A juice company dumped orange peels in a national park. Here's what it looks like now.
12,000 tons of food waste and 21 years later, this forest looks totally different.

In 1997, ecologists Daniel Janzen and Winnie Hallwachs approached an orange juice company in Costa Rica with an off-the-wall idea. In exchange for donating a portion of unspoiled, forested land to the Área de Conservación Guanacaste — a nature preserve in the country's northwest — the park would allow the company to dump its discarded orange peels and pulp, free of charge, in a heavily grazed, largely deforested area nearby.
One year later, one thousand trucks poured into the national park, offloading over 12,000 metric tons of sticky, mealy, orange compost onto the worn-out plot. The site was left untouched and largely unexamined for over a decade. A sign was placed to ensure future researchers could locate and study it.
16 years later, Janzen dispatched graduate student Timothy Treuer to look for the site where the food waste was dumped.
Treuer initially set out to locate the large placard that marked the plot — and failed.
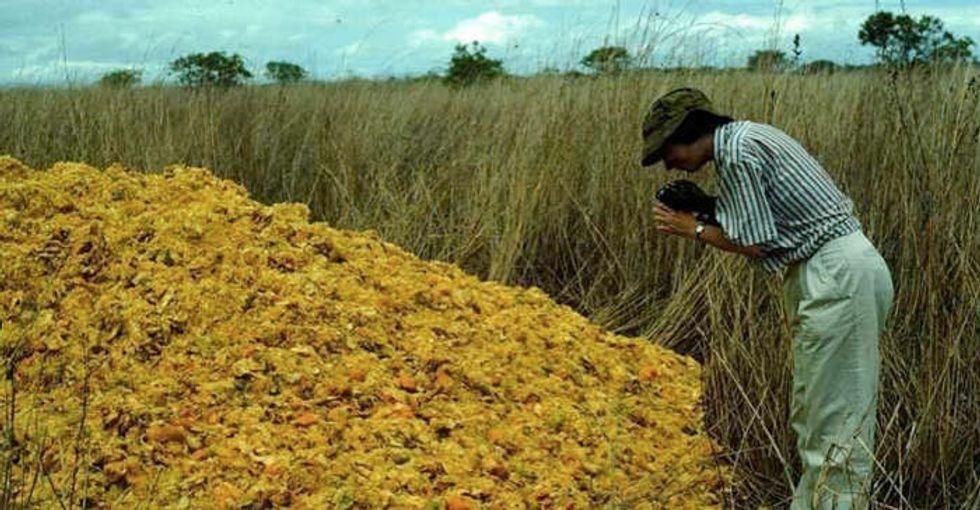

The first deposit of orange peels in 1996.
Photo by Dan Janzen.
"It's a huge sign, bright yellow lettering. We should have been able to see it," Treuer says. After wandering around for half an hour with no luck, he consulted Janzen, who gave him more detailed instructions on how to find the plot.
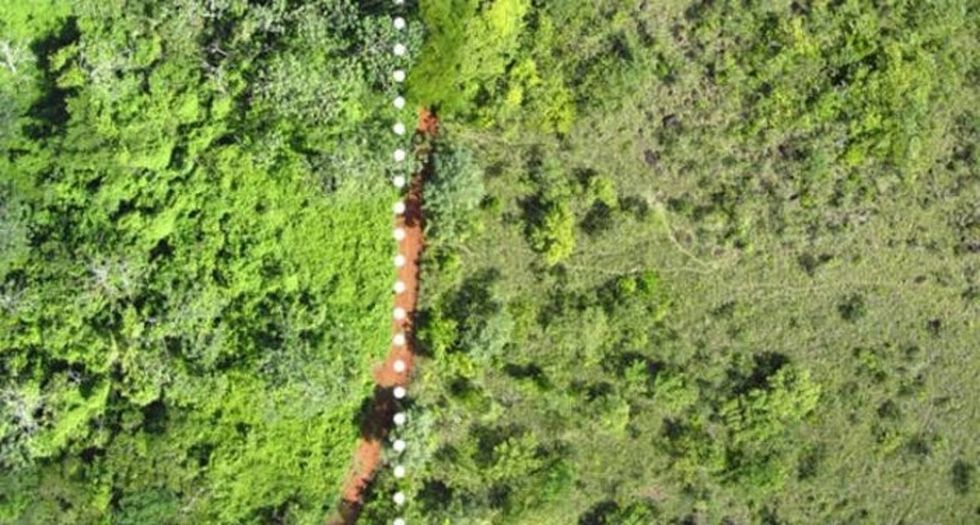
When he returned a week later and confirmed he was in the right place, Treuer was floored. Compared to the adjacent barren former pastureland, the site of the food waste deposit was "like night and day."
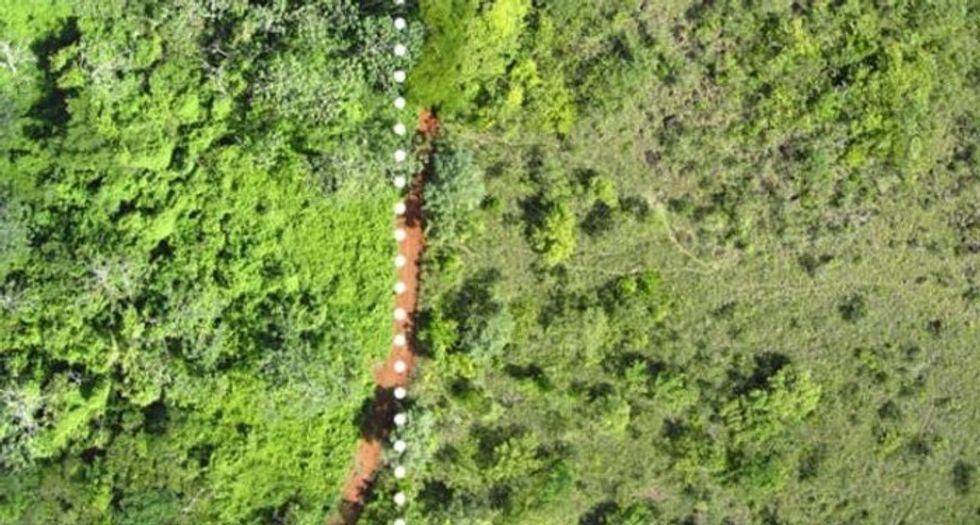

The site of the orange peel deposit (L) and adjacent pastureland (R).
"It was just hard to believe that the only difference between the two areas was a bunch of orange peels. They look like completely different ecosystems," he explains.
The area was so thick with vegetation he still could not find the sign.
Treuer and a team of researchers from Princeton University studied the site over the course of the following three years.
The results, published in the journal "Restoration Ecology," highlight just how completely the discarded fruit parts assisted the area's turnaround.
The ecologists measured various qualities of the site against an area of former pastureland immediately across the access road used to dump the orange peels two decades prior. Compared to the adjacent plot, which was dominated by a single species of tree, the site of the orange peel deposit featured two dozen species of vegetation, most thriving.
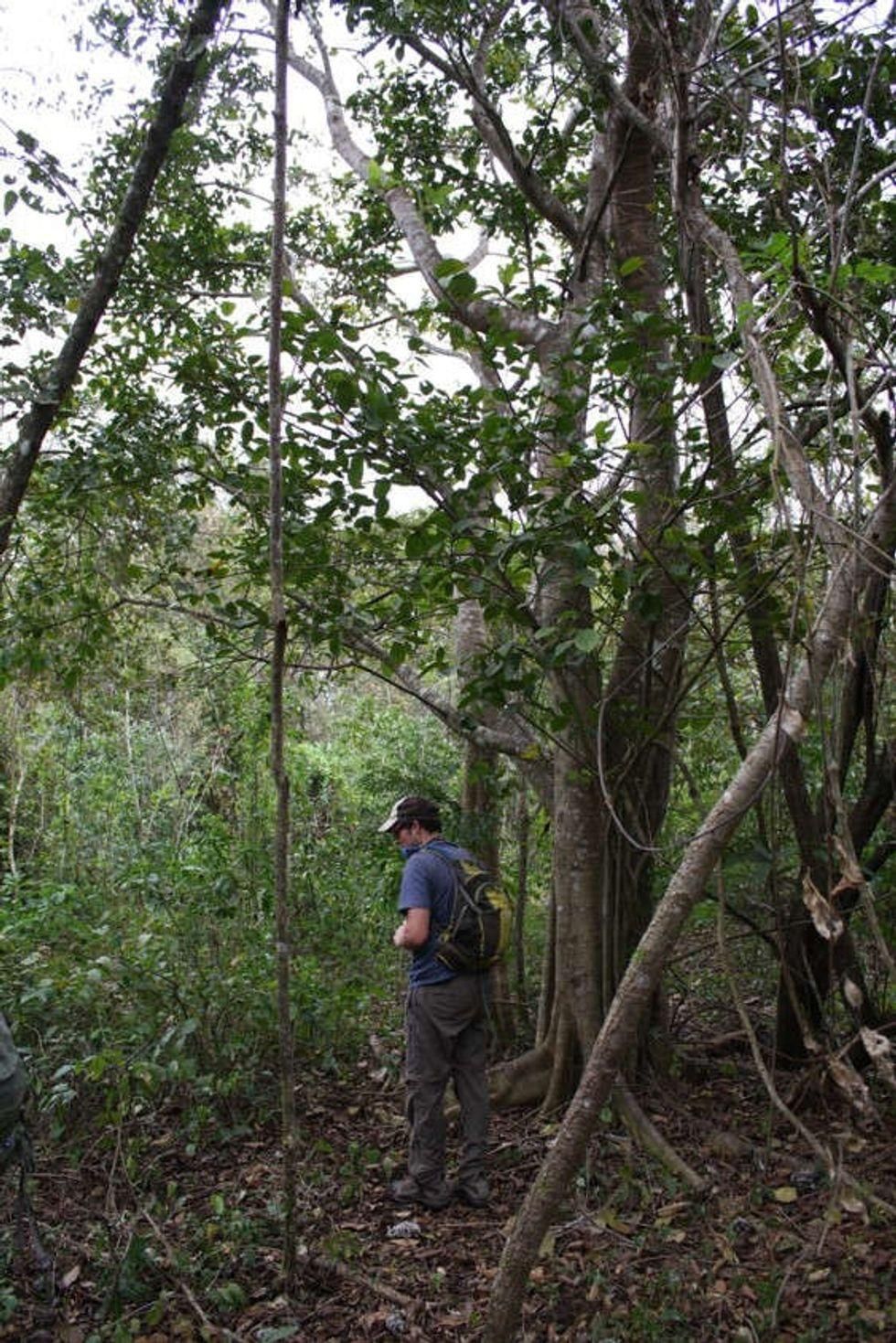

Lab technician Erik Schilling explores the newly overgrown orange peel plot.
In addition to greater biodiversity, richer soil, and a better-developed canopy, researchers discovered a tayra (a dog-sized weasel) and a giant fig tree three feet in diameter, on the plot.
"You could have had 20 people climbing in that tree at once and it would have supported the weight no problem," says Jon Choi, co-author of the paper, who conducted much of the soil analysis. "That thing was massive."
Recent evidence suggests that secondary tropical forests — those that grow after the original inhabitants are torn down — are essential to helping slow climate change.
In a 2016 study published in Nature, researchers found that such forests absorb and store atmospheric carbon at roughly 11 times the rate of old-growth forests.
Treuer believes better management of discarded produce — like orange peels — could be key to helping these forests regrow.
In many parts of the world, rates of deforestation are increasing dramatically, sapping local soil of much-needed nutrients and, with them, the ability of ecosystems to restore themselves.
Meanwhile, much of the world is awash in nutrient-rich food waste. In the United States, up to half of all produce in the United States is discarded. Most currently ends up in landfills.
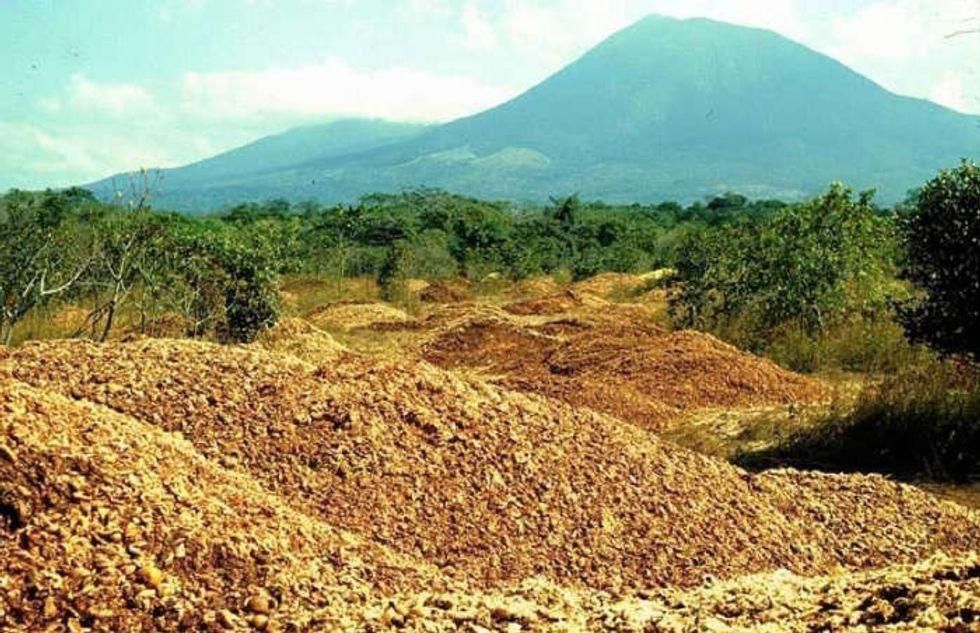

The site after a deposit of orange peels in 1998.
Photo by Dan Janzen.
"We don't want companies to go out there will-nilly just dumping their waste all over the place, but if it's scientifically driven and restorationists are involved in addition to companies, this is something I think has really high potential," Treuer says.
The next step, he believes, is to examine whether other ecosystems — dry forests, cloud forests, tropical savannas — react the same way to similar deposits.
Two years after his initial survey, Treuer returned to once again try to locate the sign marking the site.
Since his first scouting mission in 2013, Treuer had visited the plot more than 15 times. Choi had visited more than 50. Neither had spotted the original sign.
In 2015, when Treuer, with the help of the paper's senior author, David Wilcove, and Princeton Professor Rob Pringle, finally found it under a thicket of vines, the scope of the area's transformation became truly clear.

The sign after clearing away the vines.
Photo by Tim Treuer.
"It's a big honking sign," Choi emphasizes.
19 years of waiting with crossed fingers had buried it, thanks to two scientists, a flash of inspiration, and the rind of an unassuming fruit.
This article originally appeared eight years ago.
- This science fair winner is taking on global drought using oranges and avocados. ›
- Congress passes a landmark bill to help stop the epidemic of violence against Indigenous women - Upworthy ›
- A woman in the Bahamas took in nearly 100 stray dogs to save them from Hurricane Dorian - Upworthy ›
- Traveling couple reveals which national park is the best - Upworthy ›
- Texas family takes a $40 million hit to turn their massive ranch into a public park - Upworthy ›






 The Frenchman's monologue was absolutely spot on
The Frenchman's monologue was absolutely spot on Beaver in water. Photo by
Beaver in water. Photo by  An actual beaver dam on the now-thriving Price River
An actual beaver dam on the now-thriving Price River "Now your fishes will be warmed."
"Now your fishes will be warmed."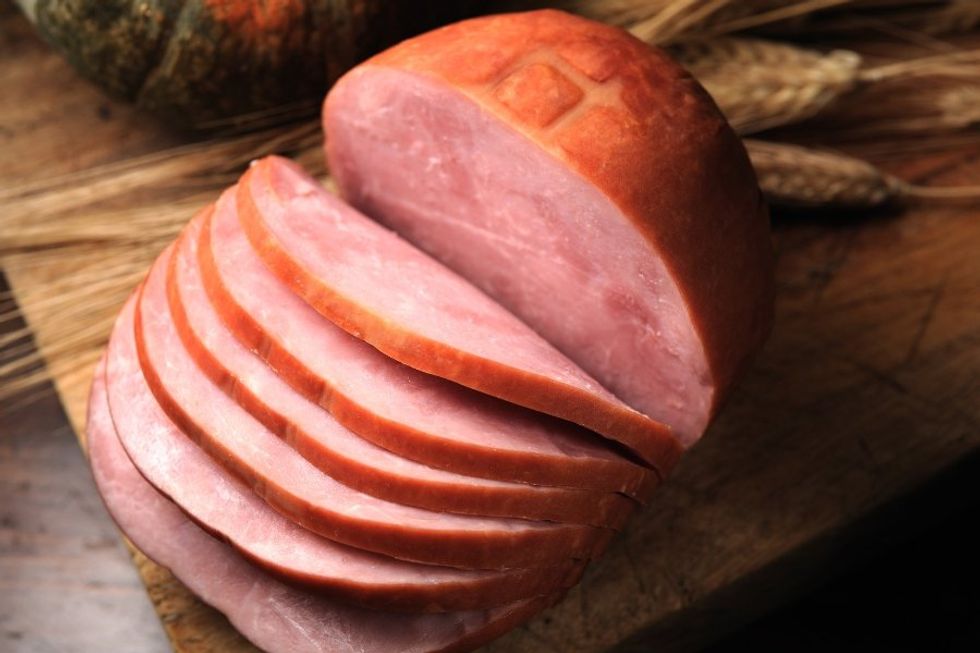 "To have one’s eyes lined with ham."
"To have one’s eyes lined with ham." "To lay your head in water."
"To lay your head in water." "Repetition teaches the donkey."
"Repetition teaches the donkey."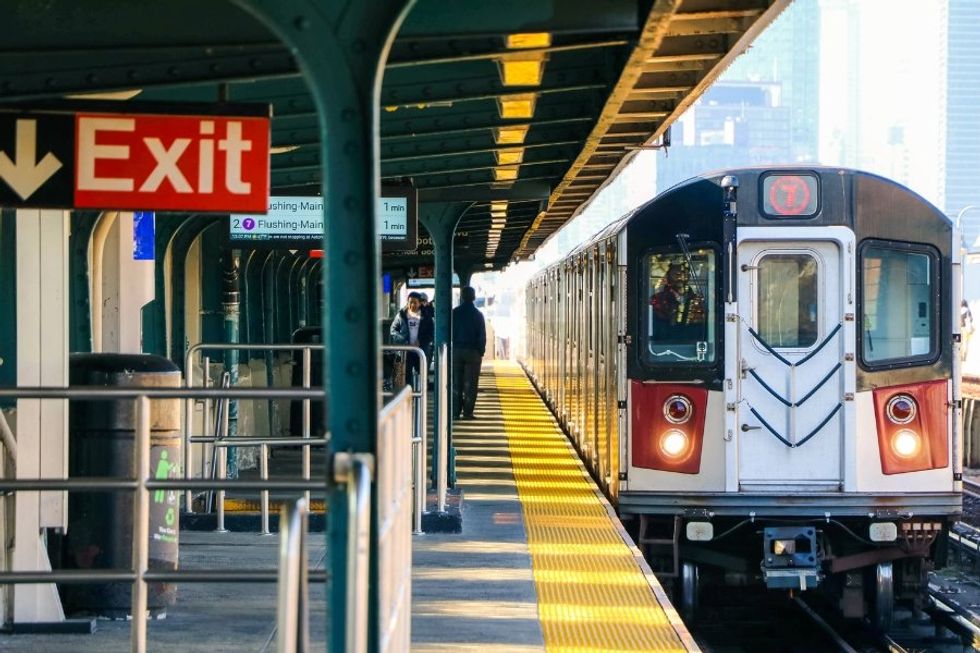 "I only understand train station."
"I only understand train station."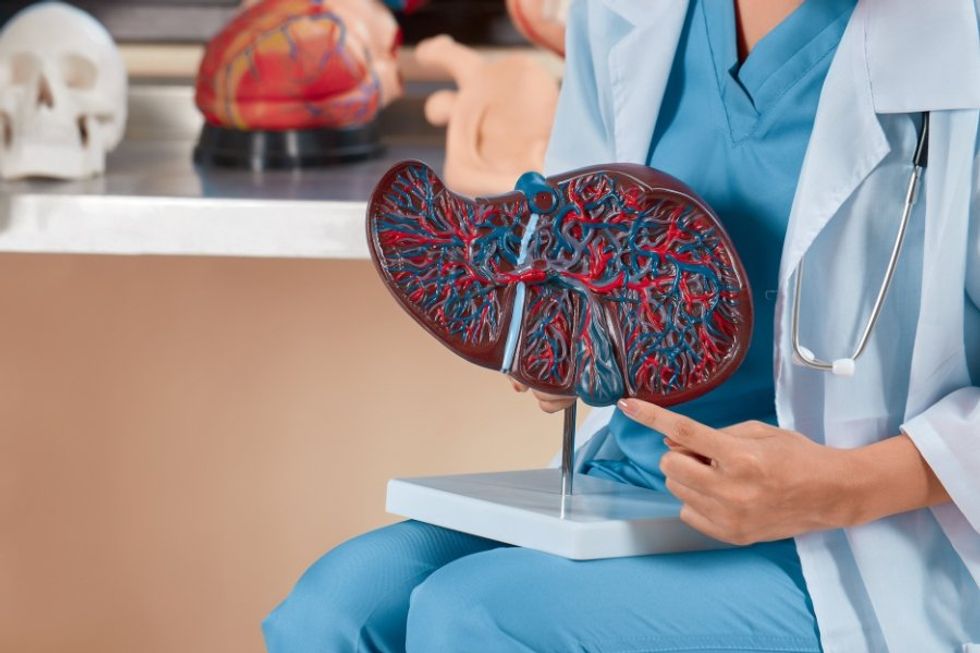 "To speak directly from the liver."
"To speak directly from the liver."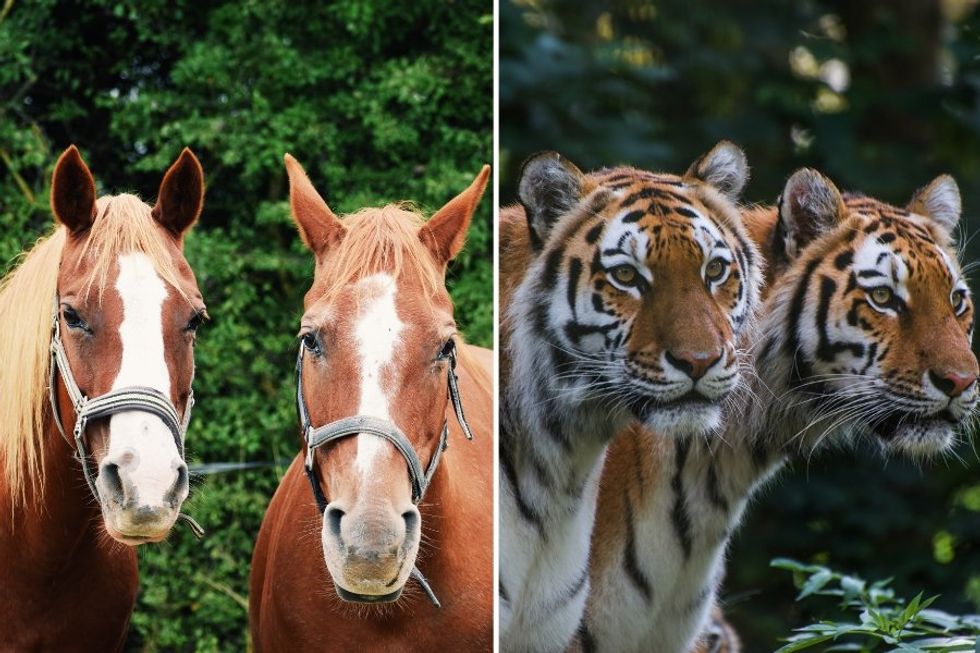 "Horse horse, tiger tiger."
"Horse horse, tiger tiger."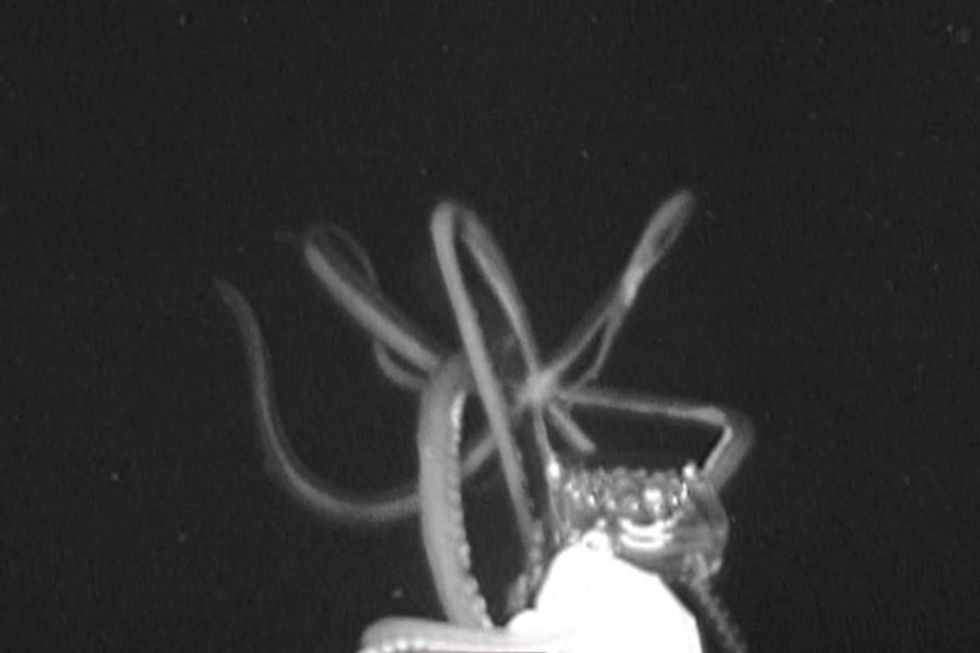 Medusa image of giant squid in Gulf of Mexico off of Mississippi Gulf CoastPhoto credit:
Medusa image of giant squid in Gulf of Mexico off of Mississippi Gulf CoastPhoto credit: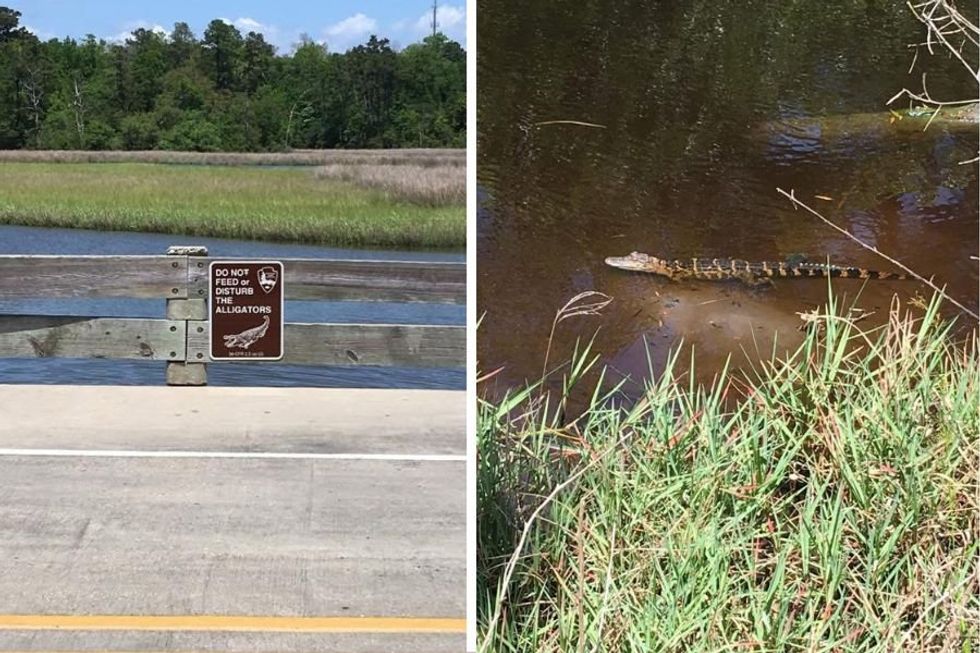  Sign warning against feeding alligators next to alligator in Mississippi marshlandsCourtesy of Jacalyn Wetzel
Sign warning against feeding alligators next to alligator in Mississippi marshlandsCourtesy of Jacalyn Wetzel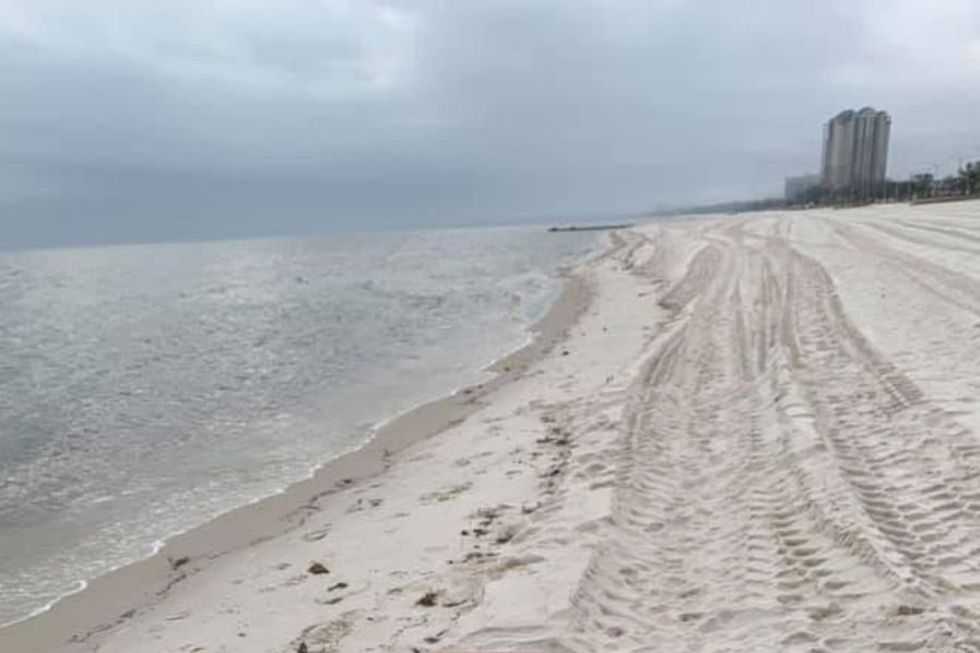 Mississippi Gulf Coast beach in BiloxiCourtesy of Jacalyn Wetzel
Mississippi Gulf Coast beach in BiloxiCourtesy of Jacalyn Wetzel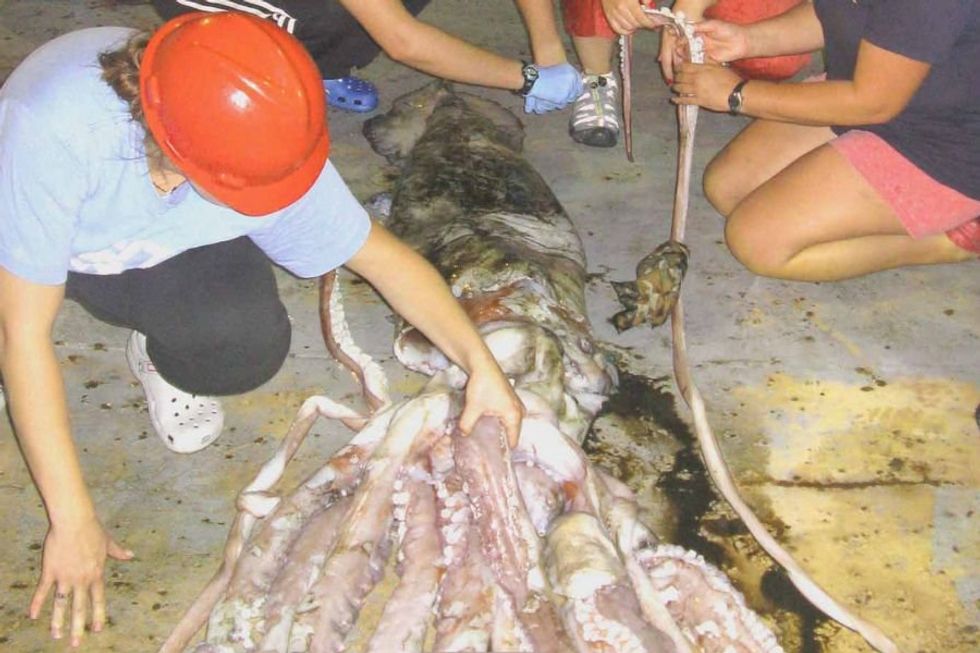 2009 photo of giant squid caught in Gulf of Mexico near Mississippi GulfPhoto credit:
2009 photo of giant squid caught in Gulf of Mexico near Mississippi GulfPhoto credit:  Thank goodness this story has a happy ending.
Thank goodness this story has a happy ending.
There's a reason why some people can perfectly copy accents, and others can't