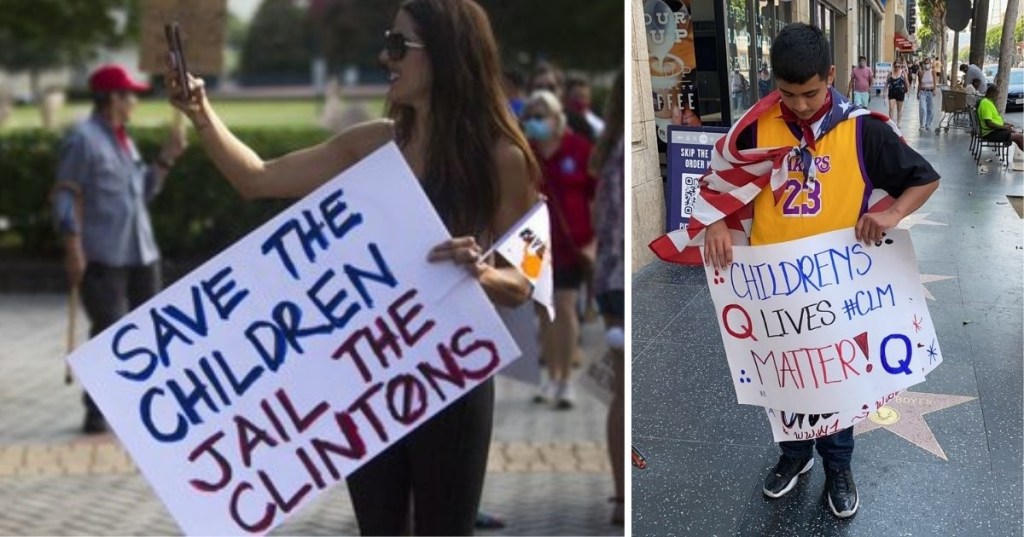
“Over 800,000 kids go missing in the U.S. every year! Child sex trafficking is the REAL pandemic. #SaveTheChildren #SaveOurChildren #ChildLivesMatter #Pedogate #Pedowood”
If you’ve been on social media in the past month or two, you’ve likely seen memes or posts to this effect. And if you’re a person with a conscience, it likely caught your eye. Children being trafficked for sex—that’s horrible!
Yes, it is. It’s absolutely horrible. Child sex trafficking is basically the worst thing human beings can do, no question. But what do those #Pedogate and #Pedowood hashtags mean?
Yes, those. Unfortunately, they point directly to a QAnon-perpetuated conspiracy theory in which the world is being controlled by an elite global cabal of pedophilic Hollywood celebrities and high-level politicians (including Tom Hanks, Oprah, Hillary Clinton, and more) who secretly traffick, abuse, and torture children so they can harvest a fear-induced hormone in their blood to make adrenocrhome, which they consume to keep them young and/or imbibe during their drug-crazed Satanic rituals.
What?! That’s crazy.
Yes, it is. It’s absolutely crazy. But there are a baffling number of people who believe it, including people who will likely soon be serving in Congress. Many of these people are sharing the #SaveOurChildren and #ChildLivesMatter hashtags right along with #Pedowood and #Pedogate. They conflate this huge number of missing kids with the issue of child sex trafficking, and then point to the celebrity/politician cabal conspiracy theory in the same breath, as if it’s all the same thing.
It is not.
The reality is that child sex trafficking is a multi-billion dollar, heinous, disgusting, global industry—but it’s not new. It’s not a sudden and massive crisis that “the media” is ignoring or that governments and NGOs aren’t addressing. Unfortunately, QAnon believers have pushed a lot of misinformation and misleading information into the awareness surrounding this issue that needs to be corrected.
To get to the heart of what child sex trafficking really looks like—and to be thorough in the debunking of QAnon’s child trafficking theories—we spoke with organizations whose work centers around stopping trafficking and protecting missing and exploited children.
The QAnon Misinformation
A common question people who have been sucked in by the QAnon world ask is: How do you know it’s not true if it’s never been investigated?
Some things are simply too ridiculous to be entertained, which honestly should be the case with the QAnon cabal theory. But since it’s somehow slipped into the mainstream, it has to be addressed head on.
So I swallowed my pride and directly asked anti-trafficking organizations—the people who specialize in this subject and are intimately involved in investigations—whether or not there was any truth to the theory. It was humiliating, frankly, but I straight up asked them: “It’s a known fact that child abusers often hide in plain sight and that high-profile people can be abusers. Based on your work, have you seen any evidence that there is a global cabal of pedophile elites who traffick children in a coordinated underground effort to harvest adrenochrome?”
Across the board, the answer was “No.”
I also asked this question: “Pedophiles and traffickers sometimes use coded symbols and code words in their communications with one another. Is there any official documentation that the words ‘pizza’ or ‘hot dog’ or ‘sauce’ have been used for such a purpose? (Or more directly, are the Wikileaks emails evidence of child sex trafficking?)”
Again, the answer was no. Of course.
(For those new to Conspiracyland, the code words question came from the claim QAnon folks make that the FBI has a list of code words and symbols that support the Pizzagate theory, which posits that Hillary Clinton and associates were discussing their dastardly pedophile deeds in code words—pizza, sauce, etc.—via emails released by Wikileaks. The FBI has documented known pedophile symbols, but none of the supposed code words in the Wikileaks emails are listed among them And the Washington D.C. police have called Pizzagate “a fictitious online conspiracy theory.”)
Erin Williamson, VP of Global Programs for Love146—an organization that has been working with sex trafficking prevention and survivor care for 17 years—says that conspiracy theories like this just makes more work for the people trying to do the work of educating the public.
“If somebody comes to know trafficking and has no preconceived notions of what trafficking is, you’re starting with a blank slate,” she says. “You can build from zero. But if someone’s coming to the trafficking movement or approaching this issue with preconceived incorrect information, then first you have to get them to the point where they realize all of the information that they’ve learned thus far is inaccurate before you can start building the accurate information. And it just is going to take so much longer to get people to a point where they actually understand what this accurately looks like.”
A national organization that asked to remain anonymous (understandable, considering how my own inbox fills with people accusing me of being a pedophile each time I write about how QAnon is bunk) told Upworthy, “Questions like this distract from the realities of how sex trafficking actually occurs. Offenders do often communicate in code but we haven’t seen any such official documentation and don’t consider the Wikileaks emails credible. Unfounded conspiracy theories minimize, distract and draw valuable resources away from the tireless work being done by child protection advocates on the ground.”
The Polaris Project, which runs the National Trafficking Hotline, offered an example of how resources get usurped by these theories. Last month, a rumor started circulating in the QAnon sphere that the Wayfair website was being used to traffick children because someone spotted an strangely expensive cabinet with a female name.
“The Wayfair theory resulted in online harassment and privacy intrusions of people mistakenly believed to be victims, as well as broad sharing of online sexual abuse material of actual victims who have not been connected in any way to Wayfair,” Polaris told Upworthy. “This harm is real for survivors who want to maintain their privacy, victims who are being re-exploited by broader distribution of their abuse materials, or bystanders whose lives can be overwhelmed by the actions of potentially well-meaning online communities.”
In addition, Polaris adds, “Conspiracies distract from the more disturbing but simple realities of how sex trafficking actually works, and how we can prevent it.”
But isn’t awareness about child sex trafficking a good thing, even if it’s not all factual?
Love146’s Erin Williamson says no.
“In the short term, it might make people aware that there is an issue of child trafficking that exists,” she says.”But if that doesn’t lead to somebody actually engaging with the issue and taking effort to join the movement to actually effectively eradicate the issue, then no. It’s harmful. It’s just a bunch of white noise that’s sucking up resources.”
“The question really is how many of the people are going to, as a result of this, actually have enough concern about child trafficking that they do more research, effectively realize what the issue is about, and then consistently or actively engage in addressing it,” she adds. “And I don’t think we fully know the percentage. My concern is that that percentage will be pretty low.”
Perpetuating these kooky cabal theories does more to hurt the child sex trafficking cause than to help it.
Those Missing Kids Numbers
But what about all those missing children then?
Every organization I spoke to pointed out that there are no hard and fast numbers because there’s no way to know exactly how many kids are being trafficked or exploited beyond what gets reported. We know that a lot of exploitation doesn’t get reported, but most kids who go missing do get reported somewhere.
Two organizations pointed me to the National Center for Missing and Exploited Children (NCMEC) for missing children statistics. The NCMEC states, “According to the FBI, in 2019 there were 421,394 NCIC entries for missing children. In 2018, the total number of missing children entries into NCIC was 424,066.” They clarify that this number represents individual reports of missing children, not the number of missing children themselves. If a child runs away multiple times in a year, each instance is counted separately and included in the yearly total, so the total number of missing children is likely less than those total numbers.
That’s a lot of children; however, the vast majority of missing kids make it back home pretty quickly. Think of kids who run away to a friend’s house and the parents can’t find them, kids who get lost temporarily, or kids who get taken or not returned by a parent in a custody dispute.
The kids who don’t return home and who are at risk of exploitation are where NCMEC comes in. In 2019, they assisted law enforcement and families with more than 29,000 cases. Less than one percent of those were non-family abductions, so the idea that loads of kids are just being snatched out of nowhere and sold for sex is totally inaccurate. In addition, NCMEC reports that 91 percent of those cases (around 26,300) were endangered runaways, and of those kids, 1 in 6 were likely victims of child sex trafficking. One is too many, of course, and these numbers are significant. But they’re nowhere near 800,000.
Statistics come in various forms, of course. The Polaris Project, which runs the National Trafficking Hotline, tells Upworthy, ” In 2019, the National Human Trafficking Hotline reported 2,582 underaged individuals involved in trafficking situations (all types).” However, they note, “It is incredibly important to note that these figures cannot be construed as prevalence.”
Again, one child is too many, and these statistics only represent a fraction of the problem. Sharing these numbers is not meant to downplay the issue at all, but rather to explain that there’s no real basis for the idea that 800,000 kids go missing and get sucked into child sex trafficking each year in the U.S.
So where did that number come from? There were some articles in the early 2000’s that cited numbers close around 800,000. But the most recent statistics are shared above.
Numbers are always a bit fuzzy. What we do know is that children are being trafficked and exploited. Far too many, far too often.
What Child Sex Trafficking Really Looks Like
Child sex trafficking is a complex industry. Sometimes it looks like children being physically transported place to place and being bought and sold for sex. Sometimes it’s kids being used to create child pornography. Sometimes it’s a drug-addicted parent renting out their children to get money for their addiction. Sometimes it’s teens recruiting other teens to engage in sex or create sexual images for money.
Love146’s Williamson explained that trafficking can look very different in different parts of the world.
“We run a program in the Philippines, and most of our children come into that program under 10,” says Williamson.. “We’ve accepted kids under the age of one into that program. In those situations, it’s really familial a lot of times, and a lot of what is happening is happening over webcams. You’ll also see reports of labor trafficking happening in other countries at very young ages.
“What we see in the United States and what we’re working with is different. We’re not seeing as many under 10 year olds trafficked. I’m not saying it doesn’t happen—it does. But more of what we’re seeing are adolescents. Preteen and teenagers who are being groomed and recruited, and while some is familial, a lot is not familial.”
Williamson explains that the term “runaway” is a bit of a misnomer because some runaways are teens who get pulled away from home by traffickers in sneaky ways.
“Part of what traffickers do is they recruit and groom,” she says. “They engage in a relationship for the purposes of exploiting this kid for trafficking. So it can appear that a kid is running away, or choosing to leave their house willingly, but it’s actually an intentionality on the part of the traffickers to make it appear that way…to make it appear that way to law enforcement, to the parents, and to the child themselves. So the child says things like, ‘I chose to go, I chose to meet up with so and so who I met online, or to meet up with so and so who I met in the park.’ So again, even when we talk about the term runaway…they’re really being groomed and recruited away from their home.”
One common theme among the organizations I communicated with is that there are well-known conditions that greatly increase a child’s chances of being trafficked.
Polaris Project says:
“Traffickers recognize and take advantage of people who are vulnerable in certain ways. There are several factors that may make a child vulnerable to sex trafficking including having an unstable living situation, having a history of domestic or sexual abuse, being frequent runaways, being involved in the juvenile justice or foster care systems, experiencing poverty or financial need, and/or dealing with addiction. While anyone can be trafficked, just as anyone can become a victim of any crime, due to factors such as historical oppression, discrimination, and generational trauma, LGBTQ+ youth and youth of color are more likely to be trafficked.”
The anonymous organization also explained that certain conditions make kids more vulnerable. “Certain kids who are homeless or runaways, belong to certain minority groups, and who have contact with the child welfare system are particularly vulnerable to this type of exploitation.”
Polaris also points out, “In the case of child sex trafficking in particular, the vast majority of victims know their traffickers and trust them. They may be professional traffickers who carefully groom young people on line and lure them into trafficking situations. They may well also be their parents, or other family members or trusted friends.”
What We Can Do About it
Learning about the realities of child sex trafficking is the first step. The issue is complex and multi-faceted, but just because it’s not simple or easy to solve doesn’t mean there’s nothing we can do.
One active thing we can do is what trafficking looks like.
“Trafficking is rarely perpetrated by a total stranger who kidnaps children,” says Polaris Project. “What we frequently see through the Trafficking Hotline are stories of people being trafficked by intimate partners, family members, and others that they know and may even love and trust.”
We can also make sure kids we are in contact with know that we are safe people they can go to if they are in an unsafe situation.
“When we talk to kids, it is always the little things that made the difference,” says Love 146’s Williamson. “It is always the neighbor who asked how they were doing, who then they realized was a safe person, that they could eventually talk to about what was happening to them in their house. It is always the teacher who they would curse out who would say ‘I’m still here for you whenever you need something.’ It is the little things that make a difference in a child’s life.”
Williamson also points out that the systemic issues we debate over in our society also impact child sex trafficking, and addressing those issues will help reduce the vulnerabilities that lead to exploitation.
“For most of us who have been working in this field long enough, there’s now a general recognition that we’re not going to arrest and prosecute our way out of this issue,” she says, “We’ve tried that. That isn’t happening. We need to go upstream. We need to deal with all of the things that make people vulnerable—the inequalities, the racism, the sexism, the homophobia. We need to address all of these issues that have all sorts of consequences, of which trafficking is one of them. It takes a while to get somebody to understand how this is all interrelated.
So when I hear somebody say, ‘Black Lives Matter? What about children’s lives? There’s been a couple of quotes like that. ‘Why are we marching for Black Lives Matter? Where’s the outcry for trafficked children?’ and comparing those two. First of all, this is not a dichotomy—we should be addressing all of this. And my thing is when you look at the statistics, especially here in the United States, trafficking is disproportionately affecting children of color. And so racism is at the heart of both of these issues, when you’re talking about the disproportionality of violence against people of color. So it’s not an either/or. It’s actually a yes/and. Which is why we have to go upstream and start addressing some of these systemic issues.”
To learn more about the real issue of child sex trafficking, check out these organizations’ websites: