“Fake news” is more than just the phrase the president uses to brush aside stories he doesn’t like. It’s a real thing, and something we should all be on the lookout for.
Below is an image of Parkland student Emma González tearing up a copy of the U.S. Constitution that went viral in 2018, sending some corners of social media into a frenzy.
There was one problem, however: It was totally fake.
The actual photo came from a Teen Vogue video shoot featuring her and some of the other Parkland students. In the real clip, González is seen tearing up a paper shooting target.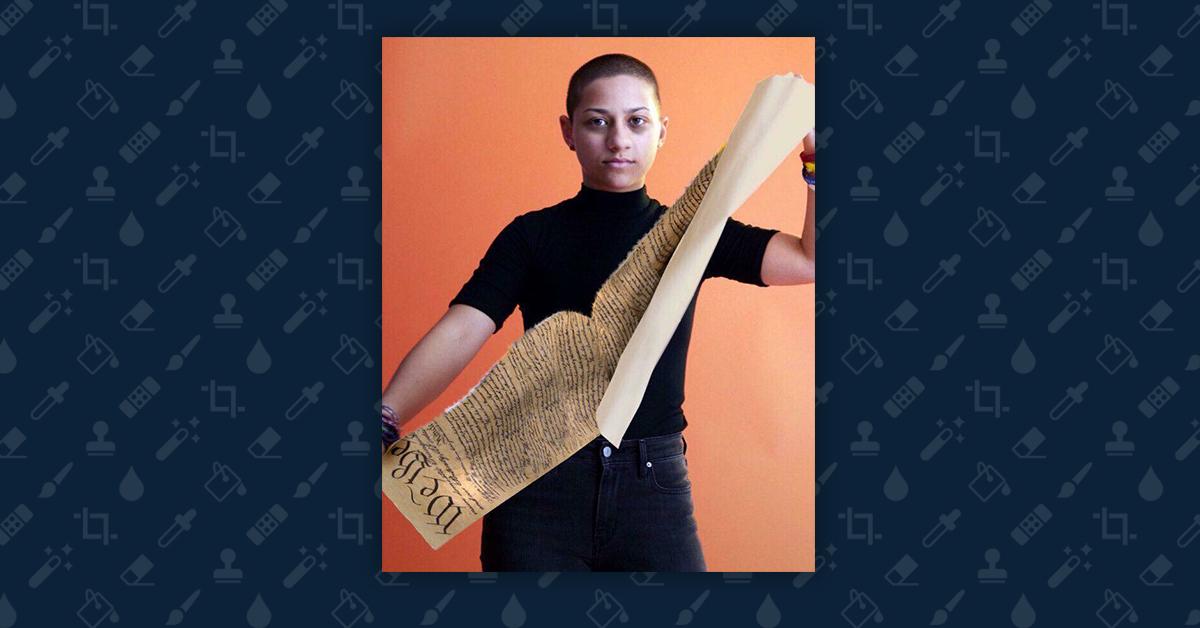
The fact-check was swift, but a lot of damage was done, as the altered image continued making the rounds.
It’s easy to be duped by online hoaxes — so we spoke with someone whose job it was to spot them every day.
At the time of this incident, managing editor Brooke Binkowski wrestled with the importance of truth and figuring out how to stop the spread of hoaxes every day for the highly trusted fact-checking website Snopes.
The site, launched in 1994, began as a collection of fact-checks on some of the internet’s early urban legends. Wanted to find out whether or not that story about the killer with a hook for a hand was true? Snopes had you covered. Needed to know whether your favorite brand of bubble gum is filled with spider eggs? The answer was just one click away.
As the site evolved its taken on more serious topics, online hoaxes, and “fake news.” Did Donald Trump wade into the waters of a flooded Texas city to save two cats from drowning after Hurricane Harvey? (No.) Did Barack Obama congratulate Vladimir Putin on his 2012 electoral victory? (Yes.)
Snopes is often cited alongside FactCheck.org and PolitiFact as some of the best, most accurate, and bias-free fact-checking websites in the world, even earning it a partnership with Facebook.
Binkowski spoke with Upworthy about how to deal with increasingly sophisticated hoaxes we all encounter online (and gave us a few behind-the-scenes secrets about how the people at Snopes do what they do best).
The following interview has been lightly edited and condensed for clarity.
Why does the truth matter, and what harm is there in sharing fake stories?
The truth matters because without being able to agree on the most basic facts, there is no democracy. Democracy depends on an informed, educated populace in order to survive. To actively suppress curiosity or obscure facts is to actively suppress democratic norms.
When you share fake or misleading stories, first of all, don’t beat yourself up about it if you were trying not to! We all fall for it. Some of it is extremely convincing.
I strongly believe that the onus should not be on the individual to sift through all the garbage to find good, vetted news on top of every other thing they have going on in their life, as I hear many suggest — that’s why journalism exists. I think people are overall extremely smart and crave information, but without vetted and transparent information, they fall for conspiracy theorizing.
That’s what propaganda and disinformation seize on. If you repeat that pattern across a country, it dramatically erodes these democratic norms. Plus, have you ever tried to talk to a really entrenched conspiracy theorist?
So I would be as mindful as you can about the sources of stories and try your best not to share disinformation — and if you do, I would try to be upfront about it and delete it so that it does not spread.
Right now is a crucial time to be mindful, even though I just said the onus shouldn’t be on the individual. It shouldn’t, but we simply don’t have enough working journalists to go around right now, because our industry has been allowed to collapse in the name of executive profit.
Can you walk us through how Snopes fact-checks a story?
We don’t have any one specific way that we fact-check a story — there’s no real formula for doing so. A lot of what we do is so disappointing when I describe it to people, because it’s not magic. It’s “just” journalism.
I try to give my writers time and space to do the research that they need to do, although sometimes it’s a little difficult when we have “conspiracizing” from all sides. So sometimes, one of us will have to head to the library to pull books or go over to the local university to look through papers on campus.
A lot of the time we do old-fashioned reporting. Our staff is all over the United States and they know their stuff, so I’ll take advantage of that and send them out on the field sometimes. We also, of course, know the repeat fake-news and satire offenders, so that makes it easy, because we can save a lot of time just by noting that they have an all-purpose disclaimer buried somewhere on their site. Sometimes we do photo or video forensics and FOIA requests (not that we get a lot of those answered, hahaha).
We try to be as thorough and as transparent with our work as possible, which is why we have a source list at the bottom of each page and maybe describe our methodology in a bit more detail than we should — but that’s how we all roll.
Which is also why, on a side note, I find the conspiracy theories about us a bit puzzling. We’re really easy to track down online, we list all our sources, and we try to be as open as humanly possible without also being boring about our methodology.
And yet people still think we’re part of a grand conspiracy. I’m still waiting for my check from George Soros/the Lizard People/the Clinton Foundation, though. It’s been, like, 20 years!
…OK, if you’re a conspiracy theorist reading that last sentence, that’s a joke. I already got my checks.
No, no, I’m sorry. I just can’t stop myself.
Photo via Teen Vogue, illustration by Tatiana Cardenas/Upworthy.
What can regular, everyday people do to avoid hoaxes and “fake news?”
My best tip that I can possible give readers is this: Disinformation and propaganda classically take hold by using emotional appeals. That is why what Cambridge Analytica did should be viewed through that lens.
One of the more sinister things that I have read that they did, in my opinion (among other things I’m sure that no one yet knows), was track people who were highly susceptible to authoritarianism, then flood them with violent imagery that was invisible to everyone else on social media, so that they were always in a state of fear and emotional arousal and highly susceptible to an authoritarian message.
That’s the type of person propaganda historically targets anyway — those who feel out of step with society and have strong tendencies toward authoritarianism — but now, groups like Cambridge Analytica are doing it faster and more surgically.
If you’re reading, viewing, or listening to a story that’s flooding you with high emotion, negative or positive — whether it’s fear, rage, schadenfreude, amusement at how gullible everyone else is — check your sources. You are being played. Do a quick search for the story, see if it has been debunked at minimum, and/or look for other sources and perspectives.
One of the most noxious things about disinformation and propaganda is that both weave some truth into their lies, which makes the lies much, much stronger.
Something I like to say about political leanings is that the right assumes it has the moral upper hand and the left assumes it has the intellectual upper hand — both are tremendous weaknesses that are easy to exploit.
Don’t let yourself be exploited. Be on guard. Don’t assume other people are sheep and don’t assume other people are morally bankrupt. Propaganda wants you to assume the worst about your fellow denizens; the people who push it out want the basic fabric of society destroyed.
It wants you hating your lovers, your neighbors, your family members, the guy at the store, the lady at the coffee shop. Propagandists want you distrusting each other, bickering, and unable to agree on the most basic facts — because then they can exploit those cracks further and consolidate power in the process.
Don’t let yourself be taken in.
The basic take-aways for the average person? Get your news from trusted sources, confirm it with a second source, check your own confirmation biases, and get familiar with reverse image search tools.
This story originally appeared on 03.30.18