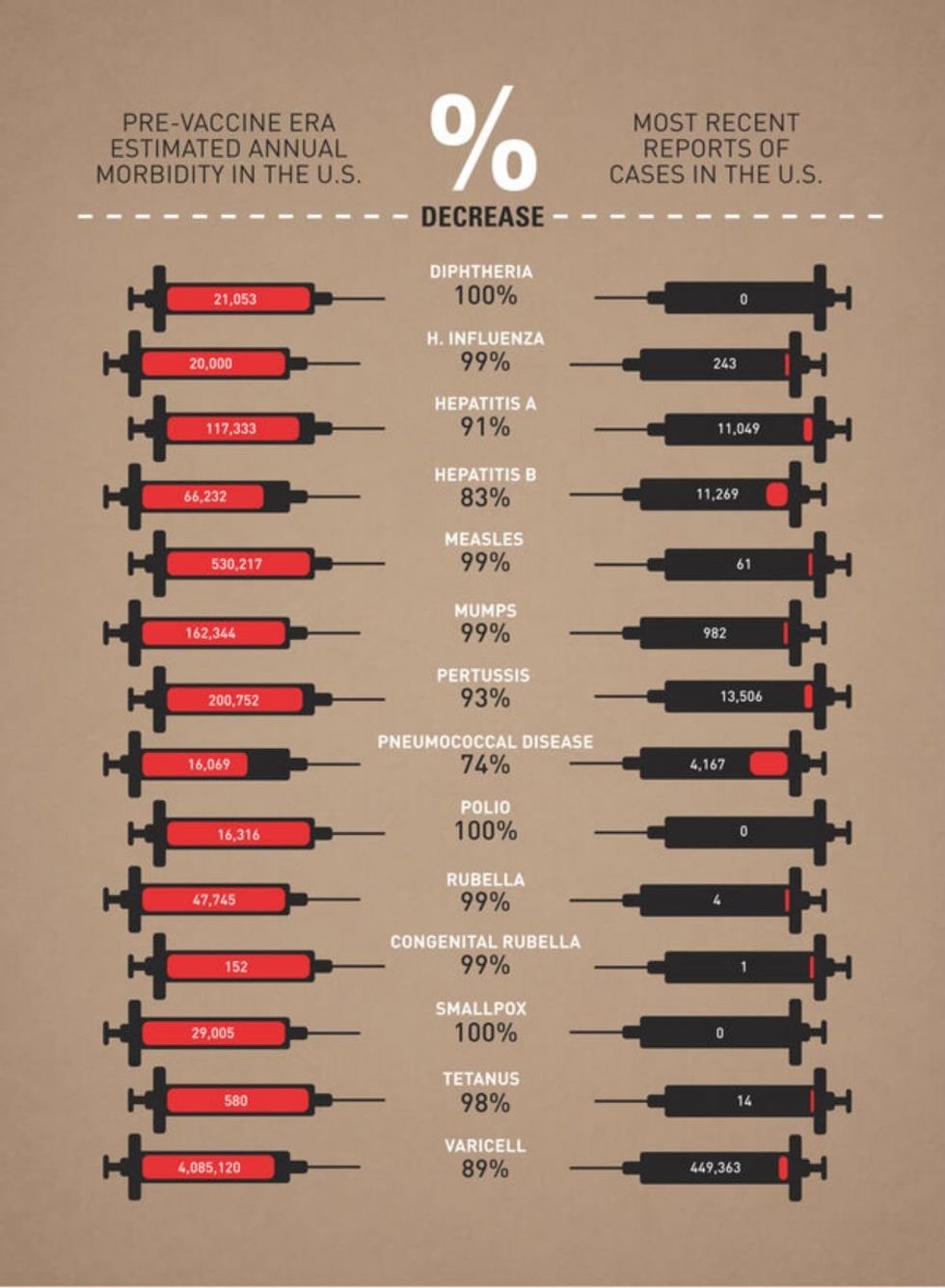
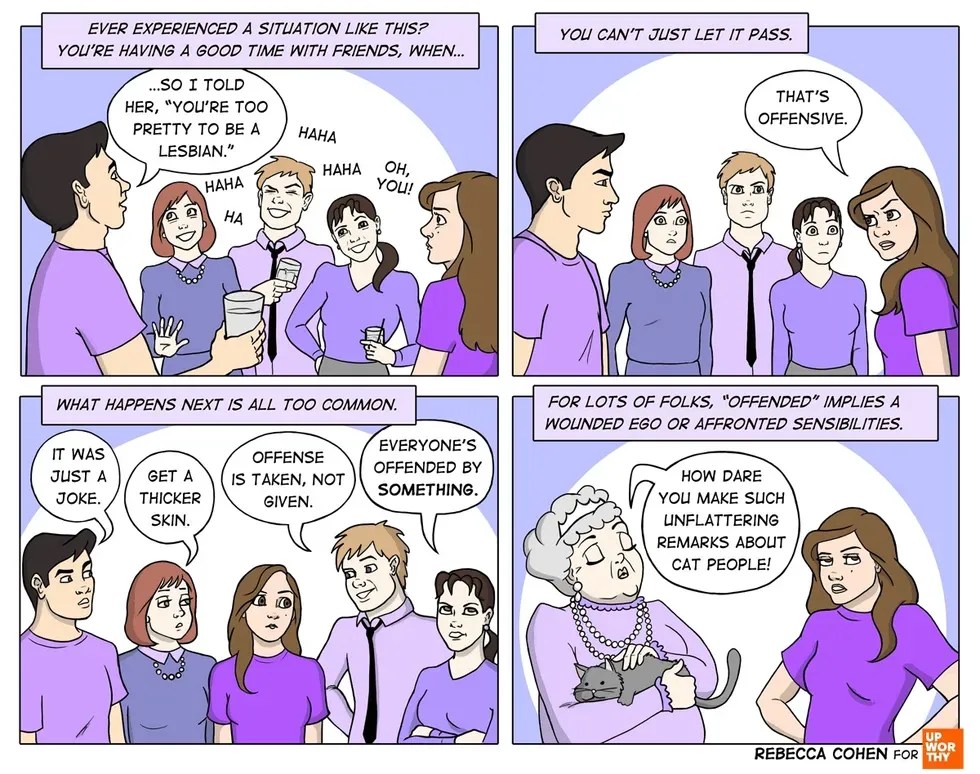
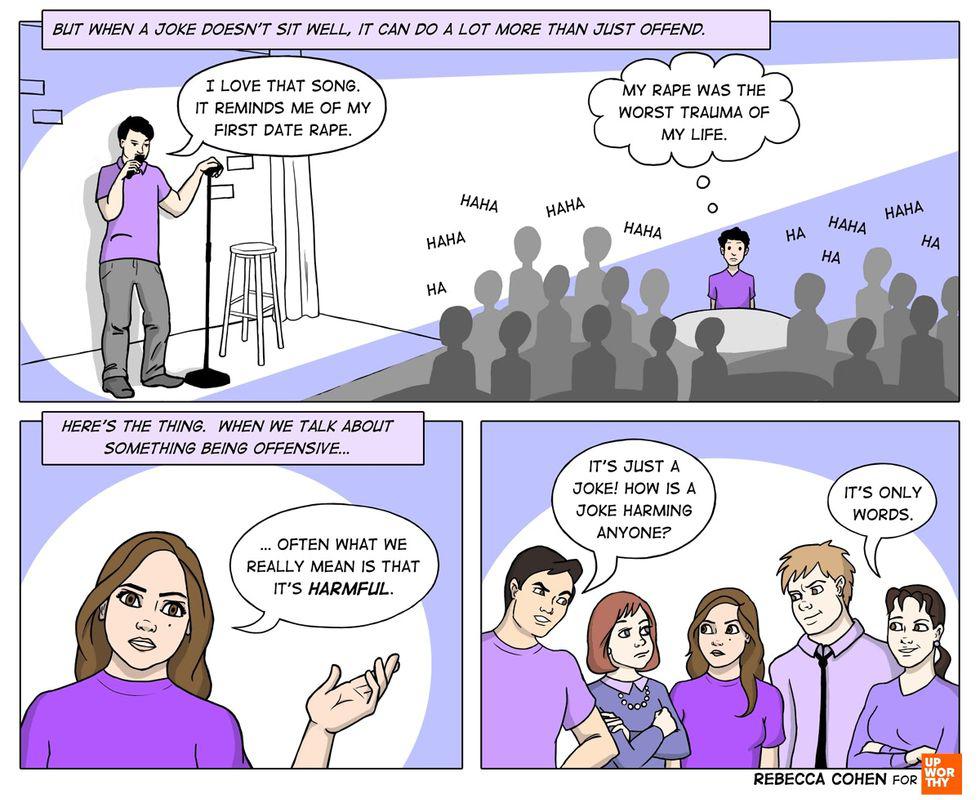
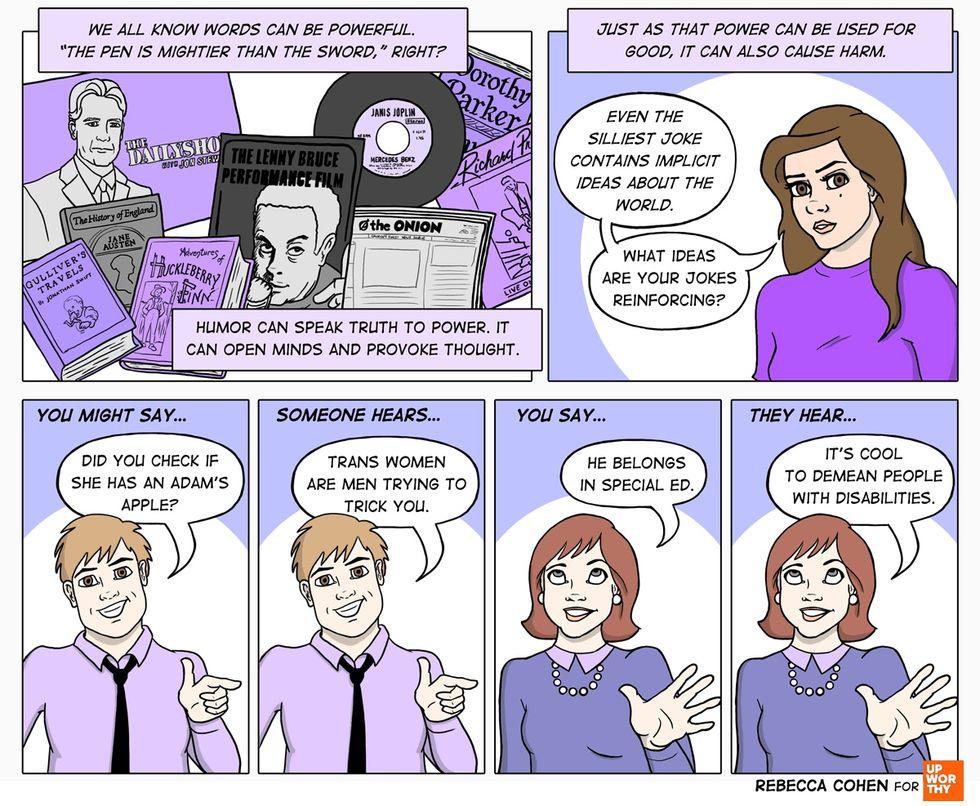
In movies, wolves are often depicted as terrifying, snarling creatures that threaten our heroes.
What kid can forget the pack of growling wolves that chase Belle’s father right up to the Beast’s castle?
Authors such as Aesop, the Brothers Grimm, and Charles Perrault all wrote children’s stories where the “big bad wolf” was the ravening villain, willing to do anything to fill his belly — even impersonate grandma for a chance to eat Little Red Riding Hood!
Image via iStock.
Over and over throughout history, literature, and movies, the wolf was used as a metaphor for trickery, evil, and cruelty. As a result, it’s easy to assume that these animals are actually something to fear.
But wolves don’t deserve this bad rap.
They are actually pretty amazing animals, and they play an important role in nature. For example, did you know that wolves can smell their prey from almost two miles away — which is about 100 times better than humans?
Here are 23 other interesting — and important — things you might not know about the gray wolf:
Image by MacNeil Lyons/NPS/USFWSmidwest.
1. Gray wolves are the largest member of the wild dog, or Canid, family.
Also known as the timber wolf, common wolf, or, in scientific circles, Canis lupus, the gray wolf is an ancestor to domesticated dogs. As adults, they can be four to six feet long and weigh up to 175 pounds.
2. Despite their name, they do not always have gray fur.
They can also have white, brownish-gray, or black coats.
Members of the Canyon wolf pack in Yellowstone National Park. Image by Jim Peaco/YellowstoneNPS.
3. They were once the world’s most widely distributed large mammal.
Gray wolves were found all across the Northern Hemisphere, including in North America, Europe, Asia, and North Africa.
4. But they lost much of their former range because of conflict with humans.
These animals were perceived as dangerous to humans and a nuisance to farmers, so they were often hunted, trapped, or poisoned. In the United States, a government-sponsored extermination plan at the beginning of the 20th century largely wiped them out from the Lower 48 states — only about 10% of their former range remains in the continental U.S. today.
5. They are usually not dangerous to people.
Wolves are actually fairly timid creatures that would prefer to avoid people. Attacks on humans are very rare. In fact, there have been very few recorded wild wolf attacks on humans in North America. In the past 100 years, no lethal attack by a wild, healthy wolf has ever been confirmed in the Lower 48 states.
Image by John and Karen Hollingsworth/USFWS.
6. While we often picture gray wolves in colder places, they can actually live in a variety of habitats, from Arctic tundras to forests and mountains to prairies and grasslands.
But whatever habitat they are in, they still need access to a large area of contiguous land to roam with lots of prey. Wolves don’t like to stay in one place for very long.
7. Gray wolves are very social. They live, travel, and hunt in packs of seven to eight.
Image via iStock.
Each pack is usually led by an alpha female and male and is made up of their extended family, including pups and older offspring.
8. The alphas often lead the hunt for prey, choose den sites, and establish the pack’s territory.
How big one pack’s territory is, though, depends on how plentiful their prey is. Some packs occupy just 20 square miles, while others are known to roam over hundreds of square miles in search of food.
9. The alphas can mate for life.
The alpha female of the Canyon pack in Yellowstone National Park. Image by Neal Herbert/YellowstoneNPS.
Usually, only the alphas breed, in order to keep pack numbers down. They mate once a year, from late January through March, and the mother usually gives birth to four to six pups in a den about 63 days later.
10. When they’re born, wolf pups are blind and deaf.
And they only weigh about a pound. But they grow up quickly — after about 10-14 days, they can open their eyes and ears, and by the time they are two weeks old, they are learning to walk (shakily). Then it only takes about another week for them to start venturing outside the den for the first time.
A gray wolf pup in its den. Image by Hilary Cooley/USFWS.
11. The whole pack helps care for the new pups.
The pups start off reliant on their mother’s milk, but after about three weeks, they are ready to eat meat. Because they are too young to hunt themselves, all of the older pack members take turns hunting and regurgitating meat to feed the pups.
12. Pups only start learning to hunt with the pack when they are six months old.
They practice their hunting skills first by playing with both their siblings and with “toys” (bones and feathers). Then they start using the skills they learned from playing to hunt small animals before joining the pack on larger hunts.
Wolf pups outside their den. Image by Dan Stahler/YellowstoneNPS.
13. When pups are fully mature, they often disperse from the pack.
Dispersing wolves have been known to travel 50 to 500 miles looking for a mate, open territory, or both. While dispersing, they usually travel quickly, as it is dangerous to be a lone wolf. One radio-collared Wisconsin wolf traveled 23 miles in one day.
14. Gray wolves have a complex communication system.
They communicate with each other through a range of sounds, including barks, whines, growls, and howls, as well as through body language, “dancing,” and scent marking.
A gray wolf howling in Yellowstone National Park. Image by Jim Peaco/YellowstoneNPS.
15. Each gray wolf has a unique howl, which allows other pack members (and scientists) to recognize them.
This enables pack members to communicate with each other over long distances. Howls can be heard up to six miles away.
16. But they don’t actually howl at the moon.
They are more active at dawn and dusk, though.
17. Wolves usually eat large hoofed mammals such as deer, elk, and moose.
A deer in Yellowstone National Park. Image by Neal Herbert/YellowstoneNPS.
But since taking down big animals can be dangerous, they usually hunt the old, young, sick, or injured ones so they don’t get hurt themselves. In some cases, they have been known to hunt livestock or pets — which is part of how they originally got their reputation — but only when their natural prey is unavailable, making such attacks relatively rare. One wolf is capable of eating 20 pounds of meat in one meal.
18. But they aren’t picky eaters.
They’ll also eat smaller prey such as beavers or rabbits, and they are known to scavenge. They even eat some insects, nuts, and berries.
19. They can survive more than a week without eating anything at all.
Image via Douglas Smith/NPS/USFWSmidwest.
20. They can reach speeds of up to 40 mph when chasing prey.
But only for a short time. When the pack is on the move (not actively chasing food), they usually travel at 5 mph.
21. They are good swimmers, allowing them to chase prey in water, too.
A gray wolf crossing Alum Creek in Yellowstone National Park. Image by Jim Peaco/YellowstoneNPS.
22. Gray wolves play a key role in helping keep their ecosystems balanced and healthy.
Because wolves are apex predators — meaning they are at the top of the food web — they help keep elk and deer populations in check. This can help other plant and animal species thrive by preventing overgrazing or defoliation. Their hunts also provide “leftovers” for other scavenging wildlife.
23. Gray wolves need our help.
In 1978, the Fish and Wildlife Service listed the gray wolf as endangered in the contiguous United States, which makes it illegal to hurt or kill them. However, in recent years there have been a number of campaigns to de-list the wolf from these protections.
Image via MacNeil Lyons/NPS/USFWSmidwest.
Gray wolves are still misunderstood and feared by people all over the country and the world. That’s why it’s important to keep dispelling myths about wolves — because these animals are pretty amazing.