You’re going along, minding your own business on the internet, when suddenly this little gem comes across your timeline:
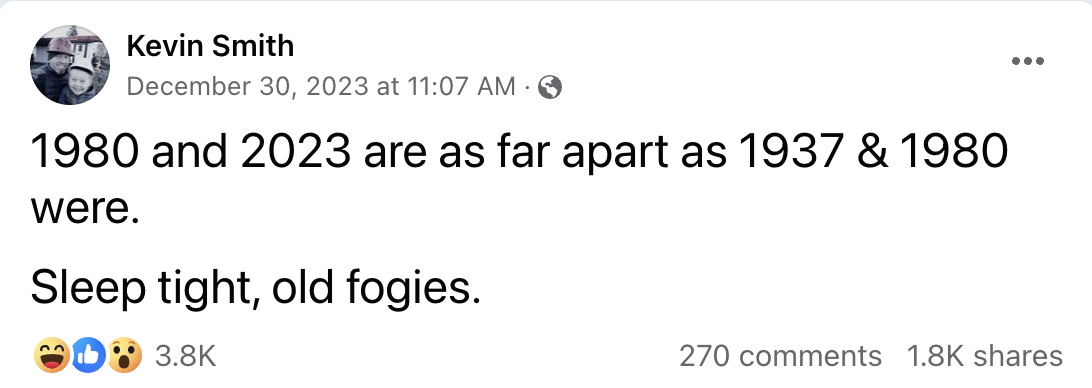
Your first reaction is, “Nuh-uh, no way,” so you pull out the calculator to do the math yourself—several times because you’re sure you must’ve missed a number somewhere. You remember how long ago 1937 seemed in 1980, and there’s no possible way that much time has passed between 1980 and now. Then, as the warped reality of time washes over you, you sit and stare in stunned silence, contemplating the existential crisis.
Why does time work this way? Why does it seem to get faster and faster and condense to make decades seem shorter and shorter as we age? And perhaps more importantly, how the heck do we stop time from feeling like a runaway freight train?
Here are a few theories about what creates the freight train phenomenon.
Time perception is relative—and kids perceive it differently
“Time flies when you’re having fun” is a saying for a reason. Time also drags when you’re doing drudgery work and feels like it stands still in moments of significance. And yet the ticking of seconds as they go by doesn’t change tempo. We measure it with steady, unchanging beats, but how it feels changes constantly.
This relativity exists in every passing moment, but it also exists in the bigger picture as well. The years felt like they passed by much more slowly when we were children, and by middle age, they feel like they pass in the blink of an eye. The pandemic gave us an even greater sense of this relativity as disruptions to our normal routines and the stress associated with the COVID-19 years messed with our sense of time. (On an odd side note, surveys show that our time perception during the pandemic varied a lot from place to place—people in some parts of the world felt that time moved more slowly, while others felt time moved more quickly.)
According to a 2023 Hungarian study published in Nature Scientific Reports, very young children perceive time differently than older children and adults. Researchers split 138 people into three age groups—pre-kindergarten, school-age and adults 18 and over—and showed them two videos of the same duration, one that was “eventful” and one that was “uneventful.” Interestingly, the pre-K group perceived the eventful video to be longer, while the older children and adults saw the uneventful video as longer.
The way the study participants described the length of the videos in gestures was also telling. Young children were much more likely to use vertical hand gestures, connoting volume or magnitude, to indicate a length of time than the other two age groups. School-aged kids and adults tended to use horizontal gestures, indicating time as linear, increasing with age.
Our neural processing slows down as we age
Professor Adrian Bejan has a theory based on how neurons process signals. As we age, our neural networks increase in size and complexity, and as a result, process visual information at a slower rate. That slower processing means we create fewer mental images each second than we did when we were younger, thereby making time seem to slow down.
“People are often amazed at how much they remember from days that seemed to last forever in their youth, Bejan shared with Harvard University. “It’s not that their experiences were much deeper or more meaningful; it’s just that they were being processed in rapid fire.”
In other words, processing the same number of mental images we did in our youth takes longer now, somewhat counterintuitively making time seem to pass more quickly. So goes the theory, anyway.
It might simply be about time-to-life ratios
Another popular theory about why time feels different as a child than it does as an adult is the ratio of any given day, week or year to the amount of time we’ve been alive. To a 5-year-old, a year is 20% of their entire life. For a 50-year-old, a year only is 0.2% of their life, so it feels like it went by much more quickly.
It’s also a matter of how much change has happened in that year. A year in the life of a 5-year-old is full of rapid growth and change and learning and development. A year in the life of a 50-year-old probably isn’t a whole lot different than when they were 48 or 49. Even if there are major life changes, the middle-aged brain isn’t evolving at nearly the same rate as a child. A 50-year-old looking back at the past year will have a lot fewer changes to process than a 5-year-old, therefore the year will seems like it went by a lot faster.
“Our perception of days, weeks, years and that kind of time seems to be especially influenced by our perspective: Are we in the moment experiencing it, or are we looking backward on time?” psychology professor Cindy Lustig told the University of Michigan.
The key to slowing it all down? Be mindful of the present moment.
Lustig has a point. When we are in the moment, our perception of time is much different than when we look back. So, being fully conscious in the present moment can help us rein in the freight train effect.
One way to do that is to be mindful of your physical existence in this moment. Feel your heart beating. Feel your breath going in and out. Cornell University psychology professor Adam Anderson, Ph.D., conducted a study that found our perception of time may be linked with the length of our heartbeats. (Study participants were fitted with electrocardiograms and asked to listen to a brief audio tone. They perceived the tone as longer after a longer heartbeat and shorter after a shorter one.) He suggests starting a stopwatch, closing your eyes and focusing on your breathing for what you think feels like a minute. Then, check your time to see how accurate your estimation was.
“This can give you a sense of how much your experience of your body is related to your experience of time,” Anderson told WebMD. “It will help teach you to enjoy the pure experience of time.”
You can also use focused breathing to purposely slow down your heart rate, and thus slow down your time perception. “We show that slow heart rates—that is, a longer duration between heartbeats—dilates time, slowing it down,” Anderson said.
Finally, try to take in the world the way you did as a small child. Take note of life’s wonders. Engage fully in whatever you’re doing. Notice details and take mental pictures as much as you can. Time goes by fast when we’re distracted, so training our attention on the here and now can help. Ultimately, we can strive to perceive time more like we did when we were little, in its full depth and magnitude instead of a narrow, straight line.
This article originally appeared last year.