The way experts create wigs on some of your favorite shows is enough to make your head spin
It's even more involved than it appears.
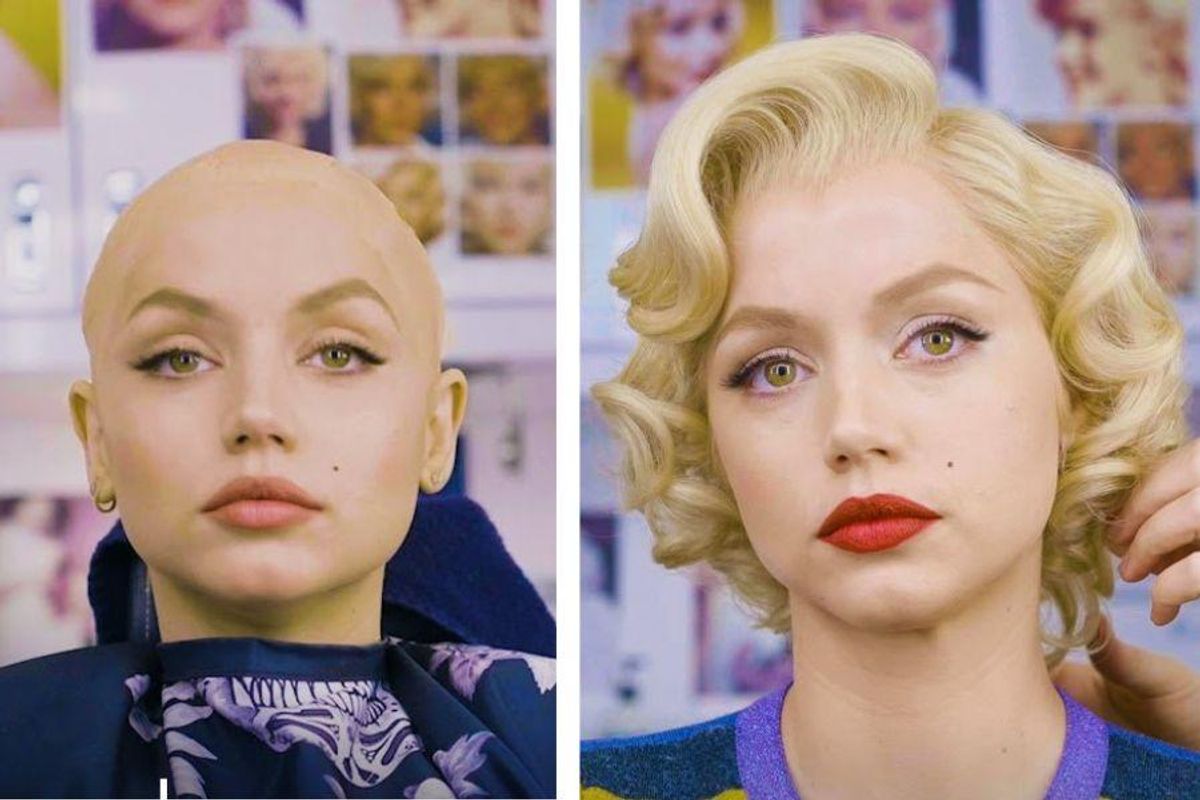

Ana De Armas transforming into Marilyn Monroe for "Blonde."
We know that there’s a painstaking amount of detail that goes into bringing characters to life on the big and small screen. But ever so often, a fascinating look behind the scenes will come along that’s so mind-blowing, one can’t help but feel a fresh level of gratitude (and awe) for the effort that goes into modern-day storytelling.
Take, for instance, the hyperrealistic wigs we see in so many films and television shows. Odds are, one of your favorite characters wears one—even when you would bet your life savings that the hairs you see are sprouting from their own head. This illusion is the result of dedicated hours upon hours from artists that are so much at the top of their game, we might as well just call them hair sorcerers.
In a video posted to YouTube by Insider, Rob Pickens, founder of Wigmaker Associates, takes viewers on a tour of the wigmaking process for some of today’s most iconic shows, from start to finish. As Pickens explains, since cameras have become more equipped to pick up every detail, wigs must become more detailed and precise to not only mimic real hair texture, but perfectly fit an actor’s head shape to look as natural as possible.
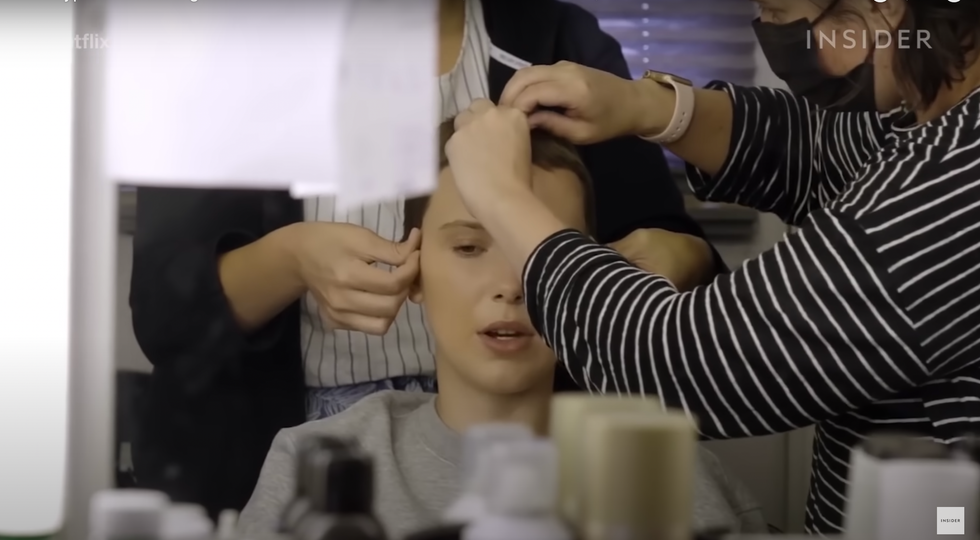
To do this, hair teams don’t just measure an actor’s head. They create a mold that completely replicates their skull shape using a headwrap made with cellophane and tape—lots of it—after which they trace over the hairline with a sharpie.

Millie Bobbie Brown's skull mold.
That headwrap then goes onto a canvas block (which more or less looks like a mannequin head), and that canvas block is filled with stuffing to match the actor’s exact head shape in a process that Pickens calls “padding the block.”
It might be a laborious endeavor, but once it’s done, that mold can be used for any production in the world. Cranium cloning, if you will.
Next, wigmakers must create a layer of superfine lace that will serve as the piece’s foundation. For very short hair styles, a silk base is used to create the look of skin that might be visible under the hair’s surface. This technique was used for later seasons of Netflix’s “Stranger Things” to create Eleven’s signature buzz cut, when actress Millie Bobby Brown couldn’t shave her head.

Millie Bobby Brown on "Stranger Things."
When actors are portraying real people with different skull shapes and hair lines, the hair team must add an extra step of creating prosthetic pieces to go under the wig’s foundation. In Hulu’s “Pam & Tommy,” for example, a prosthetic forehead was given to actress Lily James to replicate Pamela Anderson's characteristic high forehead.
The next step is the ventilating process, where each hair is stitched into the lace one by one using a variety of knotting techniques. The key here is to match an actor’s natural hair patterns, like which direction the hair at their temples prefers to go, while keeping it malleable enough to part anywhere, just like you can with real hair.
As for the hair itself, the choices come down to either real human hair or synthetic. Synthetic hair, which is more durable but has more of a light-reflecting sheen, is usually used for background actors. But for “hero wigs” that must pass the close-up test, real human hair is required.
Pickens might even add mohair (a durable, resistant hair fiber made from angora goats) to hairlines to mimic baby hairs, which he did for Ana De Armas for her portrayal of Marilyn Monroe in Andrew Dominik’s “Blonde.”
Wigs might evoke a sense of glamor, but in the world of realistic storytelling, accuracy takes precedence. When tasked with creating an aging and syphilis-ridden Al Capone (played by Tom Hardy), Pickens helped convey the story with hair that was “actually a bit sickly before we texturized it.”

Tom Hardy as Al Capone in "Capone" (2022).
But wait, there’s more. We are now to the coloring process, which, as Pickens puts it, is a blend of “alchemy and color theory and figuring out how that’s going to play on the final product.” Colorists have to understand how a scene might be lit and edited, so that they can make an educated guess as to how to color the hair so it has the desired shade in the final cut, rather than in real life.
“Reds can be quite the nightmare sometimes,” Pickens shared. “If we create a red wig and they put a blue filter over the entire thing, it could look brown.”
And just to make matters more complicated, the looks don’t just get created for the main actors. Anyone performing as a photo double or stunt performer also needs a matching (usually synthetic) wig. Stunt double wigs in particular are tricky, as they need to be durable enough to endure take after take of literally rolling with the punches, yet still be easily removed for when a stunt might go wrong. But also they must look exactly like the hero wig. No big deal, right?
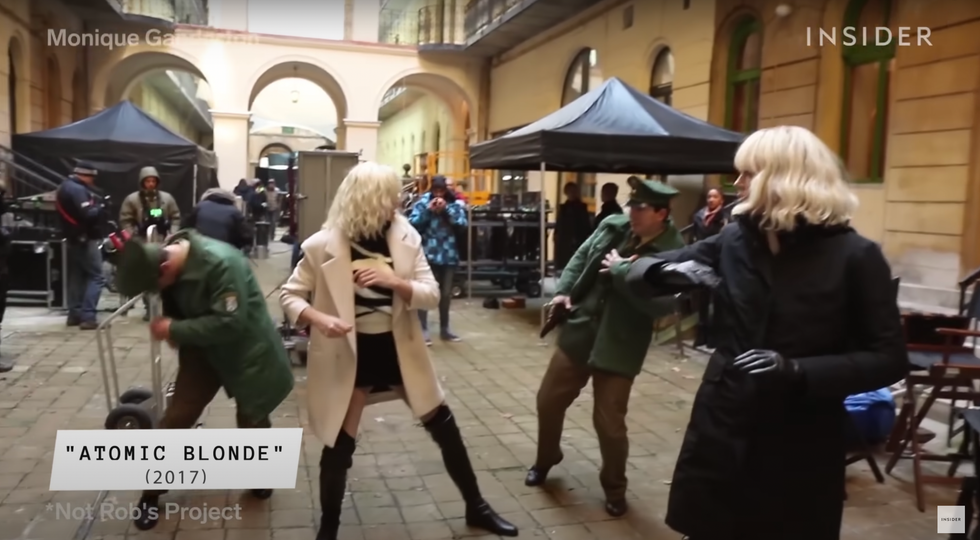

Charlize Theron and her stunt double Monique Ganderton on the set of "Atomic Blonde."
To say that people were floored to learn some of these things would be an understatement. Just check out some of these comments:
“I'm amazed by what they can create to make us believe that their wigs are their real hair because it looks so natural..So many times I've just assumed that the actors must have changed their real hair to look a certain way because it looks too real to be a wig. It was interesting to see what the process looks like.”
“I love learning stuff like this. I never would have thought about how much went into wigs. Unsung masterpieces are everywhere.”
“This is so cool. I honestly had no idea so much detail went into this. I'm impressed.”
More content is being put out now than ever before, causing many shows to have to create costumes and wigs on a mass level (read: faster and cheaper). This undoubtedly leads to a drop in quality that can sometimes take us out of a story—something we covered in a previous article. However, when artists are given the opportunity and resources to really work to their highest potential, magic happens. Kudos to the pros who completely immerse us into a story, strand by strand. Your labor of love is appreciated.
You can watch the full video below, which has even more fascinating info:
- Have you noticed your favorite shows don't look as good as they used to? This viral post explains why. ›
- An iconic scene in 'Stranger Things' has made this 37-year-old Kate Bush song a number 1 hit ›
- One couple has already won Halloween by perfectly recreating iconic 'Stranger Things' scene ›
- How movie trailers get you to want to watch the movie - Upworthy ›





 I Love You Elf GIF by MOODMAN
I Love You Elf GIF by MOODMAN "Love you!" Oops.
"Love you!" Oops. Green Flag GIF by The Last Talk Show
Green Flag GIF by The Last Talk Show Embarrassed Hide GIF by flor
Embarrassed Hide GIF by flor Eating the right foods is crucial for mental health.
media3.giphy.com
Eating the right foods is crucial for mental health.
media3.giphy.com
 Legumes, like beans and lentils, are super foods and chockful of Vitamin B9.
Photo credit: Canva
Legumes, like beans and lentils, are super foods and chockful of Vitamin B9.
Photo credit: Canva
 Spending time in nature for at least two hours a week is great for overall wellbeing.
Spending time in nature for at least two hours a week is great for overall wellbeing.  There's an innate need for human connection.
There's an innate need for human connection. Even a simple hike, no matter what the pace, is effective when combatting feeling bad.
Even a simple hike, no matter what the pace, is effective when combatting feeling bad.  Tracking your steps can help motivate you and keep you motivated.
Tracking your steps can help motivate you and keep you motivated.  Vincent Van Gogh's Self-Portrait, 1889Image via
Vincent Van Gogh's Self-Portrait, 1889Image via  Turbulent flow illustrated and animated.
Turbulent flow illustrated and animated.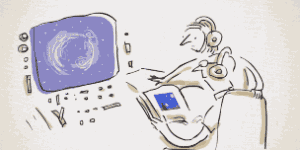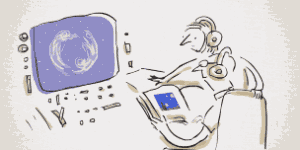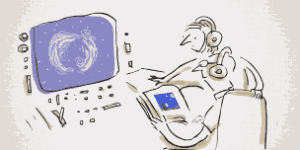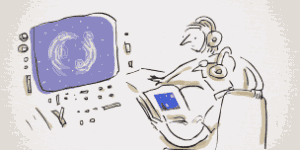 Animation of art referencing science.
Animation of art referencing science.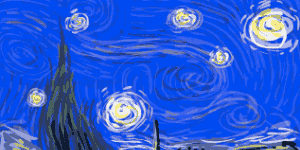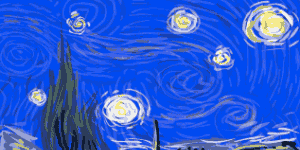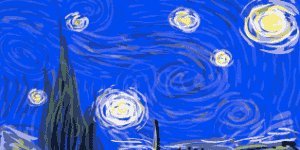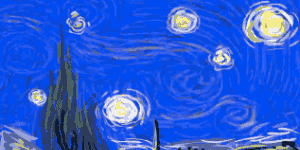 Animated Starry Night
Animated Starry Night An animated depiction of The Scream.
An animated depiction of The Scream.
There's a reason why some people can perfectly copy accents, and others can't
Turns out, there's a neurodivergent link.
A woman in black long sleeve shirt stands in front of mirror.
Have you ever had that friend who goes on vacation for four days to London and comes back with a full-on Queen's English posh accent? "Oooh I left my brolly in the loo," they say, and you respond, "But you're from Colorado!" Well, there are reasons they (and many of us) do that, and usually it's on a pretty subconscious level.
It's called "accent mirroring," and it's actually quite common with people who are neurodivergent, particularly those with ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder). According Neurolaunch, the self-described "Free Mental Health Library," "Accent mirroring, also known as accent adaptation or phonetic convergence, is the tendency to unconsciously adopt the accent or speech patterns of those around us. This linguistic chameleon effect is not unique to individuals with ADHD, but it appears to be more pronounced and frequent in this population."
Essentially, when people have conversations, we're constantly "scanning" for information—not just the words we're absorbing, but the inflection and tone. "When we hear an accent, our brains automatically analyze and categorize the phonetic features, prosody, and intonation patterns," writes Neurolaunch. For most, this does result in copying the accent of the person with whom we're speaking. But those with ADHD might be more sensitive to auditory cues. This, "coupled with a reduced ability to filter out or inhibit the impulse to mimic…could potentially explain the increased tendency for accent mirroring."
While the article explains further research is needed, they distinctly state that, "Accent mirroring in individuals with ADHD often manifests as an unconscious mimicry of accents in social situations. This can range from subtle shifts in pronunciation to more noticeable changes in intonation and speech rhythm. For example, a person with ADHD might find themselves unconsciously adopting a Southern drawl when conversing with someone from Texas, even if they’ve never lived in the South themselves."
People are having their say online. On the subreddit r/ADHDWomen, a thread began: "Taking on accents is an ADHD thing?" The OP shares, "My whole life, I've picked up accents. I, myself, never noticed, but everyone around me would be like, 'Why are you talking like that??' It could be after I watched a show or movie with an accent or after I've traveled somewhere with a different accent than my 'normal.'
They continue, "Apparently, I pick it up fast, but it fades out slowly. Today... I'm scrolling Instagram, I watch a reel from a comedian couple (Darcy and Jeremy. IYKYK) about how Darcy (ADHD) picks up accents everywhere they go. It's called ADHD Mirroring??? And it's another way of masking."
(The OP is referring to Darcy Michaels and his husband Jeremy Baer, who are both touring comedians based in Canada.)
Hundreds of people on the Reddit thread alone seem to relate. One comments, "Omfg I've done this my whole life; I'll even pick up on the pauses/spaces when I'm talking to someone who is ESL—but English is my first language lol."
Sometimes, it can be a real issue for those around the chameleon. "I accidentally mimicked a waitress's weird laugh one time. As soon as she was out of earshot, my family started to reprimand me, but I was already like 'oh my god I don’t know why I did that, I feel so bad.'"
Many commenters on TikTok were shocked to find out this can be a sign of ADHD. One jokes, "Omg, yes, at a store the cashier was talking to me and she was French. She's like 'Oh are you French too? No, I'm not lol. I'm very east coast Canada."
And some people just embrace it and make it work for them. "I mirror their words or phrase! I’m 30. I realized I start calling everyone sweetie cause my manager does & I work at coffee shop."