
This article originally appeared on ProPublica. You can read it here.
Once it was called "hysterical" movement disorder, or simply "hysteria." Later it was labeled "psychogenic." Now it's a "functional disorder."
By any name, it's one of the most puzzling afflictions — and problematic diagnoses — in medicine. It often has the same symptoms, like uncontrollable shaking and difficulty walking, that characterize brain diseases like Parkinson's.
But the condition is caused by stress or trauma and often treated by psychotherapy. And, in a disparity that is drawing increased scrutiny, most of those deemed to suffer from it — as high as 80% in some studies — are women.
Whether someone has Parkinson's or a functional disorder can be difficult to determine. But the two labels result not only in different treatments but in different perceptions of the patient. A diagnosis of Parkinson's is likely to create sympathy, but a functional diagnosis can stigmatize patients and cast doubt on the legitimacy of their illness.
Four in 10 patients do not get better or are actually worse off after receiving such a diagnosis and find themselves in a "therapeutic wasteland," according to a 2017 review of the literature by academic experts.
"This is the crisis," said University of Cincinnati neurologist Alberto Espay, the author of guidelines on diagnosing functional movement disorders. "It shouldn't be stigmatized but it is. No. 1, patients are wondering if it is real. 'Does my doctor think I am crazy?' Secondly, doctors can approach it in a way that implies this is a waste of their time."
A study published last year in a leading neurological journal stoked the growing controversy. Of patients diagnosed with functional symptoms, 68% were women. This finding, the authors wrote, "suggests that female sex may be an independent risk factor for the development" of functional symptoms.
The study prompted a furious letter to the journal's editor from Dr. Laura Boylan, a New York City neurologist. She argued that the study's results might demonstrate instead that symptoms thought to be psychogenic were actually the result of Parkinson's, and that doctors were slow to identify the brain disease in women.
"Disparities in healthcare for women are well established," she wrote, adding, "Women commonly encounter dismissal in the medical context."
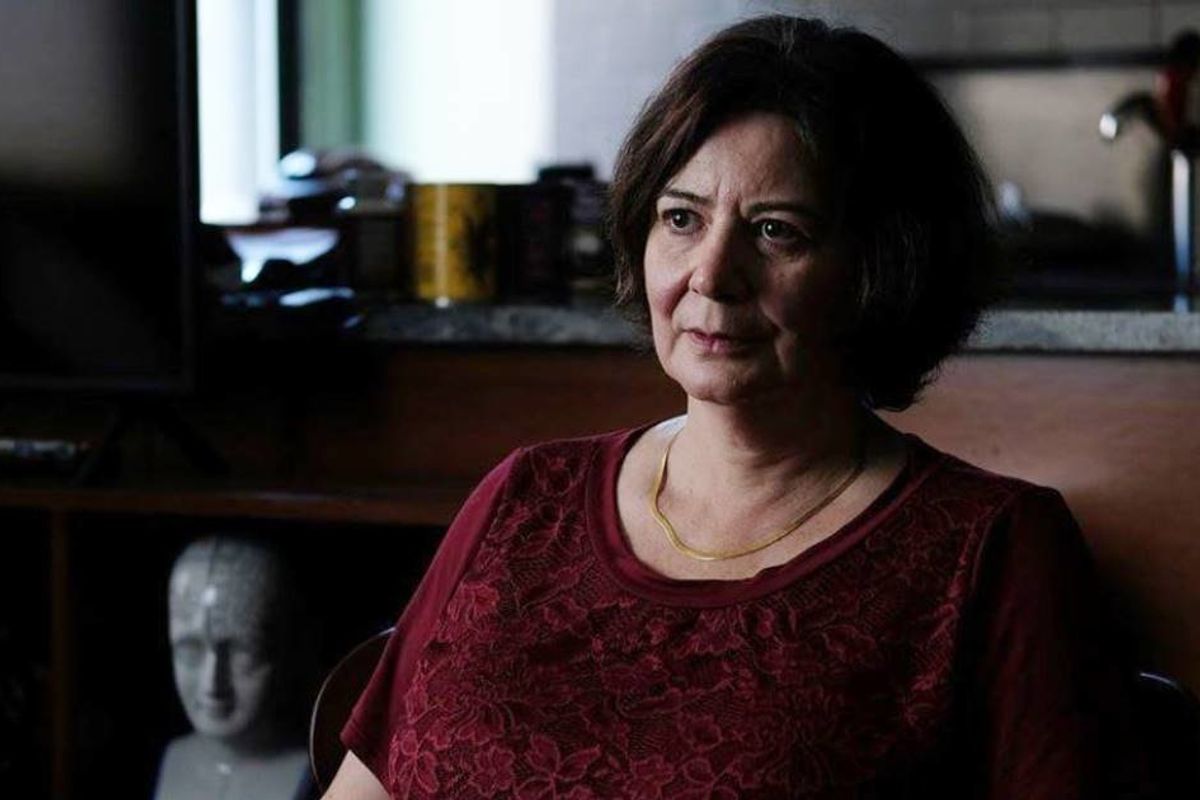
For Boylan, the issue was more than a professional debate. It was personal. She had been diagnosed with Parkinson's-like symptoms that her doctors, all top caregivers at some of the world's leading medical institutions, largely believed to be psychogenic or side effects of medication.

Most of her doctors were men, but two were women. Boylan, herself a brilliant neurologist, disagreed vehemently with them. She attributed her problems to a physiological cause, a tiny cyst in her brain, and grew despondent when other neurologists doubted her theory. She gave up her medical practice, became housebound and contemplated suicide. Even today, her case remains a mystery.
The first sign that something was wrong came in 2008.
At the time, Boylan was busy with a successful career that included work as a teacher, researcher and clinician. She was an assistant professor of neurology at the New York University School of Medicine; the director of the behavioral neurology clinic for the VA in New York City; and an attending physician at a hospital in Pennsylvania.
She was married to another neurologist, Daniel Labovitz, who is a professor at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine and practices at Montefiore Medical Center in the Bronx.
It was while driving at night on a Pennsylvania highway that Boylan experienced a vivid hallucination. She saw a cartoonish chipmunk on the steering wheel, smiling and waving at her. Another time, two blue men with red hats appeared on either side of her. She knew the images were not real, but she couldn't make them go away.
Her doctors at the time blamed the hallucinations on side effects of psychiatric medicine Boylan took for her long-diagnosed bipolar disorder. Her bipolar condition would later add another element of uncertainty to the debate over her Parkinson's-like symptoms.
Studies show that people with preexisting psychiatric disorders are more likely to develop Parkinson's — or have a functional disorder with similar symptoms. Boylan said she sees a psychiatrist for the bipolar disorder, but it's "just not a big deal in my life."
Over time, her health continued to worsen. In early 2011, during a tai chi class, she had difficulty balancing on her right leg. Later, she also noticed muscle twitching in her feet and legs.
Boylan was worried that some of her symptoms mirrored those found in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or ALS, a rare and degenerative neurologic disease that affects the ability of muscles to function. ALS, also known as Lou Gehrig's disease, was ruled out by a specialist, but an imaging scan performed as part of that exam revealed a small cyst on the front right side of her brain.
The location and type of cyst are considered rare. At the time, Boylan and the neurologist she consulted didn't believe the cyst was causing her movement problems and chalked it up as an "incidental" finding not to be concerned about.
In the fall of 2013, Boylan experienced a three-day bout of double vision that forced her to miss work. The episode was disturbing because it left her, for the first time, unable to perform her duties as a doctor.
About a week later, she went to see Janet Rucker, then a neuro-ophthalmologist at Mount Sinai Medical Center. Rucker diagnosed convergence insufficiency, a condition in which the eyes are unable to work together to focus on close by objects. Rucker thought it unlikely the brain cyst was causing the vision problem and believed it was more likely related to medication Boylan was taking, according to her notes.
Boylan returned home unconvinced by Rucker's opinion. Her vision improved enough to allow her to research the condition herself. She said she found instances where levodopa, a medication used to treat Parkinson's that she had prescribed many times for her own patients, helped alleviate the vision problem.
She decided to take her treatment into her own hands and took levodopa she prescribed for herself. Boylan knew the decision to test her own theory was a direct challenge to Rucker's competence.
While legal, self-prescribing medication is considered an unsound practice by some in the medical establishment. Physicians who treat themselves risk removing the objectivity usually present in a doctor-patient relationship, which can lead to poor decisions.
Within an hour of taking the levodopa, Boylan's eyes converged and the vision problem cleared. That wasn't all. Involuntary tremors and twitches stopped. She later wrote that she "felt years younger" and "moved much better" immediately after taking the drug.
For Boylan, the experience with levodopa confirmed what she had come to suspect; that the cyst in her brain thought to be harmless was in fact causing her Parkinson's-like symptoms. (In Parkinson's, nerve cells in the brain that help control body movements break down or die.)
If she had a functional disorder, the drug should have no effect. She excitedly dashed off an email to Rucker reporting her success and attached a video showing her eyes working properly.
"That is a pretty impressive effect," Rucker replied. She wrote that she rarely recommended the drug for convergence insufficiency, but given Boylan's improvement, "perhaps I'll recommend it more often."
Rucker, however, didn't appear to think the cyst was responsible for Boylan's double vision, calling it the "least likely" of options, according to her notes of the case. More likely, she wrote, it was related to other medications Boylan was taking.
Boylan didn't learn about the contents of the medical notes from her visit until later. Boylan, who believed her recovery proved that the cyst was the origin of her double vision, was insulted.
"That I solved this problem with levodopa, documented it, and returned to work the next day might be taken as evidence of my skill rather than having a screw loose," she later wrote to Rucker, who declined comment for this story.
Levodopa is a potent drug used to control tremors and stiffness in Parkinson's patients. The development of the drug, and what it revealed about how the brain works, was an important breakthrough that won one of the researchers involved the Nobel Prize in medicine in 2000. But levodopa can also produce side effects that include involuntary movements, from tics to sudden, jerky body motions, different from those that it had alleviated in Boylan.
Boylan decided to continue taking the drug, but wanted another neurologist to help manage her situation. She chose Elan Louis, a neurologist who had been just ahead of her in the Columbia residency program. Boylan told him she was serving as her own neurologist and that her situation was "getting acutely worse."

The two doctors saw each other at the occasional reunion, but they were not close. Boylan largely knew of Louis by reputation. He is considered one of the leading experts on movement disorders and is the editor of Merritt's Textbook of Neurology, a standard clinical guide in the field.
He practiced at Columbia when Boylan first began seeing him in late 2013 but was recruited to Yale University in 2015 to serve as chief of the movement disorders division in the neurology department.
Louis had not treated a specialist in his own field before. The relationship proved challenging. Boylan has a combination of intelligence and passion that attracts devoted friends. Louis described Boylan as "super smart" and someone who was constantly digging into the medical literature to learn as much as she could about her symptoms and the cyst in her brain.
She could also be blunt and confrontational. Boylan was one of several people arrested a decade ago for refusing to leave a U.S. senator's office as part of a sit-in advocating for single-payer health care.
She was also an early proponent of limiting the perks that pharmaceutical companies give doctors to encourage them to prescribe their drugs, a stance that irked some colleagues but also won her admirers. Boylan was not hesitant to challenge her own doctors' assessments, as she had done with Rucker. With a mix of pride and contrition, she describes herself as a difficult patient.
In one email exchange in 2015, Boylan appeared miffed that Louis did not believe that a bout of heart palpitations and dizziness was related to her brain cyst. "I wish you'd responded earlier when you found my questions odd/unreasonable," Boylan chided Louis. "At present I know more about this area than you and yet seem crazier because of it."
At least 10% of the patients who seek help for movement disorders at the Yale clinic are determined to have a psychogenic, or functional condition, Louis said. At other neurology clinics, the number is as high as 20% and second only to headaches as the reason for seeking help.
To determine if a condition is functional, neurologists identify symptoms that don't match with physiological movement disorders. In Boylan's case, the cyst was on the right side of her brain, which meant it should only cause symptoms on the left side of her body. The right leg weakness she experienced at tai chi, for instance, didn't fit with this.
Then there are a series of tests that can help determine if movements are genuinely involuntary. One group of tests is designed to distract a patient. A patient with a left arm tremor, as was the case with Boylan, might be asked to extend that arm out and then use the hand on the other arm to tap out a sequence of numbers.
As the neurologist calls out for one tap, four taps, two taps and so on, he or she is watching to see if the tremor on the left side stops as the patient focuses on the tapping.
When Louis performed these tests on Boylan, she knew exactly what he was assessing. She administered the same tests to her own patients. To Boylan, the fact Louis was even doing the tests meant he had already concluded some of her symptoms were psychogenic. "I knew I was going to fail," she said later, adding that the tests are not always a valid indicator.
"I tried so hard to do things properly that it can look extreme." Louis observed that Boylan's tremor stopped when she was distracted. "If something is truly involuntary, it should persist whether someone is paying attention or not," Louis told me. He agreed with Boylan that the tests are not foolproof, but said that they are useful in evaluating a case.
In his initial assessment of Boylan, Louis referenced the brain cyst and possible medication-induced effects as well as the possibility that "something else is going on here." The difficulty, he noted, was "piecing it all together."
To help solve this puzzle, with Louis' encouragement, Boylan consulted two neurosurgeons.
The first, at Columbia Presbyterian, wrote the cyst might be playing a role in her tremors but warned surgery should only be considered as a "last resort." The second, at Mount Sinai, was skeptical the cyst was playing a role, writing, "It is difficult for me to pin the presence of this cystic lesion on her worsening symptoms."
After the appointments with the surgeons, Boylan returned to see Louis on Nov. 14, 2013. Louis told her he saw some "psychiatric overlay" in her symptoms and said there may be something "organic beneath a lot of overlay," according to his notes.
He estimated that perhaps 70% of her symptoms were psychiatric in nature. He doubted the brain cyst was causing her rapidly worsening symptoms. It "doesn't fit," he wrote. He noted Boylan "was not happy about this but seems to have accepted it during subsequent emails/phone calls."
Louis told me that Boylan's case was "very complicated" because some of her symptoms and the cyst in her brain were rare. "Her syndrome is difficult to neatly put in one box," he said. "That is why she has defied diagnosis and had a difficult time."
A psychogenic diagnosis, he said, is hard for patients because "there is a feeling with people that it is not real, it is all in our head and imaginary and undervalues and devalues what they are going through. No one wants that."
While Parkinson's is treated with medications such as levodopa, patients determined to have a functional or psychogenic condition are often prescribed psychological regimens such as cognitive behavioral therapy. Louis said he has worked successfully with a Columbia psychiatrist to treat functional patients.
"We have had patients unable to walk who were walking out two weeks later," he said. Louis said he discussed Boylan's case with her psychiatrist to share his evaluation of her situation and to coordinate medications. Her psychiatrist referred her to behavior therapy, Boylan said. "I did a round," she said. "It helped me tolerate problems but did not change them."
The more Boylan tried to convince others that the cyst was causing her problems, the more she felt she was viewed with suspicion. It became an obsession. Louis once remarked to Boylan that no one in the world knew as much about the square inch of brain where the cyst was located as she did.
Despite their clashes, Boylan respected Louis. When he delivered his diagnosis, it caused her to second-guess her theory about the cyst. She also believed that some of her doctors used her bipolar disorder to cast doubt on her complaints.
Her symptoms worsened and the stress overwhelmed her. On Dec. 9, she was admitted to the emergency room at St. Luke's Hospital with severely elevated blood pressure and stress-induced cardiomyopathy, a heart muscle disease that makes it harder to pump blood. When a cardiologist inquired if she was under stress, Boylan tearfully told her, "My doctors think I am hysterical."
As 2014 wore on, Boylan needed increased doses of levodopa to get the relief she first experienced when self-treating her double vision. It was a vicious circle. She needed the medicine to help with her with her lack of balance, which was causing her to fall, as well as her vision and left arm tremor. But the side effects from the medicine were severe.
On a Sunday afternoon in September 2014, Boylan stumbled out of a taxicab onto the sidewalk in front of the emergency room at NewYork-Presbyterian/Columbia University Medical Center. A couple of ambulance workers noticed she was having difficulty and helped her into a wheelchair.
Boylan was gaunt. She had lost more than 30 pounds since the beginning of the year. In the preceding days she slept little. Her body was twisting up in uncomfortable and unusual positions, making it hard to walk.
Her head jerked and her knees pushed together as she bent forward. She was unable to control the movements. In a brief video taken after she was admitted to the hospital, Boylan leaned against a wall with her head slumped awkwardly to the side as she waited to use a bathroom.
To the doctors who attended to Boylan, her condition was disturbing. They knew her as an accomplished neurologist who trained and mentored a new generation of doctors. She was a familiar face at Columbia, having done her medical residency there in the late 1990s. On this day, Boylan appeared paranoid and agitated. She argued with doctors about medication and their assessment of her condition. She complained that her husband thought she was crazy.
Her case defied an easy diagnosis. "She is a quite complicated movement disorders patient," one of the treating physicians at Columbia noted.The attending neurologist at the hospital that weekend thought Boylan was suffering from "mild psychosis" with contributing factors that included fatigue and the side effects of medication.
The doctors noted Boylan recently received a distressing email about a former patient who was dying; the implication was that this was a possible source of a psychogenic effect. Louisa Gilbert, a friend of Boylan's, said that when she arrived at the hospital she found doctors treating Boylan as a "psych case."
Boylan left the hospital after one night. In the following weeks, her condition worsened. She stopped working and was largely homebound. Her diet was poor, consisting primarily of ice cream and grapefruit juice, and she continued to lose weight. She was again having trouble reading and developed severe writer's cramp that she attributed to the brain cyst.
Boylan grew dependent on others to take care of her, including Gilbert, whom she first met at boarding school. A professor of social work at Columbia University, Gilbert always admired Boylan for her resiliency. Boylan went through her last two years of medical school while a single parent. She never missed work. Now there were days when Gilbert would show up at Boylan's apartment and find her friend writhing on the floor, unable to get up.
"It was so bewildering," Gilbert said. "What the hell is going on?"
By December, Boylan was spending hours lying on the floor of her apartment while sipping orange juice to speed up the absorption of the levodopa she was taking to stave off muscle spasms. She was now separated from her husband; they would later divorce. Alone and unable to work, Boylan despaired and made plans for suicide. "I had and am still having emotional meltdown over this loss of profession/vocation/self-definition," she wrote in an email to her brother, Ross, in California.
Ross and Laura Boylan were the only children of a corporate lawyer and a homemaker. For most of their youth they lived in an apartment near the Metropolitan Museum of Art on Manhattan's Upper East Side. Their mother suffered from severe mental illness and was hospitalized a number of times. Their father was an alcoholic. The couple often argued. Laura was happiest when she was out of the apartment, and she often spent summers away from the city.
The Boylan siblings both attended boarding school at Phillips Academy in Andover, Massachusetts, but rarely interacted there. Ross was two years older and each of them moved in their own circles. Laura returned to New York City to attend Barnard College. Ross went on to Harvard University and then moved permanently to the west coast.
In her December 2014 email to her brother, Boylan wrote "bad news" in the subject line. She said the brain cyst was causing "more and more problems." She shared that she gave up clinical practice because of "fatigue, stamina, vision and other problems." She said there was a "small possibility of neurosurgery" but she wasn't sure it was worth the risk, and she doubted any surgeon would take the chance anyway. She said her symptoms were getting progressively worse and there was no cure.
Ross Boylan responded with a short note that ended with a touch of optimism. "The future is not written," he wrote.
The email from his sister caught Ross Boylan off guard. "I thought she was doing OK," he said in an interview. "Then she sends me this email, oh by the way every single sphere of my life is collapsing." The doctors she consulted seemed to be uniform in their view that her brain cyst was irrelevant and that removing it would be pointless and probably dangerous, Ross Boylan said. "It's impossible to operate, and nothing could be done about it," he said. Most concerning, it seemed to him that the "fight had gone out" of his sister.
Ross Boylan is a research statistician at the University of California, San Francisco, and his department frequently works with doctors at the medical school there. Among all the specialists at the university, he figured there must be one who could help his sister. He didn't tell Laura that he was going to try to help. He was afraid she would tell him not to bother, and he didn't want to get her hopes up in the event his efforts failed.
On a webpage for the university neurology department, Boylan came across a group photo that included his boss. It turned out his boss had done some statistical work for the research team of neurosurgeon Michael Lawton. An introduction was made. Ross Boylan gave Lawton what information he had about his sister's condition, and within days Laura Boylan was in contact with the surgeon by phone and email.
"My hunch is that operating on the cyst will help and I am ready to proceed," Lawton wrote her. "You can appreciate that we surgeons like to be certain that our efforts are going to be curative, and in your case I can't be sure. Nonetheless, I think this operation will be safe and I am ready to move forward whenever you are."
Boylan decided to go ahead with the surgery and booked a flight to San Francisco.
Lawton told me that the cyst was located in an area of brain circuitry that is disturbed in Parkinson's patients and could be the cause of her movement disorders and double vision. "It fits," he said. "It's right where that kind of lesion would produce those symptoms." Nonetheless, he said he cautioned Boylan the procedure could be done perfectly with no complications yet have no therapeutic effect.
Louis said he wasn't certain if the surgery was a good idea. "I deferred to the surgeon," he said. "There was little margin of error, and that made it a very complex decision." Others close to Boylan were concerned about the speed in which the decision to operate was made and that Boylan decided to go ahead before even meeting with Lawton in person.
Boylan herself confessed in an email to a colleague days before the operation that she felt "in over my head" in arranging the surgery and was "beginning to think this is not a good idea."
On Jan. 9, 2015, Lawton and his team performed a nearly five-hour craniotomy on Boylan in which part of the bone in her skull was removed to expose her brain. The cyst was drained and a piece cut out to prevent it from accumulating fluid in the future.
Boylan was worse off in the weeks after the surgery. The awkward, twisting movements persisted. She couldn't use her right arm. She didn't know if she would recuperate to a life worth living.
About a month after the surgery, Boylan saw neurologist Rebecca Gilbert at NYU Langone Medical Center. Boylan arrived for the appointment wearing an eye patch and an arm sling.
Gilbert's notes of the encounter make it clear she thought Boylan's symptoms, even after the surgery, might be psychogenic. A right side tremor was "inconsistent" and abnormal movements were "variable and erratic" and only "present during the formal exam."
In contrast, when "patient is telling her story, there are no abnormal involuntary movements." Gilbert wrote that she was "very concerned that at least part of this neurologic picture is psychogenic in nature."
By mid-March, just a month later, Boylan's condition improved significantly. On March 21, she sent an email to Lawton with the subject line "have turned a corner." She said her symptoms were improving and she was "back out and about in the world."
She told him he had "given me my life back." She also criticized those who questioned the wisdom of her decision to undergo the operation. "I confess that, in accord with my own pre-existing bias, some neurology pals have thought I must have found a cowboy who took a lucky long shot," Boylan wrote. "I correct them carefully in detail."
Ten days later, Boylan saw Gilbert for a follow up appointment. Gilbert wrote that Boylan "returns looking very well. She feels well neurologically and psychiatrically. She attributes her improvement to the surgery." Gilbert declined comment on Boylan's case.
By June, Boylan was back to work.
On a Sunday morning this spring, Boylan sits at a conference table in the neurology department at Bellevue Hospital in Manhattan, the country's oldest public hospital. The room is sparse save for a large, formal portrait of the former head of neurosurgery. The painting does not escape Boylan's notice. Like many of the leading figures in neurology, the former official is a white male.
Boylan, 57, is dressed casually in black pants and a flower-print blouse. A lanyard with a Bellevue identification tag hangs from her neck. On this morning, she is the attending neurologist, overseeing medical residents. In addition to Bellevue, Boylan does part-time stints at a hospital in Duluth, Minnesota, and a VA facility in Albany. She has regained the weight she lost when her illness was at its worst, as well as the mental sharpness that dulled during that time.
Across the table, a resident briefs her about a woman who arrived in the emergency room the day before. The exchange is thick with medical terms, but there is a clear point to the back and forth: They are trying to determine if the woman's symptoms are functional. The patient complained of a generalized burning sensation.
That's the type of vague complaint that could point to a psychogenic diagnosis. On the other hand, the resident said the patient reported having problems with her coordination, but not with her strength. People with functional disorders might also indicate they were weak, because they tend to have a wide array of complaints.
When the resident pulls up a scan of the woman's brain on a screen mounted on the wall, Boylan points to an area that she describes as a "little bent" with a "kink in it." This is potential evidence, she says, of a cerebral fluid leak. The woman recently underwent an epidural injection and fluid leaks are a known complication of the procedure. Boylan talks to the patient and comes away confident a leak is the problem. The remedy is intense rehydration. The patient improves, and is released the next day.
Afterward, Boylan said her own experience has prompted her to evaluate cases more carefully. She said she also has to guard against failing to recognize cases that may, in fact, be psychogenic. "I have to be careful not to lead the patient," she said.
After her surgery, Boylan requested copies of her medical records from most of the doctors who treated her over the prior five years. She was angered to find that several of them highlighted her history of bipolar disorder — in some cases it was the first item entered — and discounted the role of the brain cyst in her symptoms.
Boylan believes that many of her doctors discounted the brain cyst because of a predisposition toward diagnosing psychogenic conditions in women, and that her case is symptomatic of gender bias in the field of neurology.
"I don't believe I would be treated this way if I was a man," she said. By sharing her experience publicly, Boylan is determined to counter what she views as an ingrained suspicion of symptoms reported by women that dates back to the use of the word "hysterical" to demean them as emotionally and physically weak and prone to exaggeration.
She calls it a "pervasive and potentially lethal bias" in neurology.Gender inequality is rife in neurology. Female neurologists were last in pay and had the biggest salary gap between men and women, in a 2016 survey of salaries by specialty and gender at medical schools.
The American Academy of Neurology has had only one female president in its 71-year history even though women now constitute 40% of the professional society's membership. Female neurologists are also disproportionately underrepresented in awards handed out by the academy, according to a study last year. In 24 of the 28 years studied, the recipients of the academy's lifetime achievement awards did not include a single woman.
The more difficult question is whether this inequality spills over to clinical practice. Boylan received care from both male and female specialists, and her medical records are devoid of outright indications of gender bias. Boylan said female neurologists are trained "in a paradigm of thinking generated by men for men" in which the same symptoms are viewed differently in men and women.
Louis said there was no gender bias in his evaluation of Boylan. He said functional disorders are "far more common" in women and "if a person is that gender I am more comfortable with that diagnosis." Still, gender is "only one of many, many pieces of information" used to make a diagnosis, he said.
Dr. Sarah Lidstone, a specialist in functional movement disorders at Toronto Western Hospital, said it is "impossible to say" that gender bias doesn't exist in diagnoses of this condition. "That does factor into that." Still, she said, there appear to be real gender differences. "We don't know why. It's complicated."
Researchers are working to figure out whether women are disproportionately diagnosed with functional disorders.
"We don't know what is right or the whole truth necessarily," said Dr. Mark Hallett, a senior investigator at the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. He said one study underway is looking at whether women suffer more childhood trauma, particularly sexual abuse, than men and if that is a cause of functional disorders.
He said he didn't believe that gender bias played a significant role in the fact that women receive the diagnosis more often than men, and he said other explanations may include hormonal differences between the sexes or that women may be more likely to seek treatment.
It's impossible to know for certain how Boylan got better. The workings of the mind are complex and our understanding of diseases of the brain and of psychology is constantly evolving. It may be that, as Louis suspected, a combination of factors was at work that include both a psychogenic component and the brain cyst.
"To me, where she is now is nothing short of a miracle," said Boylan's friend, Gilbert.
I asked Lawton if Boylan might have experienced a placebo effect from the surgery. While that can happen, he said, Boylan's relief and turnaround "was pretty significant to the point that it outlasted the typical duration of most placebo effects which I think run their course."
Louis said he believes the surgery "did do some good" and at a minimum removed a cyst that was in a dangerous position. But he is not persuaded it is the main reason for Boylan's turnaround. He suspects many of her symptoms were functional, and sometimes patients with that diagnosis get better over time.
Boylan is convinced her cyst and reactions to medicine to treat the symptoms caused by it were the primary sources of her illness. She views her story as a cautionary tale: She was a woman with means, a degree in medicine and a cyst in her brain. Still, she said, "that did not spare me from being cast as hysterical."
- This orchestra's blind audition proves bias sneaks in when you least ... ›
- Parents wanted more gender-neutral kids stuff. Target listened ... ›
- Take this old-school psychology test to discover your inner demons ›





 One year of work at McDonalds grossed this worker $13,811.18.via
One year of work at McDonalds grossed this worker $13,811.18.via  A photo of a McDonald's in Hartford, CT. via
A photo of a McDonald's in Hartford, CT. via  Sometimes, "bad" language can actually be good.
Sometimes, "bad" language can actually be good.  Road rage can help release pent-up emotions, especially when they're valid.
Road rage can help release pent-up emotions, especially when they're valid.  Swearing is not morally wrong! Just take it from Bryan Cranston.
Swearing is not morally wrong! Just take it from Bryan Cranston.  Vincent Van Gogh's Self-Portrait, 1889Image via
Vincent Van Gogh's Self-Portrait, 1889Image via  Turbulent flow illustrated and animated.
Turbulent flow illustrated and animated. Animation of art referencing science.
Animation of art referencing science. Animated Starry Night
Animated Starry Night An animated depiction of The Scream.
An animated depiction of The Scream. Bring It Reaction GIF by reactionseditor
Bring It Reaction GIF by reactionseditor
There's a reason why some people can perfectly copy accents, and others can't