Animal success stories that will make you call your senator to protect endangered species.
One of the things that seems it might be on the new administration's chopping block is the Endangered Species Act. Yep, really.
The Endangered Species Act is a federal law that protects over 1,600 vulnerable animal and plant species. To enforce these protections, the law restricts logging, drilling, and other forms of land use.
These restrictions have made the Endangered Species Act a popular target for deregulation pushes. Between January 2015 and January 2017, Congress put forth 135 different bills that would have weakened it, according to the Center for Biological Diversity. The latest push seemed to come during a Senate hearing on Wednesday, Feb. 15, during which Republican senators put forth ideas to — as they put it — modernize the act.
Some advocates have called the latest push an attempt to gut the landmark bill.
Even its most ardent supporters admit the act could be improved. As recently as 2015, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service and National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration proposed changes to the law designed to engage states and improve efficiency and transparency.
That said, some of the claims made against the law have been a bit ... out there.
Some argue the law's not really about protecting endangered species anymore, but instead, it's been unfairly exploited by environmentalists in order to stymie development.
In fact, in January, Representative Rob Bishop of Utah said, "[The law] has never been used for the rehabilitation of species." He claimed it has been used as a sort of scheme to control land and said he would "love to invalidate" it.
What? There are legitimate criticisms one could throw at the act, but really? Never rehabilitated a species?
So ... it didn't help save our national bird?
Photo from iStock.
The protection of the bald eagle was one of the reasons we have the act in the first place. When Nixon signed the law, the iconic animal was in danger of disappearing. Today, partly thanks to habitat protections from the ESA, their numbers have recovered.
They were taken off the act's list of endangered species back in 2007.
Or maybe they weren't — I mean, maybe that's just fake news at this point, right?
It didn't help keep wolves from disappearing from the lower 48?
Photo from iStock.
Gray wolves were once nearly wiped off the face of the lower 48 states. Today, there are estimated to be about 1,900 wolves spread throughout various western states. And while their reintroduction to some areas has been contentious, I don't think you could honestly claim their numbers haven't improved.
What about this stellar sea lion?
Photo from iStock.
Stellar sea lions live in the North Pacific. First added to the list in 1990, by 2013, the species had recovered enough to be removed from the list.
Maybe it's surprising to learn that the American alligator was once on the list.
Photo from iStock.
Perhaps it's time to schedule a trip to Florida? The American alligator spent about 20 years on the list, but by 1987, it had recovered enough to be delisted.
Or the fastest member of the animal kingdom — the peregrine falcon.
Photo from iStock.
Peregrine falcons can dive at up to 240 miles per hour and actually have taken a liking to living on some of our skyscrapers. You might not think such an amazing animal would need protection, but they did once upon a time. They were removed from the list back in 1999.
But, in fact, all these animals (and 32 other species) have recovered to the point of delisting — thanks in part to the Endangered Species Act.
Altogether, 37 different species have been delisted due to recovery, according to the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, including humpback whales, the Louisiana black bear, and the brown pelican.
That's not to mention the other more than 1,600 plants and animals still protected under the law. While only a few have recovered enough to be fully delisted, there are still many success stories in there, like the Southern sea otter, the grizzly bear, and the California condor.
Claiming that the Endangered Species Act has never helped is ridiculous. It absolutely has helped keep the U.S. one of the world's conservation champions.
During the Feb. 15 meeting, former U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service director Daniel Ashe called the law "the world's gold standard" for government conservation.
While no law is above a review, we shouldn't back down from acknowledging all that this landmark act has accomplished.





 I Love You Elf GIF by MOODMAN
I Love You Elf GIF by MOODMAN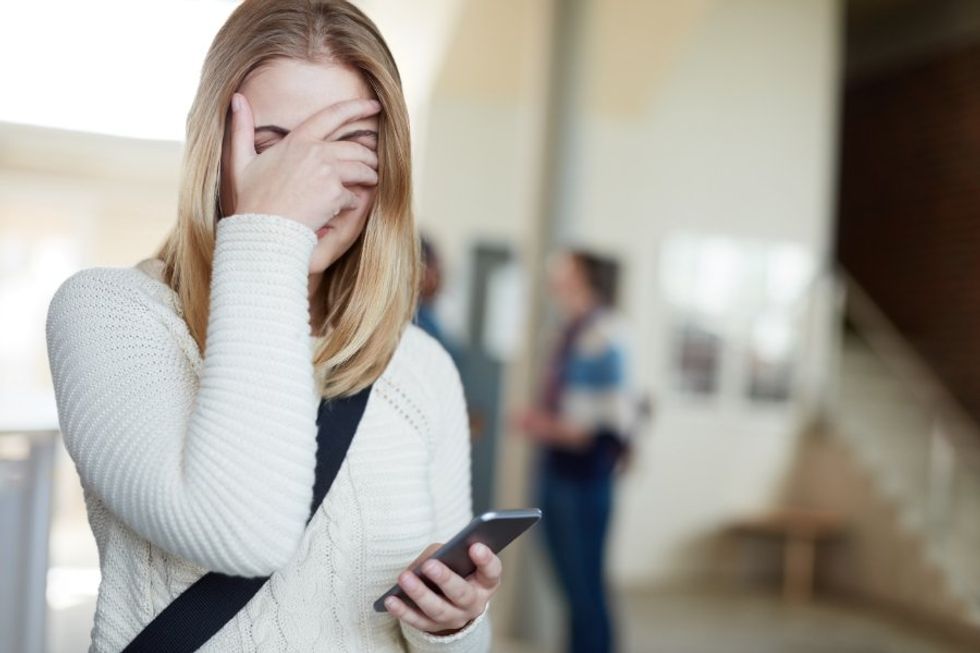 "Love you!" Oops.
"Love you!" Oops. Green Flag GIF by The Last Talk Show
Green Flag GIF by The Last Talk Show Embarrassed Hide GIF by flor
Embarrassed Hide GIF by flor Eating the right foods is crucial for mental health.
media3.giphy.com
Eating the right foods is crucial for mental health.
media3.giphy.com
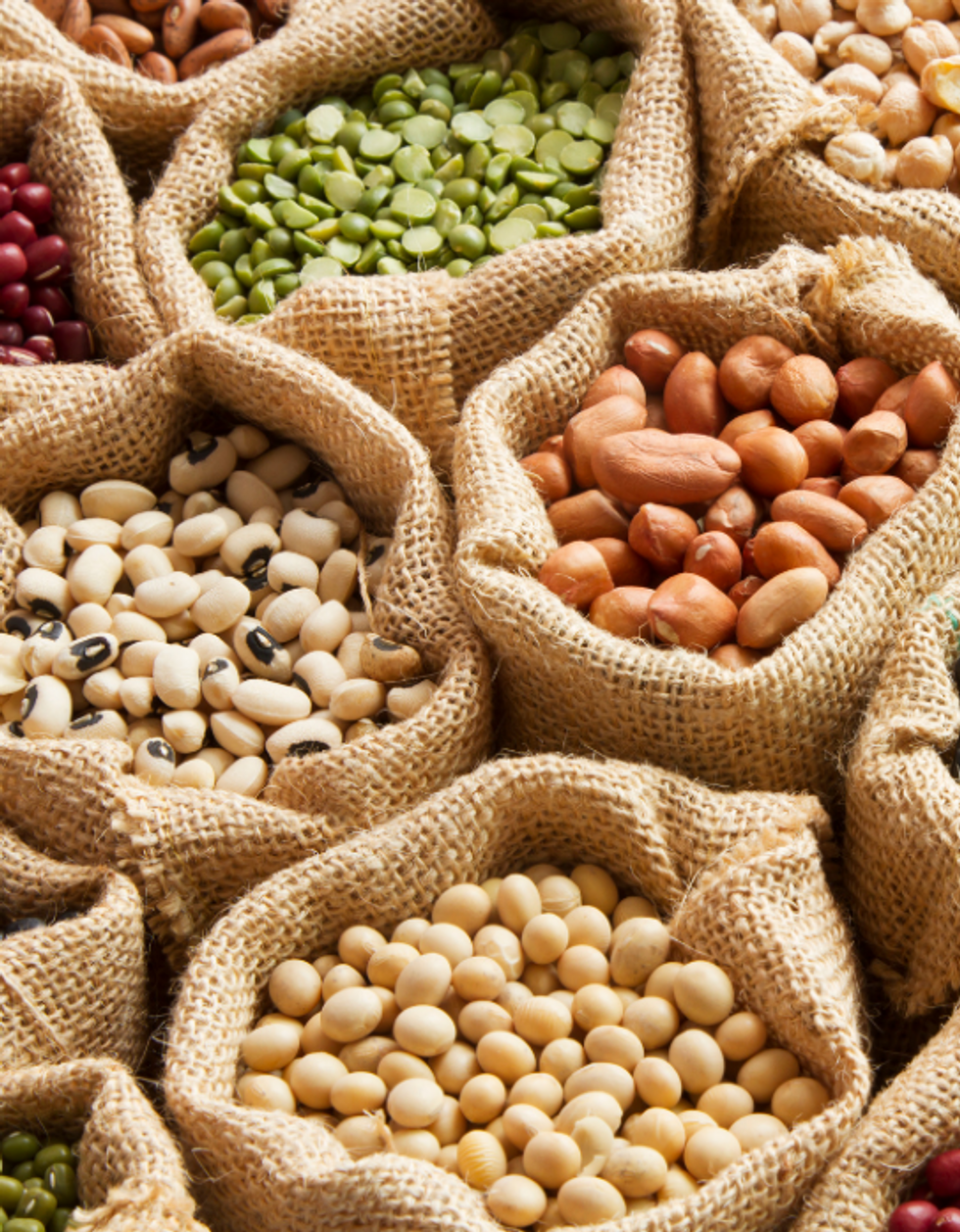 Legumes, like beans and lentils, are super foods and chockful of Vitamin B9.
Photo credit: Canva
Legumes, like beans and lentils, are super foods and chockful of Vitamin B9.
Photo credit: Canva
 Spending time in nature for at least two hours a week is great for overall wellbeing.
Spending time in nature for at least two hours a week is great for overall wellbeing.  There's an innate need for human connection.
There's an innate need for human connection. Even a simple hike, no matter what the pace, is effective when combatting feeling bad.
Even a simple hike, no matter what the pace, is effective when combatting feeling bad.  Tracking your steps can help motivate you and keep you motivated.
Tracking your steps can help motivate you and keep you motivated.  Vincent Van Gogh's Self-Portrait, 1889Image via
Vincent Van Gogh's Self-Portrait, 1889Image via  Turbulent flow illustrated and animated.
Turbulent flow illustrated and animated.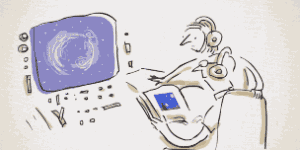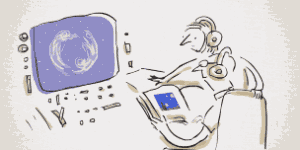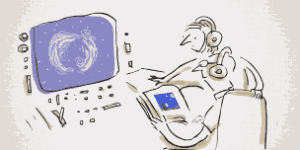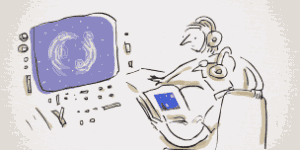 Animation of art referencing science.
Animation of art referencing science. Animated Starry Night
Animated Starry Night An animated depiction of The Scream.
An animated depiction of The Scream.
There's a reason why some people can perfectly copy accents, and others can't
Turns out, there's a neurodivergent link.
A woman in black long sleeve shirt stands in front of mirror.
Have you ever had that friend who goes on vacation for four days to London and comes back with a full-on Queen's English posh accent? "Oooh I left my brolly in the loo," they say, and you respond, "But you're from Colorado!" Well, there are reasons they (and many of us) do that, and usually it's on a pretty subconscious level.
It's called "accent mirroring," and it's actually quite common with people who are neurodivergent, particularly those with ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder). According Neurolaunch, the self-described "Free Mental Health Library," "Accent mirroring, also known as accent adaptation or phonetic convergence, is the tendency to unconsciously adopt the accent or speech patterns of those around us. This linguistic chameleon effect is not unique to individuals with ADHD, but it appears to be more pronounced and frequent in this population."
Essentially, when people have conversations, we're constantly "scanning" for information—not just the words we're absorbing, but the inflection and tone. "When we hear an accent, our brains automatically analyze and categorize the phonetic features, prosody, and intonation patterns," writes Neurolaunch. For most, this does result in copying the accent of the person with whom we're speaking. But those with ADHD might be more sensitive to auditory cues. This, "coupled with a reduced ability to filter out or inhibit the impulse to mimic…could potentially explain the increased tendency for accent mirroring."
While the article explains further research is needed, they distinctly state that, "Accent mirroring in individuals with ADHD often manifests as an unconscious mimicry of accents in social situations. This can range from subtle shifts in pronunciation to more noticeable changes in intonation and speech rhythm. For example, a person with ADHD might find themselves unconsciously adopting a Southern drawl when conversing with someone from Texas, even if they’ve never lived in the South themselves."
People are having their say online. On the subreddit r/ADHDWomen, a thread began: "Taking on accents is an ADHD thing?" The OP shares, "My whole life, I've picked up accents. I, myself, never noticed, but everyone around me would be like, 'Why are you talking like that??' It could be after I watched a show or movie with an accent or after I've traveled somewhere with a different accent than my 'normal.'
They continue, "Apparently, I pick it up fast, but it fades out slowly. Today... I'm scrolling Instagram, I watch a reel from a comedian couple (Darcy and Jeremy. IYKYK) about how Darcy (ADHD) picks up accents everywhere they go. It's called ADHD Mirroring??? And it's another way of masking."
(The OP is referring to Darcy Michaels and his husband Jeremy Baer, who are both touring comedians based in Canada.)
Hundreds of people on the Reddit thread alone seem to relate. One comments, "Omfg I've done this my whole life; I'll even pick up on the pauses/spaces when I'm talking to someone who is ESL—but English is my first language lol."
Sometimes, it can be a real issue for those around the chameleon. "I accidentally mimicked a waitress's weird laugh one time. As soon as she was out of earshot, my family started to reprimand me, but I was already like 'oh my god I don’t know why I did that, I feel so bad.'"
Many commenters on TikTok were shocked to find out this can be a sign of ADHD. One jokes, "Omg, yes, at a store the cashier was talking to me and she was French. She's like 'Oh are you French too? No, I'm not lol. I'm very east coast Canada."
And some people just embrace it and make it work for them. "I mirror their words or phrase! I’m 30. I realized I start calling everyone sweetie cause my manager does & I work at coffee shop."