participating in public panels. Already, the Ayomidês are rewriting the narrative on what’s possible for Afro-Brazilian girls to achieve. One of the earliest Ayomidês, a young woman named Debora, is now a communications intern. Another former Ayomidê, Francine, works at UNICEF, helping train the next generation of adolescent leaders. And Julia has already set her sights on becoming a math teacher or a model.
“These are generations of Black women who did not have access to a school,” Naiara says. “These are generations of Black women robbed daily of their dreams. And we’re telling them that they could be the generation in their family to write a new story.”
Mama Habiba is reframing the conversation in Nigeria

Centre for Girls' Education, Nigeria. Captured by James Roh for Pura In Mama Habiba’s home country of Nigeria, the scents of starfruit, ylang ylang and pineapple, all incorporated into the Pura x Malala Collection’s “Nigeria: Hope for Tomorrow,” can be found throughout the vibrant markets. Like these native scents, Mama Habiba says that the Nigerian girls are also bright and passionate, but too often they are forced to leave school long before their potential fully blooms.
“Some of these schools are very far, and there is an issue of quality, too,” Mama Habiba says. “Most parents find out when their children are in school, the girls are not learning. So why allow them to continue?”
When girls drop out of secondary school, marriage is often the alternative. In Nigeria, one in three girls is married before the age of 18. When this happens, girls are unable to fulfill their potential, and their families and communities lose out on the social, health and economic benefits.
Completing secondary school delays marriage, and according to UNESCO, educated girls become women who raise healthier children, lift their families out of poverty and contribute to more peaceful, resilient communities.

Centre for Girls’ Education, Nigeria. Captured by James Roh for Pura To encourage young girls to stay in school, the Centre for Girls’ Education, a nonprofit in Nigeria founded by Mama Habiba and supported by Malala Fund and Pura, has pioneered an initiative that’s similar to the Ayomidê workshops in Brazil: safe spaces. Here, girls meet regularly to learn literacy, numeracy, and other issues like reproductive health. These safe spaces also provide an opportunity for the girls to role-play and learn to advocate for themselves, develop their self-image, and practice conversations with others about their values, education being one of them. In safe spaces, Mama Habiba says, girls start to understand “who she is, and that she is a girl who has value. She has the right to negotiate with her parents on what she really feels or wants.”
“When girls are educated, they can unlock so many opportunities,” Mama Habiba says. “It will help the economy of the country. It will boost so many opportunities for the country. If they are given the opportunity, I think the sky is not the limit. It is the starting point for every girl.”
From parades, film screenings to safe spaces and educational programs, girls and local leaders are working hard to strengthen the quality, safety and accessibility of education and overcome systemic challenges. They are encouraging courageous behavior and reminding us all that education is freedom.
Experience the Pura x Malala Fund Collection here, and connect with the stories of real girls leading change across the globe.
-
One couple’s perfect response to people asking when they’re going to have kids
Choosing to have kids or not have kids is no one else’s decision but yours.
“When are you guys going to start having kids?”
Like many couples, Carrie Jansen and her husband Nic had heard this question a million different ways, a million different times.
The pressure really started to mount when the pair, who’ve been together for eight years, got married three years ago. While Carrie loves kids (she’s an elementary school teacher, after all), she and Nic simply aren’t interested in having kids of their own. Now or ever.
“It’s not what I was meant for,” explains Carrie in a Facebook message. “It’s like, I love flowers, and everyone loves flowers. But that doesn’t mean I want to grow my own. I’m perfectly happy admiring other people’s gardens.”
Carrie wanted to tell her family that they don’t plan on having kids but knew if she did, they’d say something like, “Oh you’ll change your mind one day!” and that pesky question would keep rearing its ugly head.
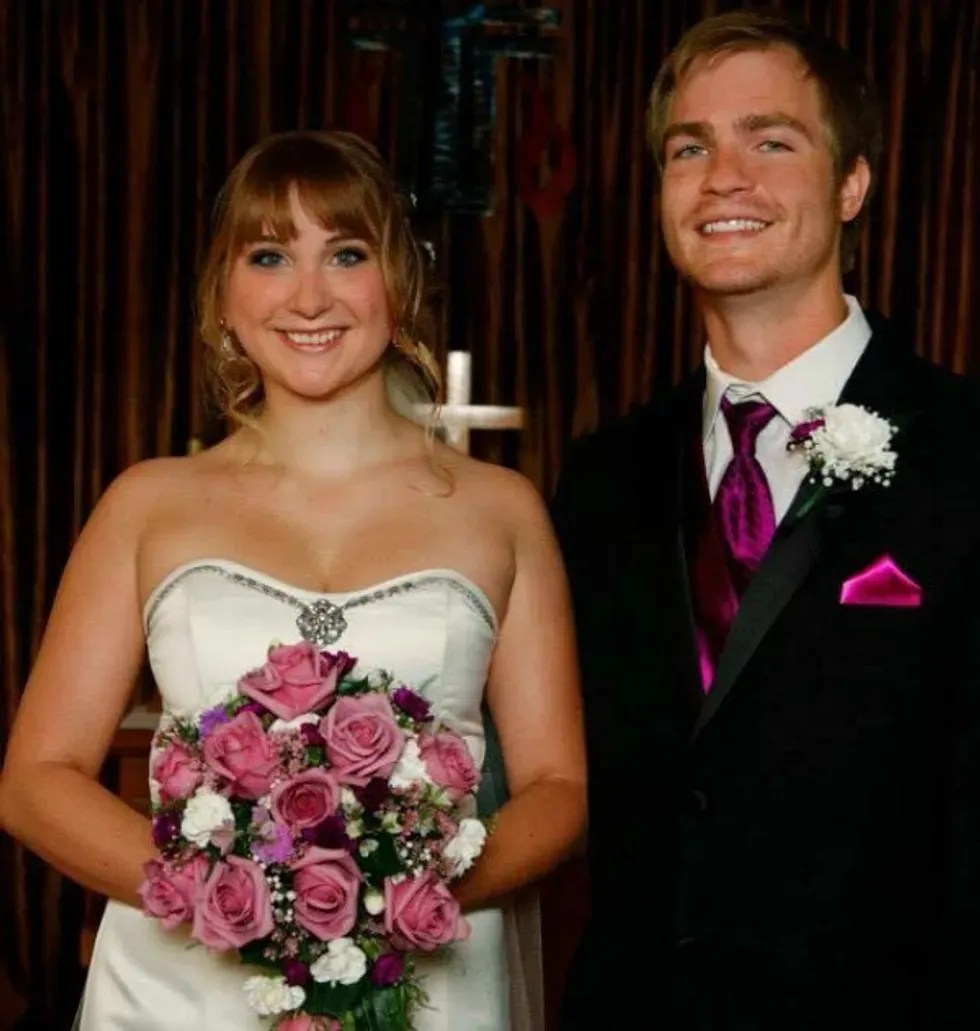

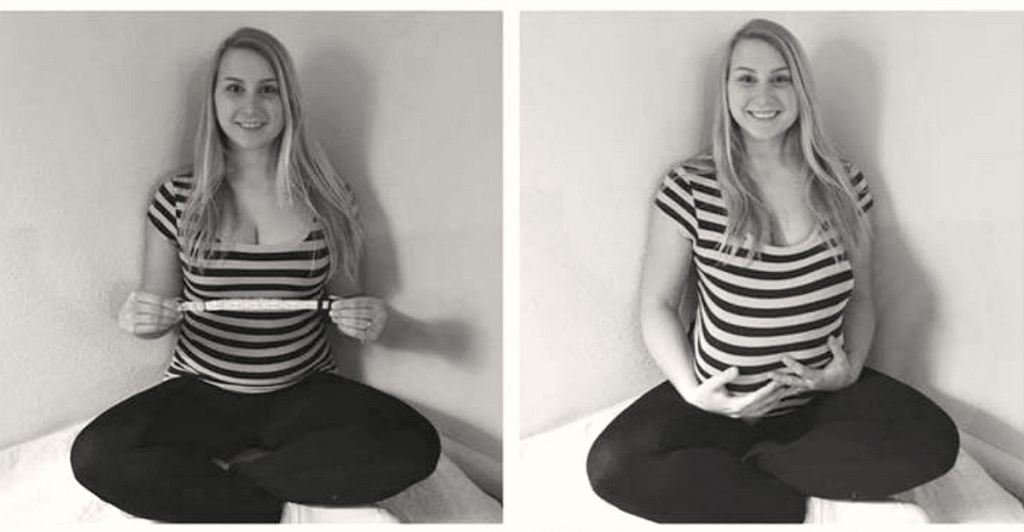
Dressed to the nines on their wedding day. Photo via Carrie Jansen, used with permission. Rather than continue to deflect the question over and over, Carrie decided to do something a little bit different.
Since the couple was adding another mouth to feed to the family, they decided to announce it with a series of maternity-style photos, revealing the twist: The new addition was a puppy named Leelu, not a baby.
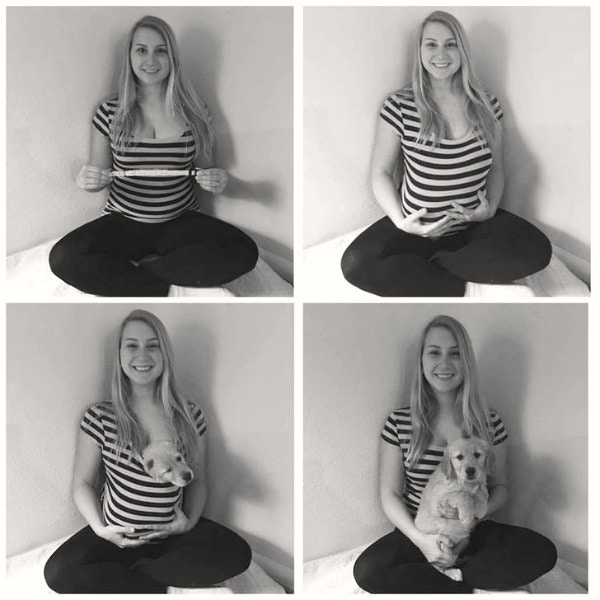

Look at my newborn baby… puppy. Photo via <a href="https://imgur.com/gallery/DLQcpW2">Carrie Jensen/Imgur</a>, used with permission. “My husband and I have been married 3 years and everyone is bugging us about having a baby. Close enough right?” she captioned the photos.
Her pictures went insanely viral, with many of the commenters giving her props for hilariously addressing the dreaded “kids ” question.

The adorable pup. Photo via Carrie Jansen, used with permission. “If you don’t want kids, don’t have kids. Seriously. Have fun with each other. I had three kids early and it’s all about them now,” wrote one user. “I wish people would just mind their business raising a kid ain’t easy and cheap,” wrote another.
“I got my husband a vasectomy for his birthday this year. Best gift ever,” chimed in a third.
Carrie was overwhelmed and inspired by the viral response. “Having children is definitely a hot topic, and one that is evolving in this generation like so many other social issues,” she says. “It’s exciting to find others that feel the same way I do.”
Carrie is hardly alone in not wanting to have kids — in fact, a record number of women are choosing not to have kids today.
In 2014, the U.S. Census Bureau’s Current Population Survey found 47.6% of women between age 15 and 44 had never had children, which is the highest percentage on record. Despite the numbers, however, because we still live in a patriarchally-driven society, women regularly face the expectation that they should be mothers, and they often are judged if they decide not to be.
Whether you want to have one kid, five kids, no kids, or a puppy, the choice should be yours and no one else’s.

The holiday photo in front of the Christmas tree. Photo via Carrie Jansen, used with permission. No one else has the right to put pressure on you to change your body and life in a drastic way. Thankfully, because of women like Carrie — and partners like Nic — who aren’t afraid to bring the subject out in the open, the expectations are slowly but surely changing.
This article originally appeared nine years ago.
-
Mom rips into husbands who expect their wives to do housework in crazy viral Facebook post
Can you do the dishes without being asked?
It’s the 21st century, and as a civilization, we’ve come a long way. No, there are no flying cars (yet), but we all carry tiny supercomputers in our pockets, can own drones, and can argue with strangers from all around the world as long as they have Internet access.
And yet, women are still having to ask their partners to help out around the house. What gives?
Recently, Blogger Constance Hall went on a highly-relatable rant about spouses assuming responsibility for housework, and women everywhere are all, ” .”
Recently while bitching about the fact that I do absolutely everything around my house with a bunch of friends all singing “preach Queen”, someone said to me “if you want help you need to be specific… ask for it. People need lists, they aren’t mind readers.”
So I tried that, asking.. specifics..
“Can you take the bin out?”
“Can you get up with the kids? I’m just a little tired after doing it on my own for 329 years”
“Can you go to woolies? I’ve done 3 loads of washing and made breaky, lunch, picked up all the kids school books, dealt with the floating shit in the pond.”
And yeah, she was right… shit got done.But I was exhausted, just keeping the balls in the air.. remembering what needs to be asked to be done, constant nagging..And do you know what happened the minute I stopped asking…?
NOTHING. Again.
And so I’ve come to the conclusion that it’s not your job to ask for help, it’s not my job to write fucking lists.
We have enough god dam jobs and teaching someone how to consider me and my ridiculous work load is not one of them. Just do it. Just think about each other, what it takes to run the god dam house.
Is one of you working while the other puts up their feet? Is one of you hanging out with mates while the other peels the thirtieth piece of fruit for the day? Is one of you carrying the weight?
Because when the nagging stops, when the asking dies down, when there are no more lists….All your left with is silent resentment. And that my friends is relationship cancer..It’s not up to anyone else to teach you consideration.
That’s your job. Just do the fucking dishes without being asked once in a while mother fuckers.
Hall’s post touches on the concept of emotional labor, which can be defined as “the process of managing feelings and expressions to fulfill the emotional requirements of a job.”
In other words, although Hall’s partner may be the one carrying out the tasks she assigns him, it is still Hall’s job to be the “manager” of the household, and keep track of what things need to get done. And anyone who runs a household knows that juggling and keeping track of chores is just as exhausting as executing them. There’s also the idea of being the “default parent.” which, more often than not, tends to be mothers. It’s a lot to handle.
At time of publication, Hall’s post was shared nearly 100,000 times. That’s a lot of frustrated ladies!
When your girl Far Kew sends you the perfect present. You will find this and more cunty cups on her facebook page ??
Posted by Constance Hall on Thursday, November 30, 2017Women in the comments section seemed to overwhelmingly agree with Hall’s post.
Let’s all learn to share the load…laundry and otherwise.
This article originally appeared seven years ago.
-
A dad’s hilarious letter to school asks them to explain why they’re living in 1968
“I look forward to this being rectified and my daughter and other girls at the school being returned to this millennium.”
Earlier in the week, Stephen Callaghan’s daughter Ruby came home from school. When he asked her how her day was, her answer made him raise an eyebrow. Ruby, who’s in the sixth grade at her school in Australia, told her dad that the boys would soon be taken on a field trip to Bunnings (a hardware chain in the area) to learn about construction.
The girls, on the other hand? While the boys were out learning, they would be sent to the library to have their hair and makeup done. Ruby’s reply made Callaghan do a double take. What year was it, again? Callaghan decided to write a letter to the school sharing his disappointment — but his wasn’t your typical “outraged parent” letter.
“Dear Principal,” he began. “I must draw your attention to a serious incident which occurred yesterday at your school where my daughter is a Year 6 student.”
“When Ruby left for school yesterday it was 2017,” Callaghan continued. “But when she returned home in the afternoon she was from 1968.”
The letter goes on to suggest that perhaps the school is harboring secret time-travel technology or perhaps has fallen victim to a rift in the “space-time continuum,” keeping his daughter in an era where women were relegated to domestic life by default.
“I look forward to this being rectified and my daughter and other girls at the school being returned to this millennium where school activities are not sharply divided along gender lines,” he concluded.
Dear Principal
I must draw your attention to a serious incident which occurred yesterday at your school where my daughter Ruby is a Year 6 student.
When Ruby left for school yesterday it was 2017 but when she returned home in the afternoon she was from 1968.
I know this to be the case as Ruby informed me that the “girls” in Year 6 would be attending the school library to get their hair and make-up done on Monday afternoon while the “boys” are going to Bunnings.
Are you able to search the school buildings for a rip in the space-time continuum? Perhaps there is a faulty Flux Capacitor hidden away in the girls toilet block.
I look forward to this being rectified and my daughter and other girls at the school being returned to this millennium where school activities are not sharply divided along gender lines.
Yours respectfully
Stephen CallaghanWhen Callaghan posted the letter to Twitter, it quickly went viral and inspired hundreds of supportive responses.
Though most people who saw his response to the school’s egregiously outdated activities applauded him, not everyone was on board.
One commenter wrote, “Sometimes it is just ok for girls to do girl things.”
But Callaghan was ready for that. “Never said it wasn’t,” he replied. “But you’ve missed the point. Why ‘girl things’ or ‘boy things’… Why not just ‘things anyone can do?’”
He later commented that he didn’t think the school’s plan was malicious, but noted the incident was a powerful example of “everyday sexism” at work.
Callaghan says the school hasn’t responded to his letter. (Yes, he really sent it.) At least, not directly to him.
Some media outlets have reported that the school claims students are free to opt in and out of the different activities. But, as Callaghan says, gendering activities like this in the first place sends the completely wrong message.
In response to the outpouring of support, Callaghan again took to Twitter.
“At 12 years of age my daughter is starting to notice there are plenty of people prepared to tell her what she can and can’t do based solely on the fact she is female,” he wrote.
“She would like this to change. So would I.”
This article originally appeared eight years ago.
-
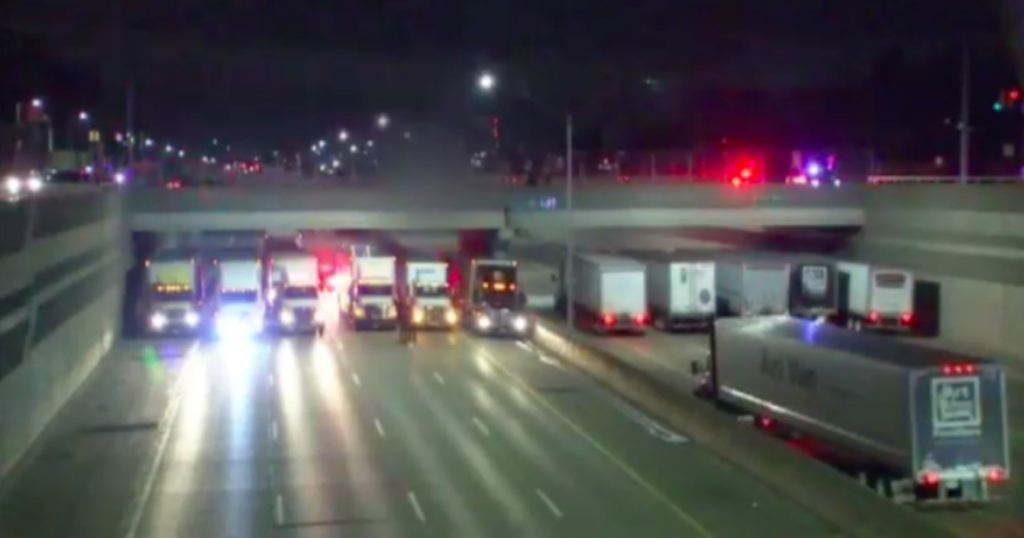
13 truck drivers parked side by side in the middle of the night to save a life
Humanity at its best.
Around 1 a.m. on April 24 2018, semi-truck drivers in the Oak Park area of Michigan received a distress call from area police: An unidentified man was standing on the edge of a local bridge, apparently ready to jump onto the freeway below.
Those drivers then did something amazing. They raced to the scene to help—and lined up their trucks under the bridge, providing a relatively safe landing space should the man jump.
Fortunately, he didn’t.
The impressive line-up wasn’t a coincidence—the drivers were prepared for exactly this sort of situation. Sgt. Jason Brockdorff of the Huntington Woods Police Department told The Detroit News that the response was something local police and truck drivers had actually trained for. But what was unusual was the sheer number of drivers who responded to the call.
“That’s a practice we use if we have a jumper,” Brockdorff said. “We try to do it every time, to lessen the distance someone would travel if they were to jump. Fortunately, that didn’t happen.”
The incident lasted nearly four hours, into the early morning. However, once the trucks were in place, the police were able to more comfortably negotiate with the unidentified man.
Eventually, the man walked off the bridge on his own and received medical attention.
In a pair of tweets, the local police department called attention to the incident to remind people in similar situations of the importance of seeking mental health services (emphasis mine):
This photo does show the work troopers and local officers do to serve the public. But also in that photo is a man struggling with the decision to take his own life. Please remember help is available through the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline at 1-800-273-8255.
You can also call a loved one, member of the clergy or 911. There are so many people that can help you make the choice to get help and live! It is our hope to never see another photo like this again.
Working together, the police and everyday strangers saved a life.
Ordinary people heeded the call of service to help a fellow person who was struggling. It’s a powerful image that’s impossible to ignore, and a reminder of humanity at its best.
This article originally appeared seven years ago.
-
Ever wonder why people 100 years ago died so much younger? It’s these 14 reasons.
1796. That’s when we invented vaccines.
An English doctor named Edward Jenner took incredible risks to try to rid his world of smallpox. Because of his efforts and the efforts of scientists like him, the only thing now standing between deadly diseases like the ones below and extinction are people who refuse to vaccinate their kids.
Unfortunately, because of the misinformation from the anti-vaccination movement, some of these diseases have trended up in a really bad way over the past several years.
Wellness involves a lot of personal choices and the tradeoff between personal liberty and shared public good.
Measles is the starkest example. In 2014, there were over 600 cases of measles in America during the first seven months of the year. According to the CDC, ten years later in 2024 there were 284 cases of measles nationwide. Though the numbers have improved in a decade, 89% of 2024’s cases came from people who are unvaccinated or refused to share their vaccine status.
Anti-vaccination movements aren’t new. Controversy, fear, and anti-vaccination rhetoric has plagued immunization efforts as far back as the early 1800s. Despite research conducted by the World Health Organization (WHO) showing that vaccines and immunization research has had a positive impact on global health, the anti-vaccination movements don’t seem to be facing eradication any time soon.
The chart below was made by graphic designer Leon Farrant and uses data from the CDC and JAMA to show that vaccines have real public health benefits. Paired with decades of improved medical care, vaccines have nearly eradicated many formerly fatal illness like Polio, Measles, Malaria, and Diphtheria. The impact of one’s personal health choices can have a significant impact on the population around them, in their communities, and even on a national level. It makes that trade-off all the more complicated and one not easily distilled into one convenient political or religious ideology.
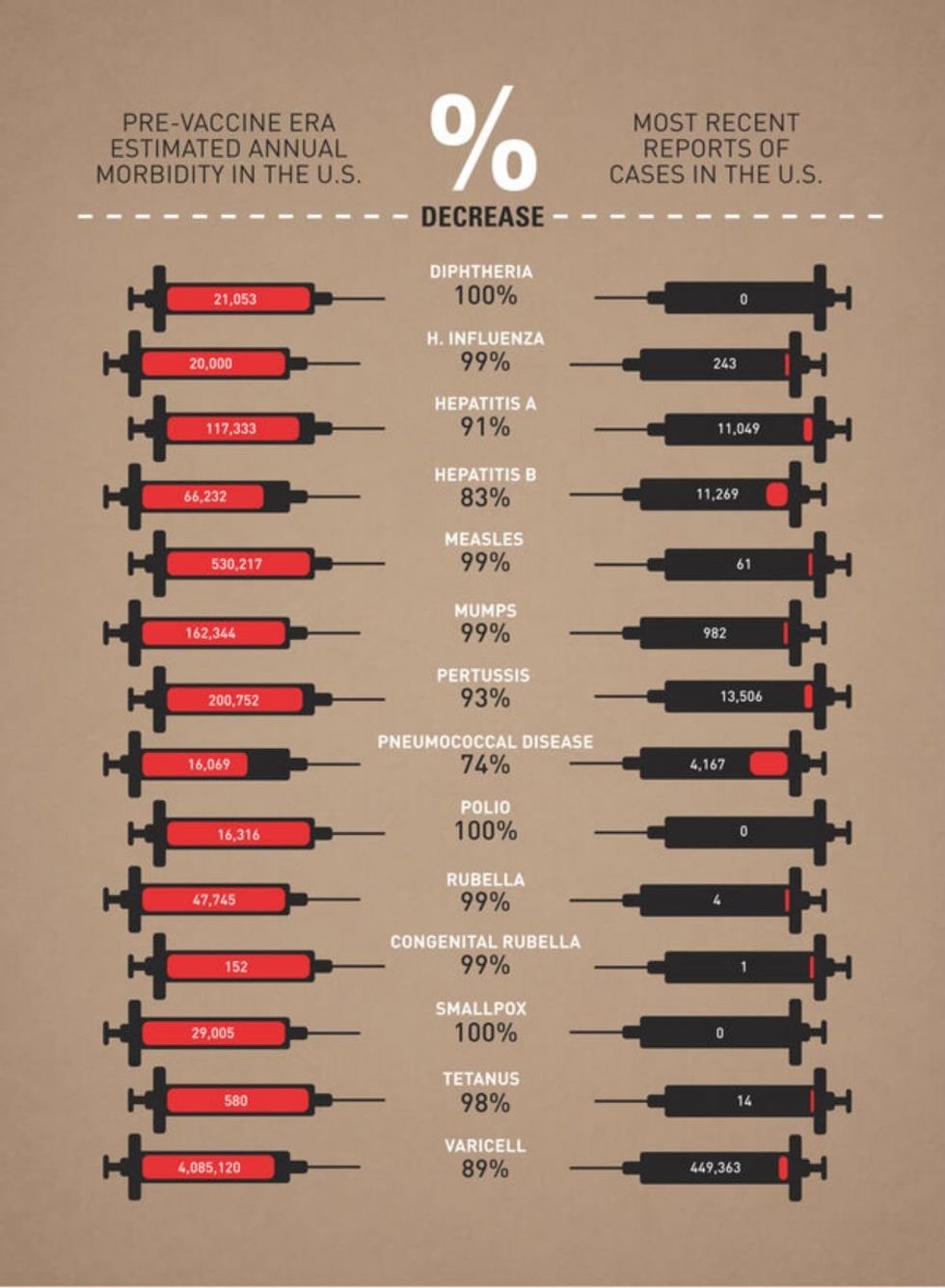
Infographic by designer Leon Farrant based on 2012/13 data.
<a href="https://assets.rebelmouse.io/eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJpbWFnZSI6Imh0dHBzOi8vYXNzZXRzLnJibC5tcy8xOTQ4NTEzMi9vcmlnaW4uanBnIiwiZXhwaXJlc19hdCI6MTc0MjUyMjA2M30.LpX4PtyDQj18b8Y394cDyUgINF1Mw7Jn9Qu2VI4o1ws/img.jpg?width=980"></a><a href="https://www.behance.net/leon_farrant">image from Leon Farrant</a>Obviously, the topic of vaccinations has become immensely more complicated and controversial over the years, especially since the onset of COVID-19 in 2020. But history teaches us valuable lessons and information is power. No matter how you feel about vaccines today, this chart is a reminder that medical science can be used for incredible good. Without breakthrough vaccinations in the past, many of us would likely not be here to have the debate about our personal choices now and in the future.
This article originally appeared eleven years ago.
-
This artist brilliantly tackles the concept of ‘being offended’ in a colorful comic.
Maybe we need a new word for ‘offended.’
Self proclaimed “feminist killjoy” Rebecca Cohen is a cartoonist based in Berkeley, California.
Here’s what she has to say about her role as an artist taken from her Patreon page.
She says:
“In these trying times, the world needs a hero to resist the forces of tyranny.
That hero is definitely not me.
I just draw funny pictures and like to share my opinions. I’m Rebecca, also known as @gynostar.”
Enjoy one of her comics below.
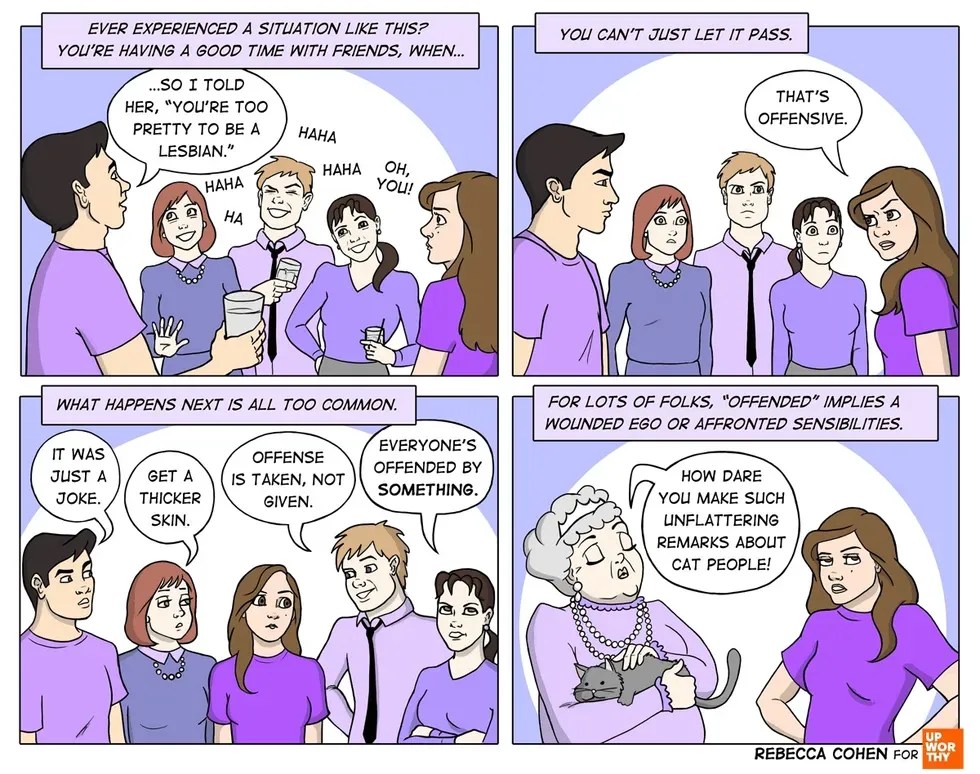
An all too common exchange. All images by <a href="https://rebeccacohenart.tumblr.com/post/152073543260/new-comic-for-upworthy-about-why-i-avoid-calling">Rebecca Cohen</a>, used with permission. 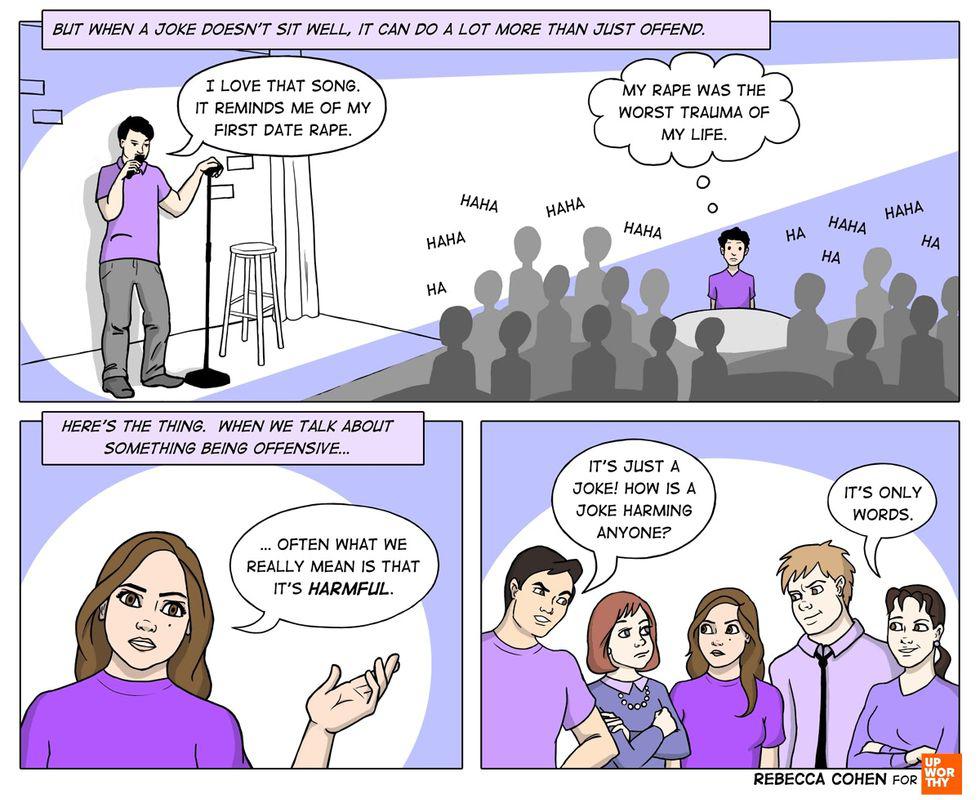
It’s only words. All images by <a href="https://rebeccacohenart.tumblr.com/post/152073543260/new-comic-for-upworthy-about-why-i-avoid-calling">Rebecca Cohen</a>, used with permission. 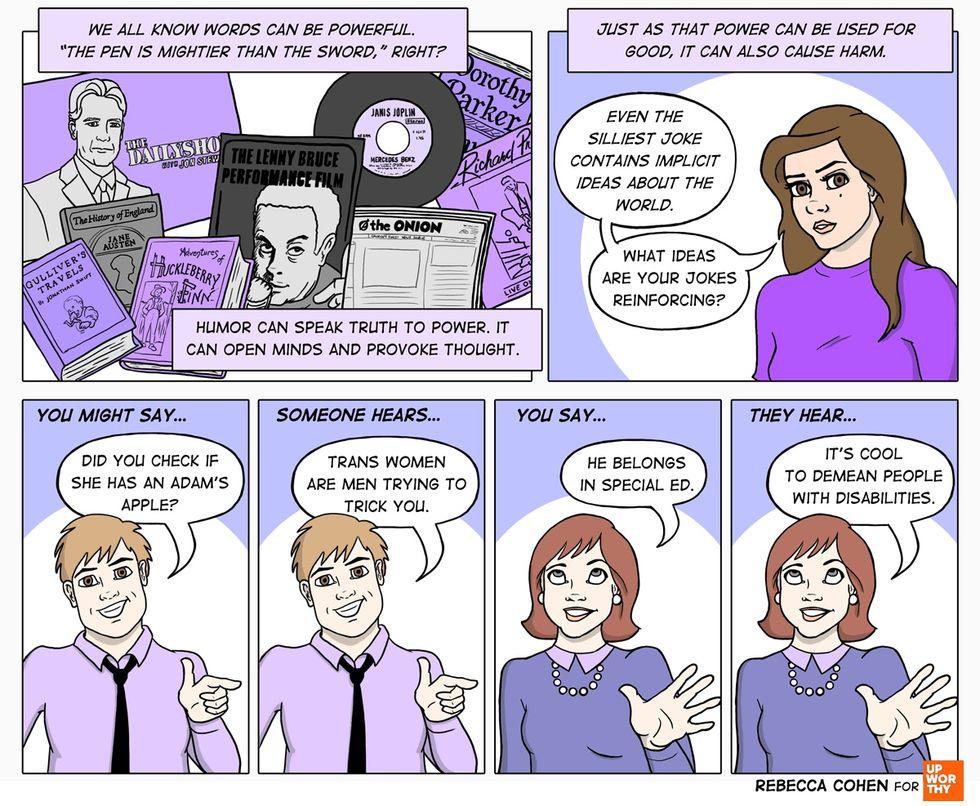
Simple jokes contain implicit ideas. All images by <a href="https://rebeccacohenart.tumblr.com/post/152073543260/new-comic-for-upworthy-about-why-i-avoid-calling">Rebecca Cohen</a>, used with permission. 
Discussing the impact of words. All images by <a href="https://rebeccacohenart.tumblr.com/post/152073543260/new-comic-for-upworthy-about-why-i-avoid-calling">Rebecca Cohen</a>, used with permission. This article originally appeared eight years ago.
-
5 years’ worth of photos show how testosterone affected one person’s life.
A journey as a trans person in photographs.
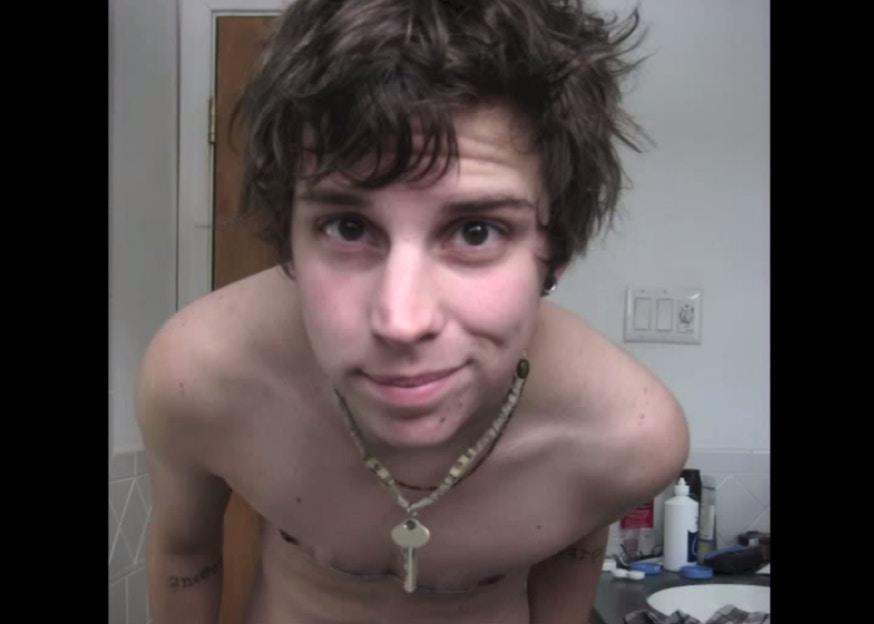
Even though he was born “Katherine Elizabeth,” Skylar lived like a regular little boy for most of his childhood.
He was happy.
This is Skylar.
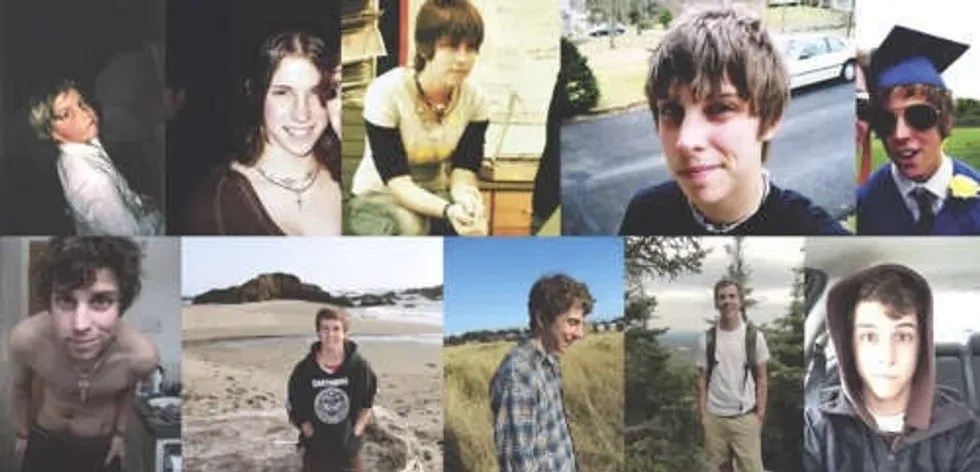

A photo collection of a young Skylar. Photo from YouTube video.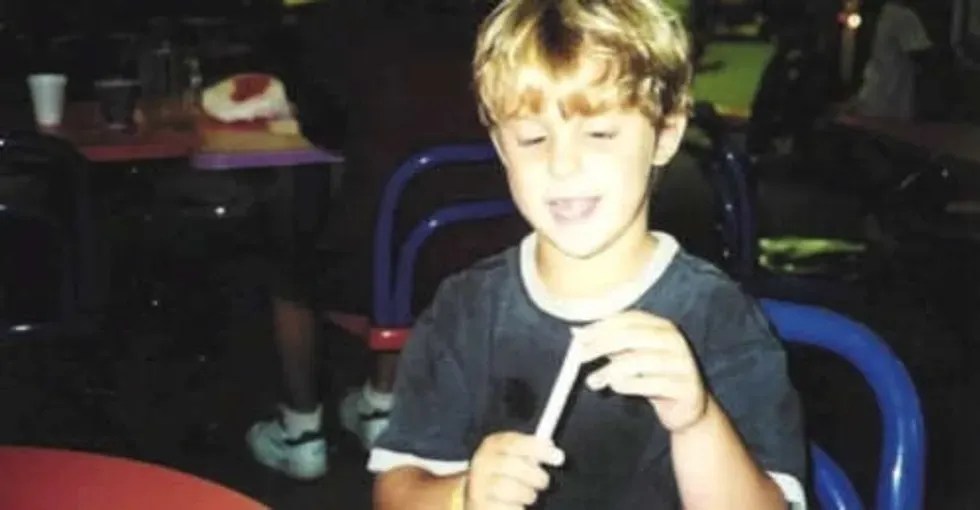 
Little Skylar. Photo from YouTube video. But when puberty hit, he started feeling intense pressure to be “normal” and fit in. So he tried to present as more traditionally “feminine.”

Puberty happens. Photo from YouTube video. But he couldn’t shake the feeling that he was denying a huge part of himself. Late in high school, he started taking testosterone.

Eating and feeling more comfortable. Photo from YouTube video. Skylar started feeling more comfortable immediately. And before he knew it, he was at his “dream school,” having the time of his life. And taking lots and lots of pictures of himself.
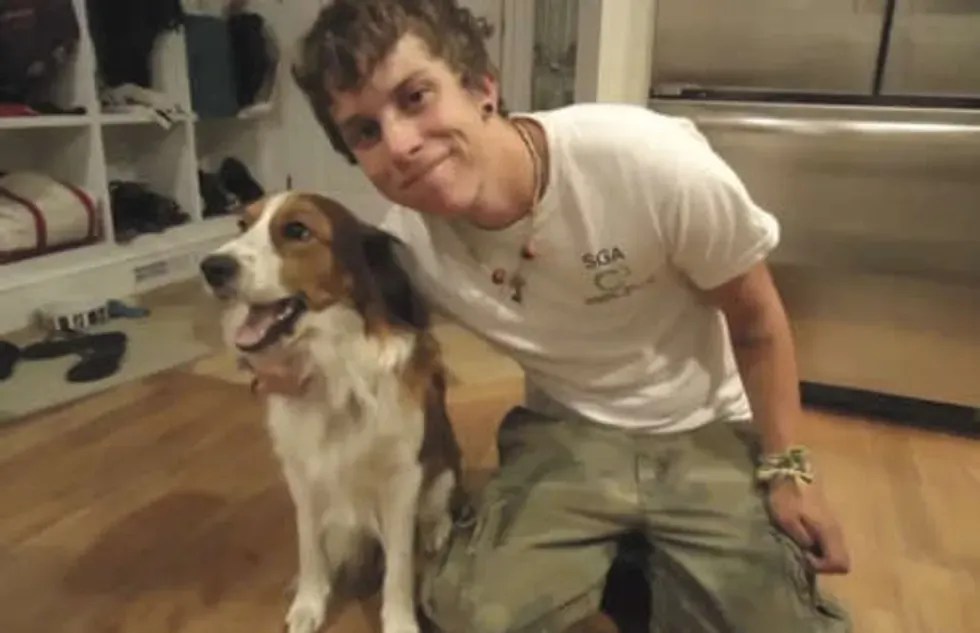

A person and their dog. Photo from YouTube video. Access to medical care played a big part in Skylar becoming the person he is today, but that wasn’t all.
Check out his story and walk five years in his shoes. It’s definitely a perspective we don’t see often enough:
This article originally appeared on 08.30.14
-
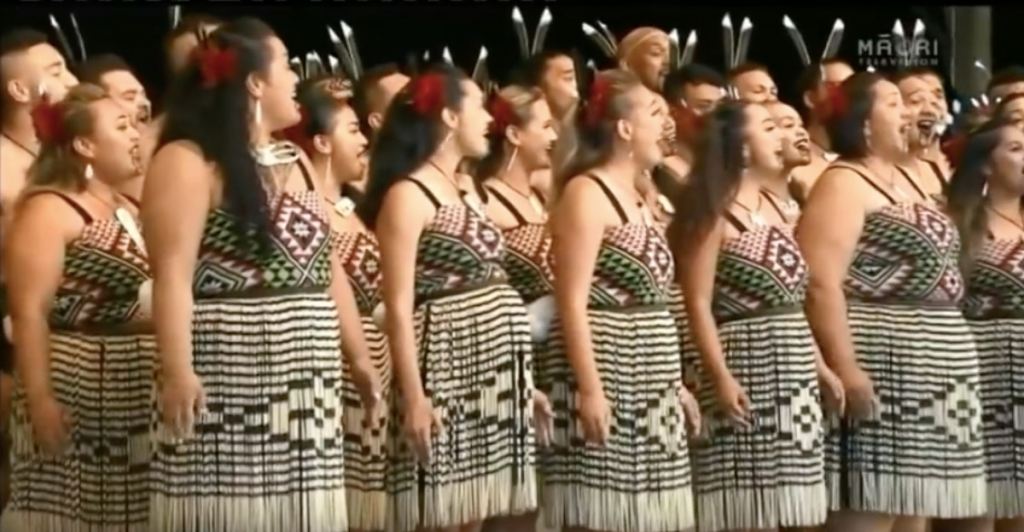
This Māori group’s kapa haka performance of Bohemian Rhapsody will make your day
Somehow it totally works.
Queen’s Bohemian Rhapsody has been covered dozens of different ways. But you’ve never seen it performed like this.
As one of the most iconic songs in rock music, Bohemian Rhapsody is recognizable no matter how it’s done. As children, my brother and I used to belt out Galileos and Figaros in the backseat of our parents’ Volkswagon whenever the song came on (yes, just like in Wayne’s World). While other kids learned about Beelzebub in Sunday School, I learned about him from Queen’s perfect harmonies. If there were an anthem from my classic rock-filled childhood, it would be Bohemian Rhapsody.
It’s one of those songs that is hard to cover well, though it hasn’t stopped people from trying. I’ve enjoyed some renditions, but nothing has caught my attention or delight more than this kapa haka version from New Zealand.
A Māori choir in native garb sang the song live in the Māori language, and it is something to see.
The group Hātea Kapa Haka performed the song on February 21 at New Zealand’s national kapa haka festival, Te Matatini, in Wellington. The festival brings 46 kapa haka (Māori performing arts) groups together to compete against one another.
Newshub reports that Hātea Kapa Haka collaborated with musical artist William Waiirua to create a “Bohemian Rhapsody” cover in the Māori language, both as a tribute to Freddie Mercury and to celebrate the Oscar-nominated movie about his life.
The group had previously created a music video for their cover, but seeing it performed live is something else. The voices, the harmony, the presentation—everything—is wonderful.
This kind of cultural mashup reminds us how small our world has become.
The contrast between Queen’s 1970s British rock and the Māori people’s traditional kapa haka could not be more striking. And yet, the melding of the two totally works. Music has the power to bring people together, and this performance is a great example of how it can bridge cultures with beautiful results.
Watch the live performance here:
And if you want more, check out the music video too:
William Waiirua got more help from Hātea Kapa Haka than he bargained for when his car broke down… For more Queen, check out this playlist: https://umusicNZ…
This article originally appeared on 03.01.19

















