WWI vets got the short end of the stick in the Great Depression. This was their answer.
Veterans risk their lives in the name of their country. But they often end up vulnerable when they return home.
On some occasions throughout our history, treatment of veterans has gotten so bad that it has led to major political change.
That's what happened on July 28, 1932, in Washington, D.C., when a confrontation between homeless vets and U.S. military personnel so outraged the public that it swayed a presidential election and had major repercussions.
The aftermath of the military action against the vets and their families is eerie at the Anacostia Flats with the Washington Monument in the background. Image via "Bonus Army"/PBS.
President Herbert Hoover, a Republican, was faced with an unsightly controversy: Thousands of destitute veterans had been camped out in the capital, forming one of several "Hooverville" encampments around the country. Hoover ordered the nation's military to march on the veterans, torch their makeshift homes, and run them out of town.
His opponent in the coming election, Democrat Franklin Delano Roosevelt, knew the move would incense the public. Upon hearing the news, he is said to have remarked, "Well, this will elect me."
The clash was one of the darkest chapters in the history of American veterans and still resonates today.
The unrest began when veterans demanded their lost wages be paid sooner than Congress wanted to.
When veterans of World War I returned home in the early 1920s, they petitioned Congress to offer some sort of compensation for lost wages; military pay was far below what they could have earned at home in the factories. Congress passed a law to compensate them, but the certificates issued to the veterans were not payable until 1945.
Meanwhile, in 1932, the Great Depression was in full swing, and those veterans became part of the destitute masses who had no money, no food, no jobs, and, in some cases, no homes.
Veterans eventually took to the streets. Here's a flier for the march. Image via Library of Congress.
Unemployment nationwide reached nearly 24% that year, so prospects were dim for everyone.
Feeling like they'd been rather chewed up and spit out by their country after doing what they felt was their duty, 15,000 to 20,000 veterans made their way to Washington to set up camp and make their case. They were known as the Bonus Expeditionary Force, later shortened to the Bonus Army.
They occupied abandoned structures along Pennsylvania Avenue between the Capitol and the White House and set up camp in nearby parks and the Anacostia Flats, a swampland east of the Capitol that had been converted into a park in the early 1900s. Those areas swam with tent cities and even some shacks erected from nearby scrap piles. Such encampments were known as "shantytowns" or "Hoovervilles" after the president who would not meet with them, talk to them, nor hear their stories.
These makeshift homes were filled with veterans from The Great War, both black and white, along with their families.
One of the shantytowns in the Anacostia Flats in 1932. Image via Library of Congress.
Protesters in Hooverville camps wanted to convince the public to support their cause.
Conditions of the camps were as shipshape as they could muster, and the veterans were highly disciplined, with their own post office, library, and newspaper. It was thought that if they did not keep things clean and organized, the public might go against them.
Another view of Hooverville shantytowns in the Anacostia Flats. Image via Library of Congress.
In fact, there was a risk of this; the infamous tactic of the Red Scare was used against them by Hoover and his military commanders. Basically, they were called Communists and agitators. It was to no avail, however; these tens of thousands of citizens remained within a stone's throw of the White House — sometimes on the lawn itself — and they continued pushing for relief.
"I never saw such fine Americanism as is exhibited by you people. You have just as much right to have a lobby here as any steel corporation. Makes me so damn mad, a whole lot of people speak of you as tramps. By God, they didn't speak of you as tramps in 1917 and '18." — Retired Marine Corps Gen. Smedley Butler, speaking to the veterans.
On June 15, 1932, with pressure mounting, the House of Representatives passed the Patman Bonus Bill, which would have taken care of the bonus payments in cash immediately. But in what sounds like something out of today's headlines of partisan politics, the Senate shot it down two days later, by a vote of 62-18.
More veterans head to Washington via rail car. Image via Wikimedia Commons.
Thousands of veterans headed to Washington in response to the defeat of the legislation to compensate them.
Initially, the local police were cooperative and even sympathetic; their chief, Pelham Glassford, had been a World War I veteran himself.
The Bonus Army camps out on the Capitol lawn, July 1932. Image via Library of Congress.
But by the end of July, some of the officialdom in D.C. had grown weary of these veterans. On July 28, Secretary of War Patrick Hurley ordered police to evacuate the buildings that the veterans occupied. In the skirmish that ensued, two veterans were killed.
The police begin their "removal" of the veterans. Image via National Archives.
Hoover then made the fateful order: The Army would rout them from the city entirely.
It was none other than Gen. Douglas MacArthur, with the help of Maj. Dwight Eisenhower, that removed the 1932 Bonus Army from the city, with an assist from Maj. George Patton, who was in charge of the cavalry brigade that headed the action.
They first cleared the abandoned buildings, then MacArthur made a decision to follow the veterans into the Anacostia Flats.
Hoover, sensing the political catastrophe this entire episode might create, twice sent word to MacArthur not to cross the 11th Street Bridge that led to the flats.
MacArthur ignored Hoover's suggestions and moved his troops ahead.
One of the Hooverville shantytowns burns in the Anacostia Flats with the Capitol dome in the distance. Image via National Archives.
The soldiers marched on the veterans and their tent homes, setting them ablaze.
Tear gas canisters flew ahead of them, bayonets flashed in the sun, a machine-gun brigade brandished its terrifying weapons, and a half dozen tanks lined up behind them for visual reinforcement.
The cavalry on its way to rout the veterans and begin the inferno. Image from "Bonus Army"/PBS.
When it was over, at least one baby died from the tear gas, and one veteran's wife miscarried from the same. Added to this toll were the two veterans killed by police a few days earlier, and 54 injuries from both skirmishes.
Almost immediately, MacArthur held a press conference where he tried to perform impromptu damage control, claiming the Bonus Army was composed of revolutionaries and Communists and that they had threatened the very institution of government.
Hoover's statement the next morning called into question the patriotism and loyalty of the veterans.
It didn't work; the general public held it against Hoover during the presidential elections that year. In newsreels at movie theaters nationwide, a chorus of boos would erupt when news of the military action against veterans took place.
Roosevelt was elected by a massive margin later that year. In addition, the Democrats won significant majorities in both houses of Congress.
While FDR himself did not support the Bonus Army, he did not forget the political cost that actions such as those perpetrated by Hoover exacted. Soon after his election in 1932, FDR established the Civilian Conservation Corps, which created jobs for 25,000 veterans and other Americans. Similarly, when a smaller Bonus Army went to D.C. a year later, rather than send troops, he sent Eleanor to meet with them.
A 1932 Bonus Army "cinderella stamp." Image via Steve Strummer/Wikimedia Commons.
In 1936, Congress passed legislation to honor all bonus payments — nine years early.
Ultimately, the plight of veterans led to the Servicemen's Readjustment Act of 1944 — known as the G.I. Bill of Rights — which offered multiple benefits, including college education for veterans, though it was rife with racial bias against African-Americans.
Here's a short video explaining the Bonus Army demonstrations, including testimony from eyewitnesses. The original 30-minute version is by PBS.
Politicians risk a lot when they treat veterans with callousness — and worse.
When unemployment benefits, food stamps, or other programs that help veterans are slashed, there are ramifications. And when deplorable conditions at VA hospitals are brought to light, it casts a shadow on whatever administration is in power at the time.
The story of the Bonus Army should make politicians more cautious when it comes to veterans' issues, but it shouldn't have to come to that. Veterans — like the rest of us — have a right to a good home and a good job in the United States of America.
- Marine Corps Sergeant gave his son an emotional first salute as a commissioned officer - Upworthy ›
- World War II veterans reunited after 78 years - Upworthy ›
- How military families stay connected over the holidays - Upworthy ›
- Listen to the sounds of the last moments of WWI - Upworthy ›
- Woman from Great Depression photo didn't about fame for 40 years - Upworthy ›
- Woman featured in iconic Great Depression photo didn't know she was famous until 40 years later - Upworthy ›
- People share the frugal habits they learned from relatives who lived through the Great Depression - Upworthy ›

 A Generation Jones teenager poses in her room.Image via Wikmedia Commons
A Generation Jones teenager poses in her room.Image via Wikmedia Commons
 A Target store at night.via
A Target store at night.via  An aisle at a Target.via
An aisle at a Target.via 
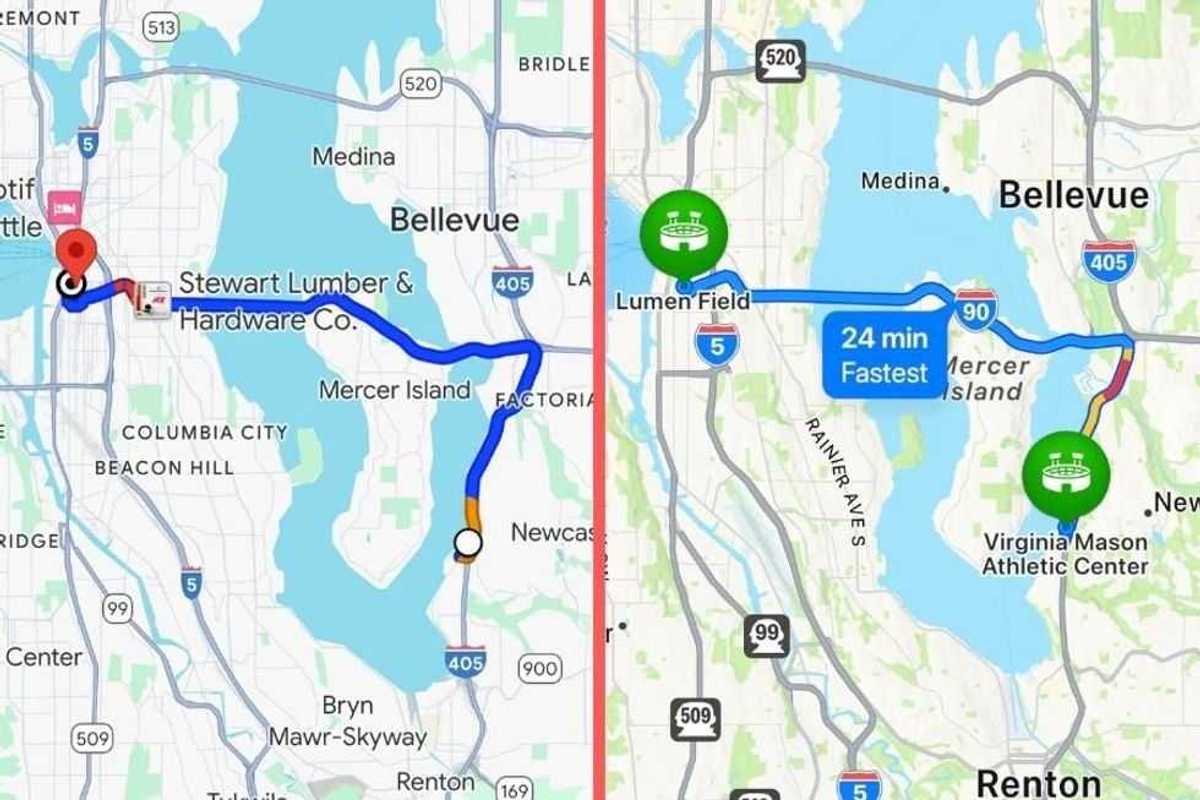
 Which map app is best?
Which map app is best? We've become pretty finicky about our map apps in the modern age.
We've become pretty finicky about our map apps in the modern age.