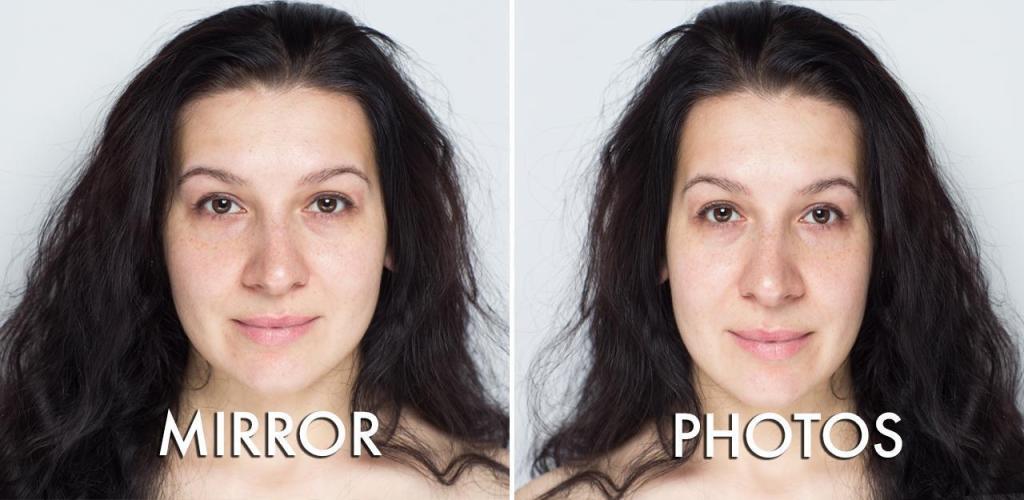
Usually the greatest fear after a wild night of partying isn’t what you said that you might regret, but how you’ll look in your friends’ tagged photos. Although you left the house looking like a 10, those awkward group selfies make you feel more like a 5, prompting you to wonder, “Why do I look different in pictures?”
It’s a weird phenomenon that, thanks to selfies, is making people question their own mirrors. Are pictures the “real” you or is it your reflection? Have mirrors been lying to us this whole time??
The answer to that is a bit tricky. The good news is that there’s a big chance that Quasimodo-looking creature that stares back at you in your selfies isn’t an accurate depiction of the real you. But your mirror isn’t completely truthful either.
Below, a scientific breakdown that might explain those embarrassing tagged photos of you:
The mirror is a reflection. It’s not the real you.
Although we’re the most comfortable and familiar with the face staring back at us while we brush our teeth in the morning, the mirror isn’t really the real us. It’s a reflection, so it shows how we look like in reverse. Because we’re so used to seeing the reverse version of ourselves, seeing how we look in pictures can be jarring. And unless you’re blessed with a perfectly symmetrical face, the photo version of yourself can be even more wonky.
“We see ourselves in the mirror all the time—you brush your teeth, you shave, you put on makeup,” Pamela Rutledge, director of the Media Psychology Center, told The Atlantic. “Looking at yourself in the mirror becomes a firm impression. You have that familiarity. Familiarity breeds liking. You’ve established a preference for that look of your face.”
Scientists call this the “mere-exposure” effect. Basically, it’s a behavior concocted by psychologist Robert Zajonc that says people react favorably to things they’re most familiar with. So, when you see a flipped version of yourself, you immediately hate it or even find it grotesque because it’s the opposite of what you’re used to.
So although we think we look better in a mirror, we’re more psychologically inclined to feel that way even if we truthfully look better in photos. Weird, huh?
The camera lens also plays a part.
So if your reflection isn’t the real you, does that mean your ugly selfies are your “true self”? Although mirrors show a flipped version of yourself that tones down the harshness of your asymmetries, the myth that “pictures never lie” isn’t true either. After all, most people take more than one selfie before they find their most flattering one, and usually it takes a combination of angles, lighting, and duck lips before landing one that’s Instagram-worthy.
But the problem might not be your angles, it could be lens distortion. Because of the proximity of your face to the camera, the lens can distort certain features, making them look larger than they are in real life. Pictures also only provide a 2-D version of ourselves. Depending on your features, if you have a soft, round face, photos can flatten your features and further distort the “real” you.
For example, just changing the focal length of a camera can even change the width of your head. As Gizmodo writer John Herrman pens, the fancier the camera, the better you’ll look in the picture:
“Telephoto lenses are usually seen as more flattering, giving the impression that the subject is flattened, and slightly compressing the width of your foremost features, like your nose or breasts. So you might want to think twice before fleeing the pesky paparazzi and their fancy zoom lenses; it’s the tourist with the pocket cam whose snaps will make you look fat on the Internet.”
And because cameras don’t show the 3-D version of you, it’s easy to “trick” cameras to present a reality that’s not even true. Professional models have perfected this, which is why people can do photo sorcery like this by merely tweaking their angles:
It’s also the camera flash.

Although good lighting is the key to all flattering photos, a harsh flash from your iPhone can actually make you look a lot worse, especially if it’s taken in a dark room. In fact, according to OKCupid, harsh camera flashes add seven years to your face.
In addition to making you look shiny and greasy, cameras can’t adjust to lightness and darkness the ways our eyes naturally can. Cameras can only focus on highlights or shadows, and sometimes that can result in lighting that can be less than flattering. A good rule of thumb is to stick to natural or outdoor lighting instead.
Your smile could also be the culprit.

Everyone knows what it’s like to pose for an awkward photo, like a driver’s license or a passport. The photos never turn out looking nice, and they hardly look like our natural smiles. When you’re looking at yourself in the mirror, you’re relaxed, confident, and more likely to smile and act naturally.
If someone shouting “Say cheese!” at you makes you feel self-conscious about your unphotogenic reputation, obviously you’re going to tense up and have a photo that looks different and foreign from the version you see in the mirror. It’s best to relax when taking pictures and try to focus on something else. That tense, forced awkwardness will always translate to a bad photo.
It’s possible you’re less attractive than you think.

But no matter how many factors you want to blame for your crappy pictures, it all boils down to psychology. Perhaps the reason you look different in pictures is because the version of yourself you like best is a figment of your imagination.
According to a 2008 study, people tend to think they’re more attractive than they really are. In the experiment, researchers photoshopped pictures of participants to make them look more attractive and then mixed those with photos of strangers. Next, they asked the subjects to pick their picture out of a line-up. People were quicker at picking photos where they looked more attractive, concluding that “attractiveness” was the version of themselves they were most familiar with.
However, other experts have also said the opposite, that people tend to think they’re less attractive than they really are. Whatever the case, if you’re beating yourself up about why you look different in mirrors and pictures, there’s a good chance that all your fear and anxiety is just in your head. It’s sort of similar to how people hate the sound of their own voice. Perhaps the key to looking better in pictures is taking as many selfies as you can to help familiarize yourself with both the “mirror” and “camera” version of yourself.
“People who take a lot of selfies end up feeling a lot more comfortable in their own skin because they have a continuum of images of themselves, and they’re more in control of the image,” Pamela said. “Flipped or not flipped, the ability to see themselves in all these different ways will just make them generally more comfortable.”
Or, you know, just download FaceTune. Might as well fight science with science.
This article originally appeared on 7.21.21