Here are some essential facts about refugee resettlement to share with the misinformation mongers
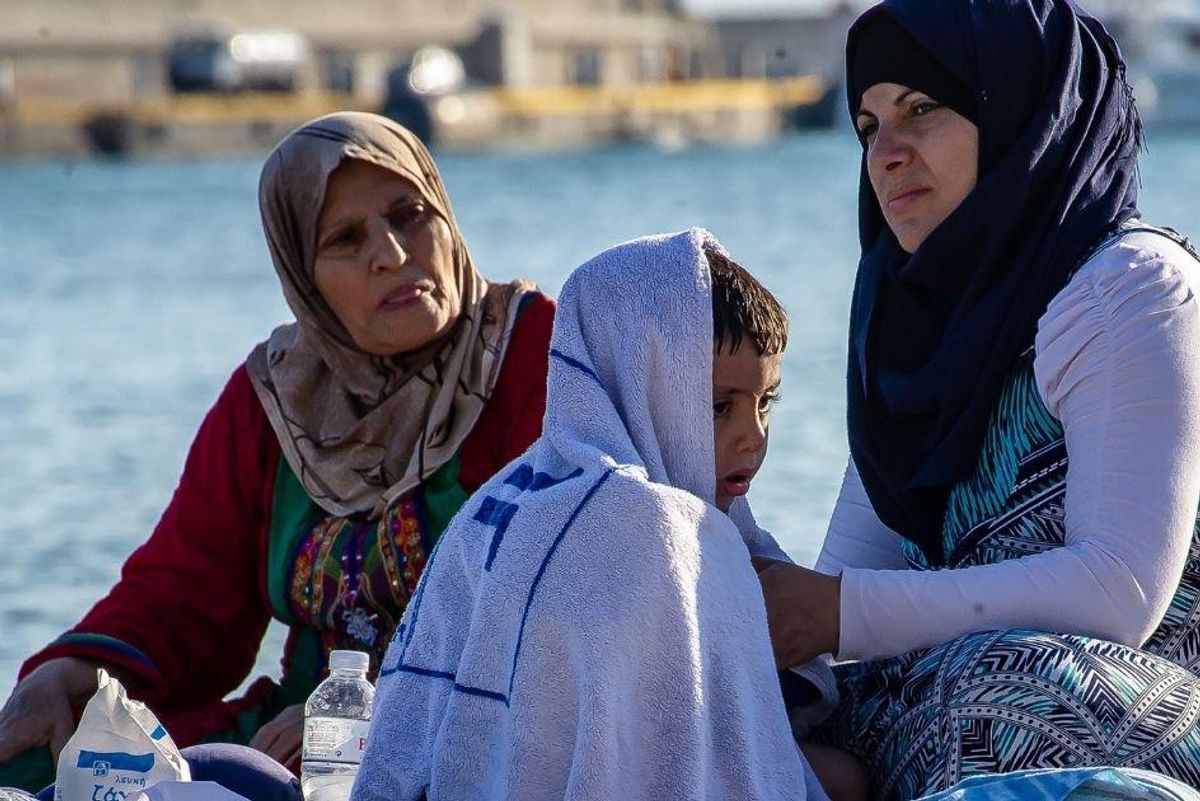

As we watch reports of thousands of Afghans fleeing Afghanistan in the wake of a Taliban takeover, the question of where they will go looms large. The world was already in the midst of a refugee crisis, with 82.4 million people forcibly displaced at the end of 2020—double the number there were just ten years earlier. Of those, more than 20 million are official refugees registered with the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR).
Between ongoing civil wars, increasing disasters driven by climate change, religious persecution, and more, humanity has more people in need of a safe country to call home than at any other time in history.
The dramatic and visible nature of the dangers facing Afghans targeted by the Taliban has prompted an outcry of support for refugees, which is heartening to see. The U.S. has a long and proud history of welcoming refugees, right up until the Trump administration drastically slashed the refugee ceiling—the maximum number of refugees we resettle—to historic lows.
Even with the Biden administration raising the refugee ceiling for 2021 from Trump's 15,000 to a much larger 65,000, we're still below our historic norm. According to experts interviewed by The Guardian, the nation's refugee resettlement infrastructure was nearly demolished during Trump's presidency. Those systems will take time to build back up again.
But successfully welcoming refugees requires not only systematic logistics but social and political will, which can be hampered by misinformation and fearmongering. It's vital to have the facts straight before listening to people saying it's too expensive or too risky to bring refugees into the country.
FACT: Refugees and migrants/asylum-seekers at the southern U.S. border are not the same thing.
I often see people say "We already have too many refugees coming across the border already," but the vast majority of people trying to cross into the U.S. from Mexico are not official refugees. They are migrants or asylum-seekers, which means their claims for needing refuge have yet to be vetted and processed. "Refugee" is a specific designation under international law, and refugees are processed through a different protocol than migrants and asylum-seekers at the border.
The refugee ceiling is for legally recognized refugees. In the past decade, according to State Department data, 28 percent of refugees have come from Africa, 63 percent from Asia, 5 percent from Europe, and 4 percent from Latin America and the Caribbean.
FACT: Refugees are the most vetted people to ever step foot in the U.S.
A common myth is that refugees pose a security risk to the country, but that's not backed up by either logic or evidence. The vetting process for refugees (which you can see in detail here) is the most stringent of any group to enter the United States. It can take up to two years for a refugee to get cleared to resettle here. If someone with ill intent wanted to enter the country, going through the refugee resettlement program would absolutely be the hardest and longest way to do it.
Additionally, refugees (and all immigrants, actually) are not the ones committing terrorist attacks in the U.S. A 2017 Cato Institute study found that the chance of an American being murdered in a terrorist attack by a refugee is about 1 in 3.86 billion per year. Immigrants of all kinds are also less likely to commit crimes than native-born citizens.
FACT: Resettling refugees is good for our economy.
Another common myth is that refugees are a drain on our resources. While there is an initial cost of bringing people in and helping them get on their feet, analysts have found that refugees actually have a net positive impact on the economy. One reason is that refugees are more likely to start businesses than native-born citizens or even other immigrants. And in an analysis of Census data, Economics professor Ramya Vijaya found that refugee women were more likely to be working or actively looking for work than native-born women.
Obviously, we have to have the budget for the initial investment, but that's essentially what resettling a refugee is—an investment. We don't seem to have a problem finding money for guns and bombs, so finding money to help the people who end up paying the price for our wars seems like it shouldn't be too hard, especially when we know we're going to get that money back in the long run.
FACT: Refugees in general have the character qualities we want to see in our country.
I know some Afghan refugees who have been stuck in Jakarta for years, waiting for a chance at resettlement. (Indonesia allows them to stay but they can't work or get a bank account and are basically just living in limbo relying on the charity of others.) And honestly, they are some of the kindest, most hard-working, earnest, smart, and resourceful people I've ever encountered. I have often lamented that I couldn't bring them here myself (or trade them for some of my fellow Americans who could use a change of perspective).
Every human being is unique, of course. But the nature of being a refugee means having to overcome incredible difficulties. It means having to problem-solve and find a way, even when a situation seems impossible. It requires courage, resilience, and fortitude. These are all qualities of character we value as a society.
And what better way to build goodwill and loyalty around the world than to offer people fleeing danger safe refuge and opportunity? Refugees who get resettled are grateful when they are welcomed into a community and usually want to repay the generosity offered to them.
Seriously, refugee resettlement is pretty much all upside for the U.S., unless you're afraid of diversity or have some irrational fear of foreigners.
If you think the U.S. should try to bring in more refugees than the current refugee ceiling allows, sign this petition from the International Rescue Committee.
- Setting the record straight on what it's really like to host a refugee ... ›
- This American city has a winning way of making refugees feel ... ›
- In a brilliant move, Penn Museum hires refugees as guides to ... ›
- Airbnb offers free housing to 20,000 Afghan refugees - Upworthy ›
- Where do Afghan refugees go? - Upworthy ›
- Afghan refugees need us. So do millions of other refugees. - Upworthy ›
- When African students faced discrimination fleeing Ukraine, Asmara’s World stepped up - Upworthy ›





 I Love You Elf GIF by MOODMAN
I Love You Elf GIF by MOODMAN "Love you!" Oops.
"Love you!" Oops. Green Flag GIF by The Last Talk Show
Green Flag GIF by The Last Talk Show Embarrassed Hide GIF by flor
Embarrassed Hide GIF by flor Eating the right foods is crucial for mental health.
media3.giphy.com
Eating the right foods is crucial for mental health.
media3.giphy.com
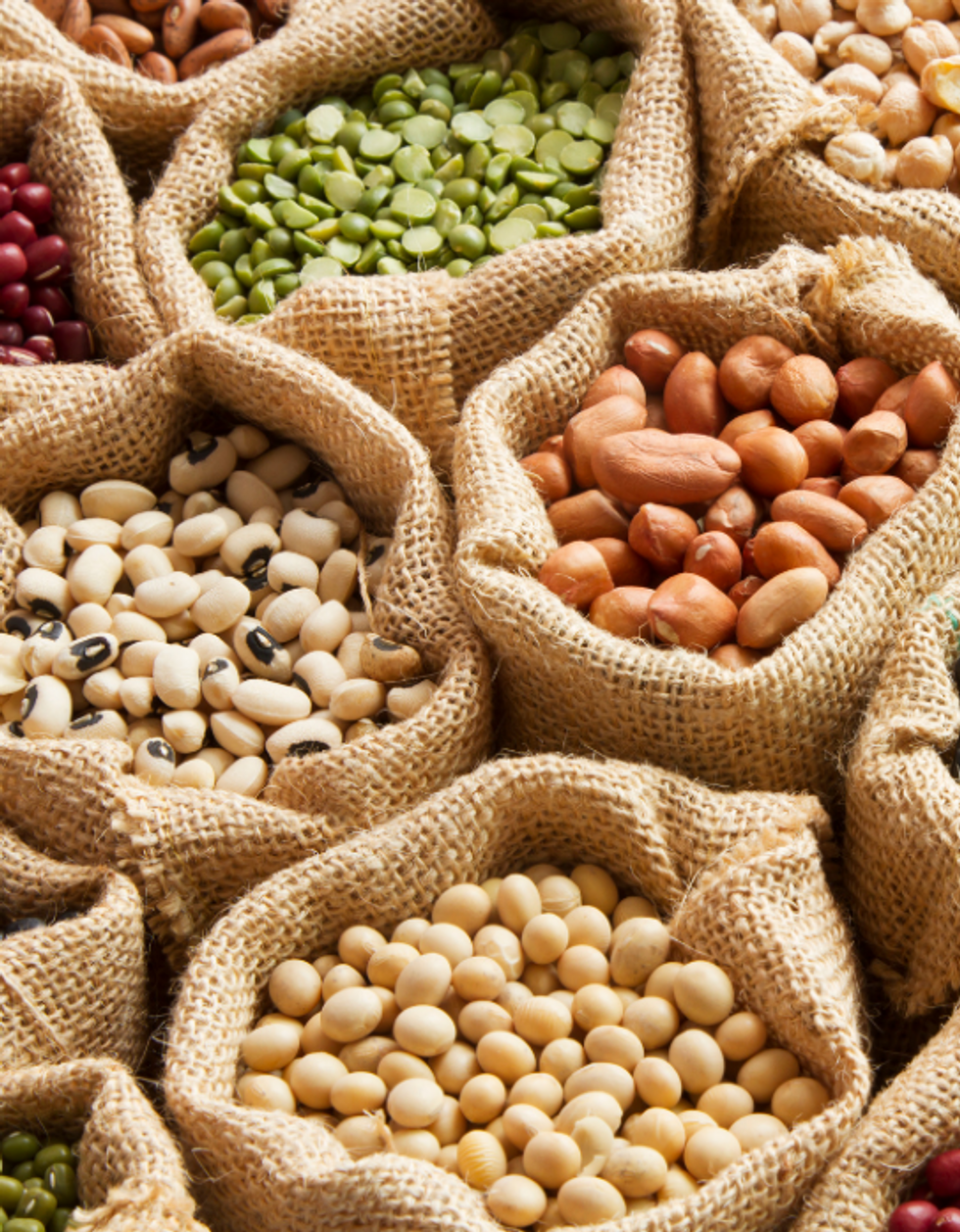 Legumes, like beans and lentils, are super foods and chockful of Vitamin B9.
Photo credit: Canva
Legumes, like beans and lentils, are super foods and chockful of Vitamin B9.
Photo credit: Canva
 Spending time in nature for at least two hours a week is great for overall wellbeing.
Spending time in nature for at least two hours a week is great for overall wellbeing.  There's an innate need for human connection.
There's an innate need for human connection. Even a simple hike, no matter what the pace, is effective when combatting feeling bad.
Even a simple hike, no matter what the pace, is effective when combatting feeling bad.  Tracking your steps can help motivate you and keep you motivated.
Tracking your steps can help motivate you and keep you motivated.  Vincent Van Gogh's Self-Portrait, 1889Image via
Vincent Van Gogh's Self-Portrait, 1889Image via  Turbulent flow illustrated and animated.
Turbulent flow illustrated and animated.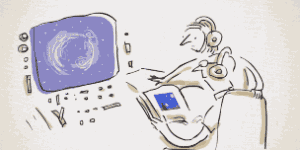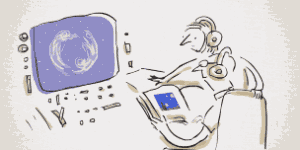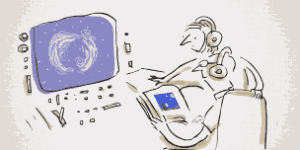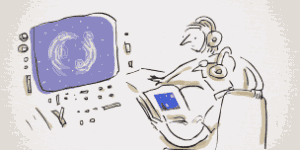 Animation of art referencing science.
Animation of art referencing science. Animated Starry Night
Animated Starry Night An animated depiction of The Scream.
An animated depiction of The Scream.
There's a reason why some people can perfectly copy accents, and others can't
Turns out, there's a neurodivergent link.
A woman in black long sleeve shirt stands in front of mirror.
Have you ever had that friend who goes on vacation for four days to London and comes back with a full-on Queen's English posh accent? "Oooh I left my brolly in the loo," they say, and you respond, "But you're from Colorado!" Well, there are reasons they (and many of us) do that, and usually it's on a pretty subconscious level.
It's called "accent mirroring," and it's actually quite common with people who are neurodivergent, particularly those with ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder). According Neurolaunch, the self-described "Free Mental Health Library," "Accent mirroring, also known as accent adaptation or phonetic convergence, is the tendency to unconsciously adopt the accent or speech patterns of those around us. This linguistic chameleon effect is not unique to individuals with ADHD, but it appears to be more pronounced and frequent in this population."
Essentially, when people have conversations, we're constantly "scanning" for information—not just the words we're absorbing, but the inflection and tone. "When we hear an accent, our brains automatically analyze and categorize the phonetic features, prosody, and intonation patterns," writes Neurolaunch. For most, this does result in copying the accent of the person with whom we're speaking. But those with ADHD might be more sensitive to auditory cues. This, "coupled with a reduced ability to filter out or inhibit the impulse to mimic…could potentially explain the increased tendency for accent mirroring."
While the article explains further research is needed, they distinctly state that, "Accent mirroring in individuals with ADHD often manifests as an unconscious mimicry of accents in social situations. This can range from subtle shifts in pronunciation to more noticeable changes in intonation and speech rhythm. For example, a person with ADHD might find themselves unconsciously adopting a Southern drawl when conversing with someone from Texas, even if they’ve never lived in the South themselves."
People are having their say online. On the subreddit r/ADHDWomen, a thread began: "Taking on accents is an ADHD thing?" The OP shares, "My whole life, I've picked up accents. I, myself, never noticed, but everyone around me would be like, 'Why are you talking like that??' It could be after I watched a show or movie with an accent or after I've traveled somewhere with a different accent than my 'normal.'
They continue, "Apparently, I pick it up fast, but it fades out slowly. Today... I'm scrolling Instagram, I watch a reel from a comedian couple (Darcy and Jeremy. IYKYK) about how Darcy (ADHD) picks up accents everywhere they go. It's called ADHD Mirroring??? And it's another way of masking."
(The OP is referring to Darcy Michaels and his husband Jeremy Baer, who are both touring comedians based in Canada.)
Hundreds of people on the Reddit thread alone seem to relate. One comments, "Omfg I've done this my whole life; I'll even pick up on the pauses/spaces when I'm talking to someone who is ESL—but English is my first language lol."
Sometimes, it can be a real issue for those around the chameleon. "I accidentally mimicked a waitress's weird laugh one time. As soon as she was out of earshot, my family started to reprimand me, but I was already like 'oh my god I don’t know why I did that, I feel so bad.'"
Many commenters on TikTok were shocked to find out this can be a sign of ADHD. One jokes, "Omg, yes, at a store the cashier was talking to me and she was French. She's like 'Oh are you French too? No, I'm not lol. I'm very east coast Canada."
And some people just embrace it and make it work for them. "I mirror their words or phrase! I’m 30. I realized I start calling everyone sweetie cause my manager does & I work at coffee shop."