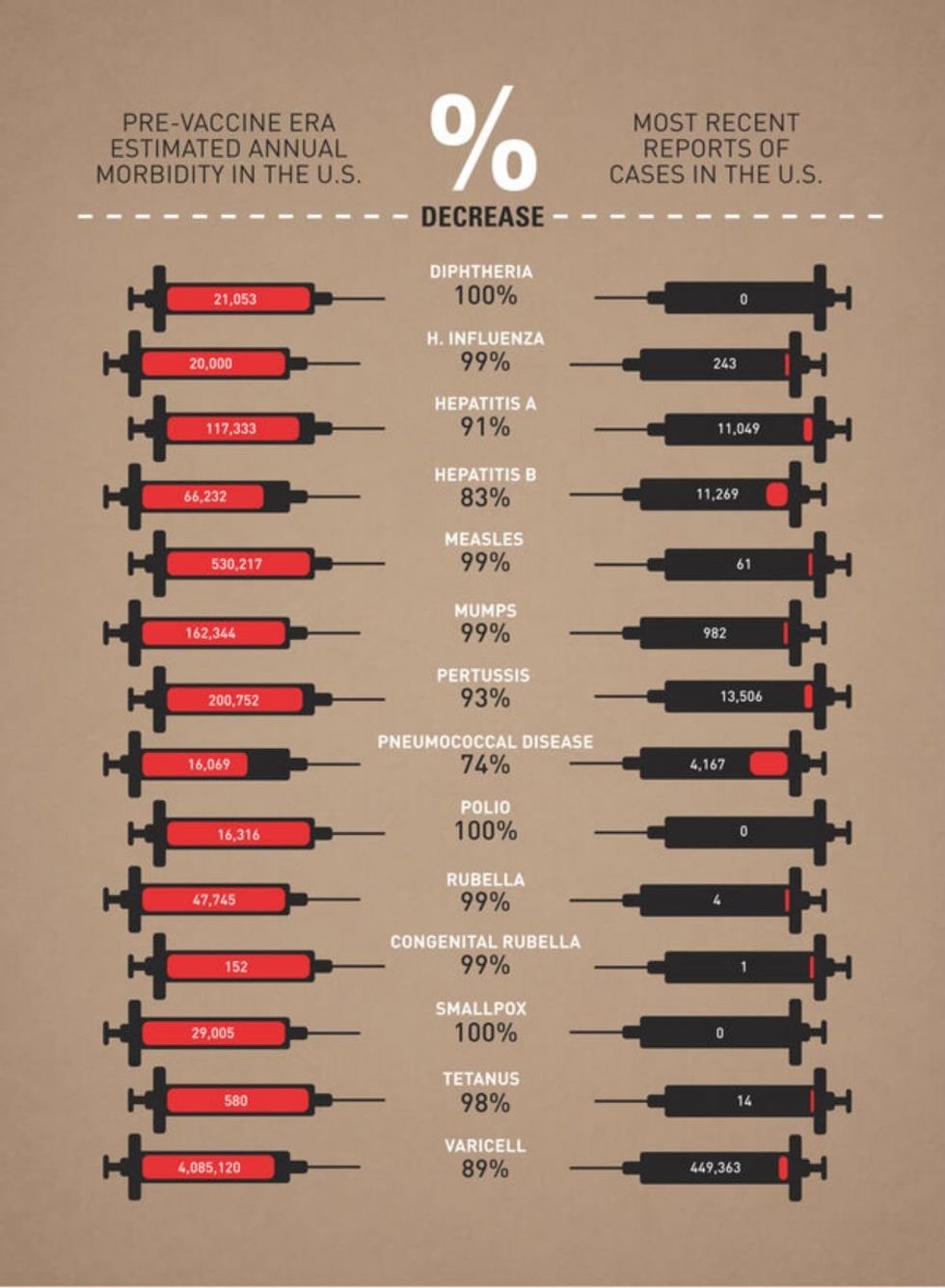
In a recent study from the Journal of the American Medical Association’s JAMA Pediatrics, researchers found something that should make us all stop and think.
Pediatricians, it seems, might treat their young patients differently based on the color of their skin. At least that was the case for the doctors in this study when it came to the way they administered pain medication to children with appendicitis.
Image by iStock.
In short, the study concluded that black children with appendicitis were less likely to receive painkillers than white children with appendicitis, even when the doctors perceived the children’s pain levels to be similar.
This wasn’t a small study either. It spanned seven years — from 2003 to 2010 — and involved more than 900,000 cases of appendicitis.
So what happened? Why did so many doctors treat black children differently?
“If there is no physiological explanation for differing treatment of the same phenomena, we are left with the notion that subtle biases, implicit and explicit, conscious and unconscious, influence the clinician’s judgment,” Dr. Eric Fleegler and Dr. Neil Schechter of Boston Children’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School explained.
We’ll come back to this particular study in a minute, but in case you’re thinking, “How does this affect me?!” let’s get right to one of their points: bias. And more specifically, implicit bias.
There’s a type of bias that almost every single one of us has, no matter how much we love all of our fellow humans, no matter how accepting we are, and no matter how hard we work to treat everyone the same: implicit bias.
People tend to shut down when we talk implicit bias as it relates to race because the immediate response is “I’m not racist!”
I hear you. I’m not racist either.
I’m so white I’m nearly translucent. My children — the people I love most in this world — are African and Asian. The sun rises and sets over them as far as I’m concerned.
My kiddos and me a few years ago.
I work hard every single day to spread anti-racist messages because I want the world to be better for my kids. My commitment to reducing racism is the reason I found my way into the job I have and love.
And still, no matter how much I love them and how hard I work, I have implicit biases. I know I do. I may not know what they are, but they’re there – entrenched in the recesses of my mind after a lifetime of media messaging and personal experiences.
And guess what? You have them, too.
I reached out to Dr. Isaiah Pickens, a New York City-based licensed clinical psychologist and writer, to talk about implicit biases — what they are and, more importantly, what we can do about them.
Here’s how he explained implicit bias to me:
“Implicit biases are attitudes and beliefs that are skewed in a particular direction but are outside of our awareness.”
He says that we can develop attitudes and beliefs that influence how we understand and interact with others as well as the decisions we make. And this happens involuntarily — totally not on purpose. We don’t even know we’re doing it.
Implicit biases aren’t things you’re aware of, which means you can unintentionally discriminate against others because of them.
Also, take this in for a minute: Our implicit biases aren’t all negative. They can be both favorable and unfavorable. An example of the former could be the lifelong impression a person forms — “Asians are so smart!” — after having an Asian classmate who was a great student back in fifth grade.
Here’s the crux of the issue, though, and the reason we need to care about implicit biases: We don’t know we have them, and because of that, Pickens says, we “unintentionally discriminate against others.”
Implicit biases don’t mean we’re all a bunch of racists.
We need to really understand what Pickens is saying because so many people are unwilling to acknowledge they have implicit biases for fear of being labeled a racist.
“Does unintentional discrimination mean that a person is racist? No,” he says. But when we fail to admit we have them, we don’t do anything about them. And we we don’t do anything about them, “people of color experience racism from others who may truly believe their actions are innocuous.“
That last part is the whole point of talking about this. It’s the human resources manager who unintentionally skips over a resume because the person has an ethnic-sounding name. It’s the school administrators who care about all of their students, but unwittingly more harshly punish black students because they perceive them as older than they actually are.
Photo by iStock.
Pickens gave me another example: It’s “a teacher professing to be colorblind often calling on white students … [because] the teacher doesn’t want to embarrass ‘other’ students because he thinks they didn’t do their homework.”
How’d we end up with these implicit biases?
We develop implicit biases from all of the messaging we’ve been getting since we were old enough to absorb it — our families, society, our social networks (both in person and online), and the media. And these messages, Pickens says, are reinforced by our experiences in life.
Image by iStock.
We develop biases for honorable reasons, too: “To better navigate the world and keep ourselves and those we love safe,” he explains. “If we think someone is a potential threat, then we may avoid that person or become preemptively combative to ensure that person doesn’t physically harm us, take our job, or challenge our value system.”
Fair enough. But here’s where we unintentionally go wrong: “A couple of experiences supporting these beliefs may lead us to automatically respond with unconscious bias toward most people who appear similar to the person we think is threat,” Pickens concludes.
I asked Pickens how we stop these biased thoughts. Because if we don’t even know we’re having them, how can we keep from having them?
It turns out that it’s more about opening ourselves up to a bigger world than making an effort to stop unknowingly thinking certain things. Experiences and an open mind are the best ways to fight implicit bias.
He suggests the following useful and somewhat surprising tips:
1. Do not strive to be color-blind. Color-blindness in the context of race describes the way of viewing all people “the same” — saying we don’t see skin color. That’s silly, though, because every person who has sight does see skin color. “No one is color-blind,” Pickens says bluntly. He says we should see differences — and celebrate them — while at the same time acknowledging that sometimes differences can lead to unfair treatment.
Most importantly, he emphasizes the cold, hard reality of insisting we’re color-blind: “When we pretend that we do not see these differences, we often reinforce the implicit biases we outwardly stand against.” We may be doing the very things we say we’re against because we’re not acknowledging our implicit biases.
2. Connect directly with people who are different in meaningful ways. The more positive interactions we have with people who look “different” than ourselves, the more we combat our implicit biases.
Photo by iStock.
Humans tend to spend their time around people who look like them, so it can feel awkward to intentionally seek out interactions, connections, and friendships outside of our circles, but we need to do it. Pickens suggests working on a shared work project with someone or attending a community gathering you might not otherwise choose to join. It’s important, he explains, to begin by “admitting your limited connection with others — and subsequently, limited knowledge — then being willing to learn more.”
3. Train yourself to be more mindful and aware. Focus on “others’ perspectives, experiences that counter stereotypes, and our personal susceptibility to have biases outside of our awareness,” Pickens says.
I also came across this tool by Harvard University to help you discover your implicit biases. It covers many areas, such as race, gender, and sexual orientation.
So what about those pediatricians who treated their patients differently based on the color of their skin?
Pickens says it’s apparent to him that they’re biased, but “whether implicit beliefs about race are the driving force for differential treatment is harder to decipher.”
He explains that implicit biases and treating people differently occur together — but it’s hard to know why. “[U]nconscious beliefs likely play a major role in differential treatment, but how and why implicit biases arise remains an area that requires further exploration,” he explained to me.
So until we figure that part out, the best course of action for us is to acknowledge that we have implicit biases — even though we may not know what they are — and keep that fact in mind as we move through life. It might positively affect how we interact with and treat others every day.