When writer Meera Subramanian traveled to India, she wasn't sure exactly what she'd find.
In an excerpt from her book, "A River Runs Again," she tells us what she discovered:
It was the girls who talked most passionately. Several spoke of becoming more comfortable with their bodies after having been taught what was happening to them, after resolving at least some of the mysteries of adolescence. They had lost their shyness by learning about the details of biology…
Scene from rural Bihar. Photo courtesy of Allison Joyce/Redux.
In rural Bihar — one of India's most impoverished states — Subramanian sat in a small brick one-room schoolhouse, listening to a group of local teenagers talk about their lives. One young woman in particular caught her attention...
Sobha was the most self-possessed. Her forehead was marked with a sparkly bindi that matched an S-shaped pendant hanging from her neck. She sat attentively as the others spoke, only once interjecting, “We should say the truth." But once she had the floor, she commanded the room. All distracted chatter stopped.
“'What sort of place is this?' you'll say if you come to my village. From Bodh Gaya, there's a river and a hill, and behind them is the village, like a cave. People were afraid to go inside. Even my father didn't want to stay in the village. It was claustrophobic." There had been changes, she said. Some villagers now had phones, and one road was being paved. She learned about the Pathfinder training course from village elders, who said all girls between fifteen and eighteen should attend.
Subramanian writes that Sobha and the other teenagers had just finished a three-day training on the basics of sexual health through an organization called Pathfinder International, led by two bold advocates, Pinki and Binod.
But “my situation was common in the village," [Sobha] said, “where each household might have six sisters, five sisters. So we made a group with at least one girl from each house. We took the training and then we went back home to teach others." She had to periodically gulp to catch her breath, as though she had been waiting a very long time to speak and felt the importance of each word.
Pathfinder mural in Bihar. Photo courtesy of Allison Joyce/Redux.
Sobha said she was able to get a Pathfinder poster of the life cycle of a human being passing from birth through adolescence, followed by marriage and a young couple weighing birth-control options, and later holding a child as it is being immunized. She used the poster to begin talking with others in the village. Pinki and Binod exchanged looks; they had no idea that one of their students had gone rogue and appointed herself as trainer.
When Sobha finished, Pinki asked if she would continue to work with Pathfinder to organize more training courses. Sobha eagerly agreed.
Subramanian was deeply moved by what she saw. These teenagers weren't just learning about reproductive health; they were learning to find their true voices:
We emerged from the small schoolhouse into an afternoon damp with mist. Though their hair was neatly pulled back and their clothes were modest, I saw the girls as powerful goddesses, devis eager for justice, who stepped in where the male gods were failing, determined to quietly, or not so quietly, dismantle a world that treats them as second-rate citizens.
Pinki and Binod. Photo courtesy of Allison Joyce/Redux.
As she continued her travels, Subramanian found even more reason to hope for a future of real equality and sustainability throughout India.
India is undergoing a radical test. Girls from all over South Asia are leaning in, tipping the balance, and hairline fractures are appearing in the ancient system of chauvinism. Whether sexual violence is on the rise or decline is difficult to know. Whether the aggression is men's bitter reaction to the power they perceive they are losing to women is likewise uncertain.
But what is known is that it is now news. The rise of both women and men who are unwilling to accept the status quo has been startling and encouraging. There are women who bring their daughters into the streets to protest, boys like Sanoj who fight for the rights of their sisters, men like Pinki's father who struggle to educate their daughters.
In her new book, "A River Runs Again," Subramanian writes about the real change happening — not just in Bihar, but all across the country. From villagers reviving a dead river to an engineer-turned-farmer bringing organic food to the plates of everyday Indians. And, perhaps most heartening of all, women and girls are taking the lead.
Everyone is thirsty. Girls and women, after centuries of serving tea to the men in their lives, are reaching for their own cups. I don't want to believe that power is finite. Let the teapot be topped off, let the servings be stretched. Because everyone is striving. In today's India, men and women, boys and girls, share each other's desires for what Pinki calls “self-independence."
Pathfinder training for local men in Bihar. Photo courtesy of Allison Joyce/Redux.
Maybe this is why Pathfinder has found that its trainings are substantially more effective when they teach young men and women simultaneously. It's not just about giving knowledge to the girls or teaching the boys to be respectful. It's about what arises in the ākāșa, that ethereal space between the two sexes. It's about what happens when their lives come together.
The stricter laws against rape that passed at record pace in 2013 might translate into less violence against women. And increasing government support for safety nets and social security could make aging parents less dependent on sons, helping to balance the economic scales that favor a boy child over a girl...
In a country that has historically discriminated harshly against women, both men and women are now coming together to fight for equality. Of course, there's still work to be done...
Resistance remains. Some local government officials have responded to the rash of rapes by suggesting India lower the legal age of marriage to help curb such crimes. “Boys and girls should be married by the time they turn sixteen," they argue, “so that they do not stray." In the face of such logic, the problems can seem intractable. But traditions can be lost in just a single generation. So can the beliefs that it is necessary to marry off your daughter at the onset of puberty and that it is her fault if she does not deliver a son, and do so immediately.
Pathfinder materials. Photo courtesy of Allison Joyce/Redux.
...but Subramanian has seen firsthand what happens when people defy expectations and find their own voices:
I have seen the shift in my own family. My Indian grandmother was married at the age of ten. Her four daughters were married in their late teens and twenties. My father, one of her middle sons, completely broke rank, marrying an American when he was thirty. I wasn't married until the tender age of forty-four and have chosen not to have children. Among my cousins' grown children who remain in India, arranged marriage remains the norm, but some are holding out against matches they're not willing to accept. Each generation has had fewer children than the one before it, and the levels of education for both males and females tick upward. Our population growth is stable.
But we are a family with relative means. For the vast majority of Indians still struggling to survive, larger structural changes are needed. They are within reach. Kerala once had the highest population growth in India, but since 1971 it has invested heavily in women's education, accessible family planning, and comprehensive health care. With neither threat nor coercion, the fertility rate more than halved in a single generation, from over four to under two…
Those teenagers in Bihar are part of a whole new generation. It starts with education...
To stabilize population growth is to rally for literacy, because reading and understanding words on a page develops the same skills needed to read and understand our own bodies. Through this knowledge comes power and autonomy. And speech. The girls I met in Bihar ... spoke in feisty voices, their excitement coupled with impatience as they told the stories of their lives. What they found was that learning how to speak — to a husband, a mother-in-law, a doctor, a police officer — is a powerful tool. With this transformation of a private voice into a public voice a public identity is born, one prepared to dissent and stand up for oneself.
“People ask us, 'Why do you go to these meetings? Do they give you something?'" Reena Kumari, an eighteen-year-old Bihari girl told me. “I say, 'When you go to pray, do you get something?' They say, 'Well, that one girl who did the training met a boy and ran away.'" She laughed, and continued speaking quickly, in a strong voice. “We argue back — you had her for fifteen years and they had her for three days and you're saying we influenced her?" she said.
“There is a flaw in your nurturing, not in our friendship."
“You fight back with their parents?" I asked.
...and it ends with a new generation that can speak their minds and own their futures.
“Hum bolti hain!" she said. “We speak up! Before training, we didn't know anything, but after, we do. We learned how to find the right words to negotiate. There are so many changes."
Scene from rural Bihar. Photo courtesy of Allison Joyce/Redux.
To negotiate such changes is to ask for everything you want, knowing you might only get a fraction. It is to remain unflinching as you look forward into the future of India's women and girls and the generations they will bear. The path ahead is difficult, littered with obstacles, still under construction. But I can imagine the youth I met in Bodh Gaya [in Bihar] growing up in this new India, their India, moving forward down this road… They shape the way as they go. They link their fingers, they quicken their pace, and their voices, rising up into that space between spaces, are unafraid.





 A Baby Boomer couple.via
A Baby Boomer couple.via  A Baby Boomer couple.via
A Baby Boomer couple.via 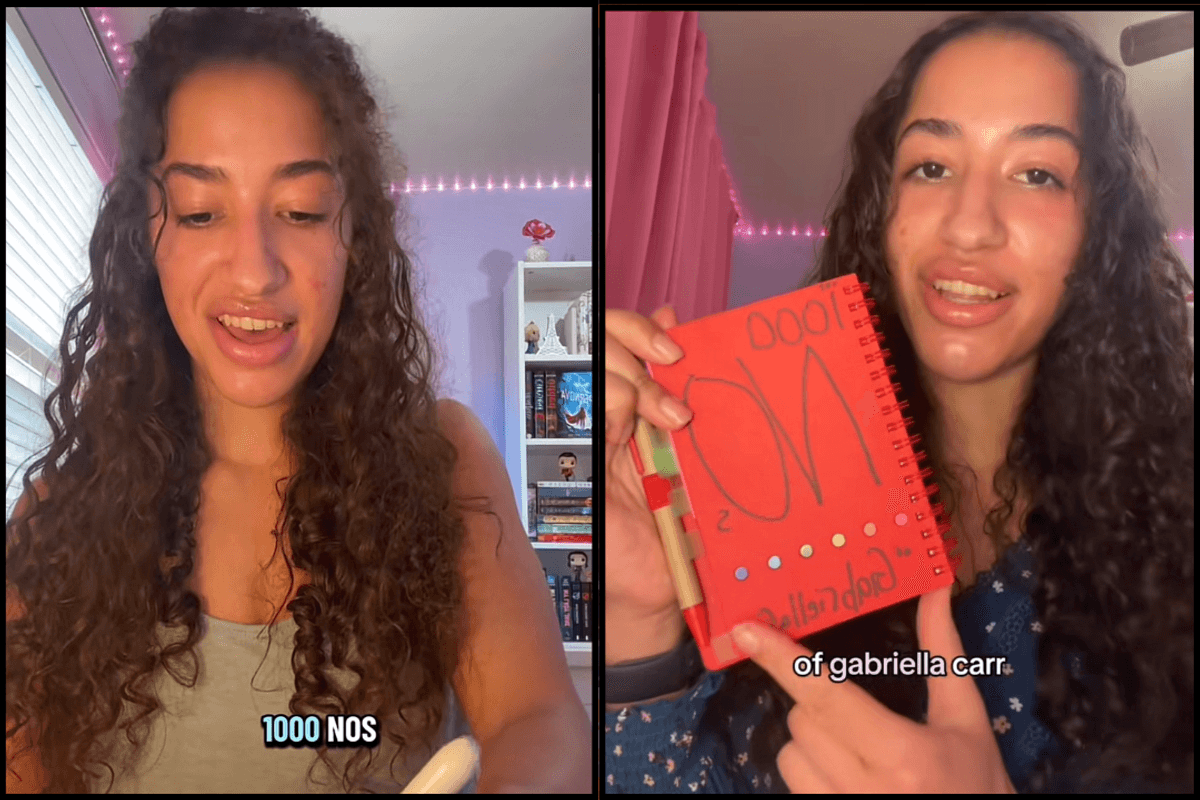
 This is where Gabrielle tracks her rejection journey.
This is where Gabrielle tracks her rejection journey. Social rejection feels just like physical pain to the brain.
Social rejection feels just like physical pain to the brain. Asking questions can be a form of bravery.
Asking questions can be a form of bravery.
 Woman working, productively.
Woman working, productively.
 An exhausted mom and her baby.
An exhausted mom and her baby. A mom yawns while feeding her baby.
A mom yawns while feeding her baby.