Mark Zuckerberg makes stunning apology to parents during Congressional testimony
"I'm sorry for everything you have all been through."

Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg.
Senators grilled the top executives from TikTok, Meta, X, Discord and Snapchat on Capitol Hill Wednesday for a U.S. Senate Judiciary hearing about the impact of social media on children. The hearing examined child sexual exploitation online and featured the testimony of children who have suffered abuse and bullying online.
The hearing was a rare time when Republicans and Democrats fought on the same side of an important issue.
"Elizabeth [Warren] and I see an abuse here that needs to be dealt with,” Republican Senator Lindsay Graham told the committee. “Senator Durbin and I have different political philosophies, but I appreciate what you've done on this committee. You've been a great partner. To all my Democratic colleagues, thank you very, very much. To my Republican colleagues, thank you all very, very much.”
“There is pretty clearly a bipartisan consensus that the status quo isn’t working,” New Mexico Attorney General Raúl Torrez told the hearing. “When it comes to how these companies have failed to prioritize the safety of children, there’s clearly a sense of frustration on both sides of the aisle.”
During the hearing, Senator Graham highlighted the story of South Carolina State House Rep. Brandon Guffey, whose son died by suicide after being a victim of sexual extortion.
When asked if he had any response to the victims whom his products have harmed, Meta’s CEO, Mark Zuckerberg, was apologetic.
"I'm sorry for everything you have all been through," Zuckerberg said. "No one should go through the things that your families have suffered, and this is why we invest so much and we are going to continue doing industry-wide efforts to make sure no one has to go through the things your families have had to suffer."
At one point, Zuckerberg stood up and faced a group of parents who were holding pictures of their children who were victims of online harassment.
We’re dealing with a fundamental decision as to whether social media companies should be able to face lawsuits like any other company in America.
Senate Majority Whip Dick Durbin was clear that he believes social media companies are a significant cause of many of the problems facing America’s youth. “They’re responsible for many of the dangers our children face online,” Durbin said in his opening statements. “Their design choices, their failures to adequately invest in trust and safety, their constant pursuit of engagement and profit over basic safety have all put our kids and grandkids at risk.”
The tech CEOs continuously touted their companies’ online safety features throughout the hearing. Zuckerberg noted that Meta spent $5 billion on security and safety in 2023.
Graham suggested that Congress work to repeal Section 230 which would give social media companies greater accountability. The federal law protects social media companies from being responsible for lawsuits arising from user-generated content.
“You have a product that’s killing people ... You can’t be sued, you should be!” Graham said. “It is now time to repeal Section 230.”
The purpose of the hearing was to work toward legislation that would make social media safer for young people. But it’s unclear whether the hearings will result in anything meaningful.


 A UPS truck with package deliveries.Image via Wikipedia
A UPS truck with package deliveries.Image via Wikipedia
 Cher was the biggest phenomenon on the planet for the better part of the '70s and '80s.Casblanca Records/
Cher was the biggest phenomenon on the planet for the better part of the '70s and '80s.Casblanca Records/

 A high school volunteer with her senior "tandem."
A high school volunteer with her senior "tandem."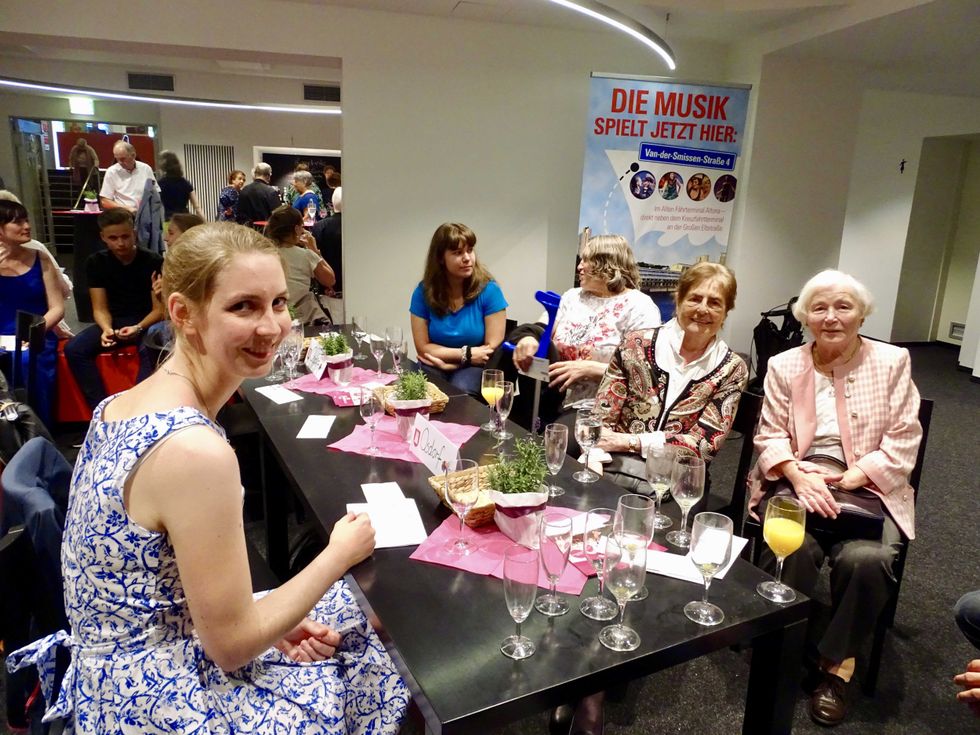  KH2 makes leaving the house more accessible to senior citizens.
KH2 makes leaving the house more accessible to senior citizens.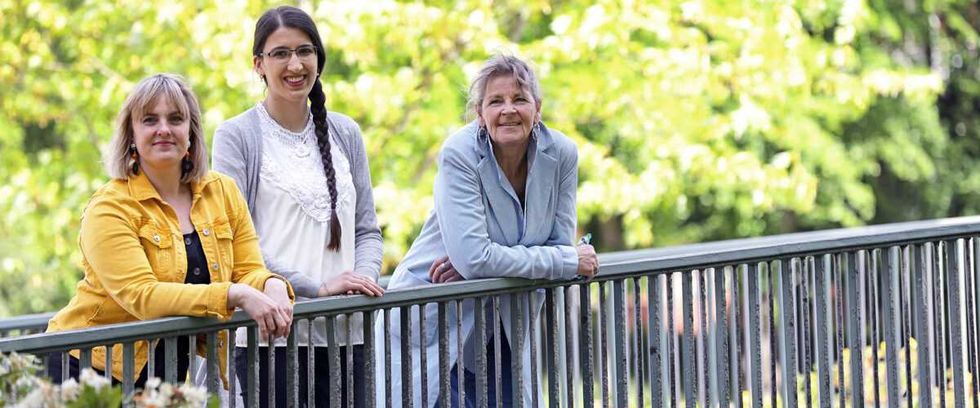  Many "culture buddies" stay in contact after the program ends.
Many "culture buddies" stay in contact after the program ends.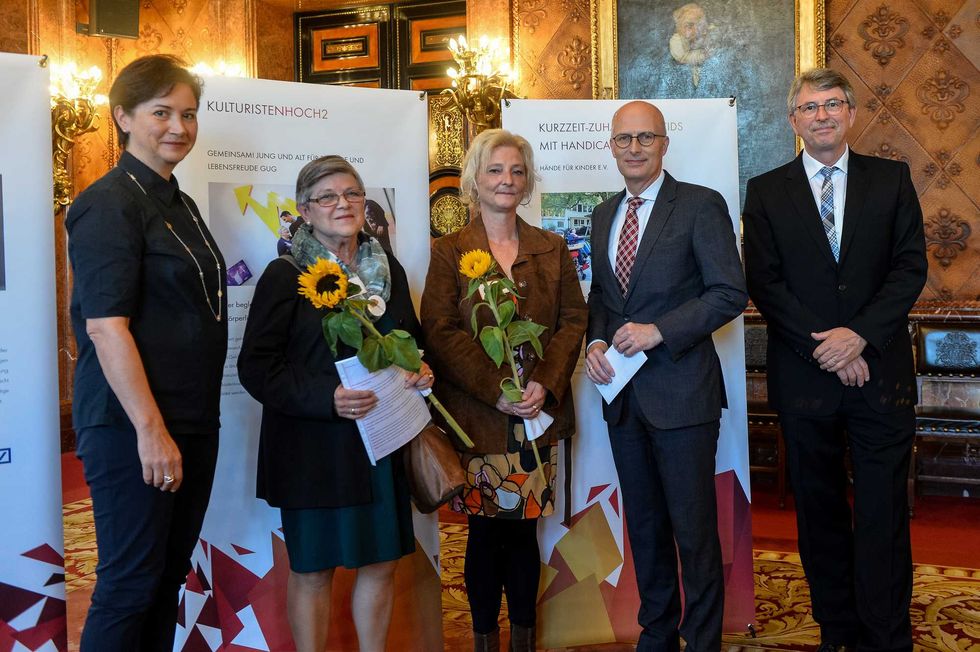  KH2 provides students with excellent life skills and lasting connections.
KH2 provides students with excellent life skills and lasting connections.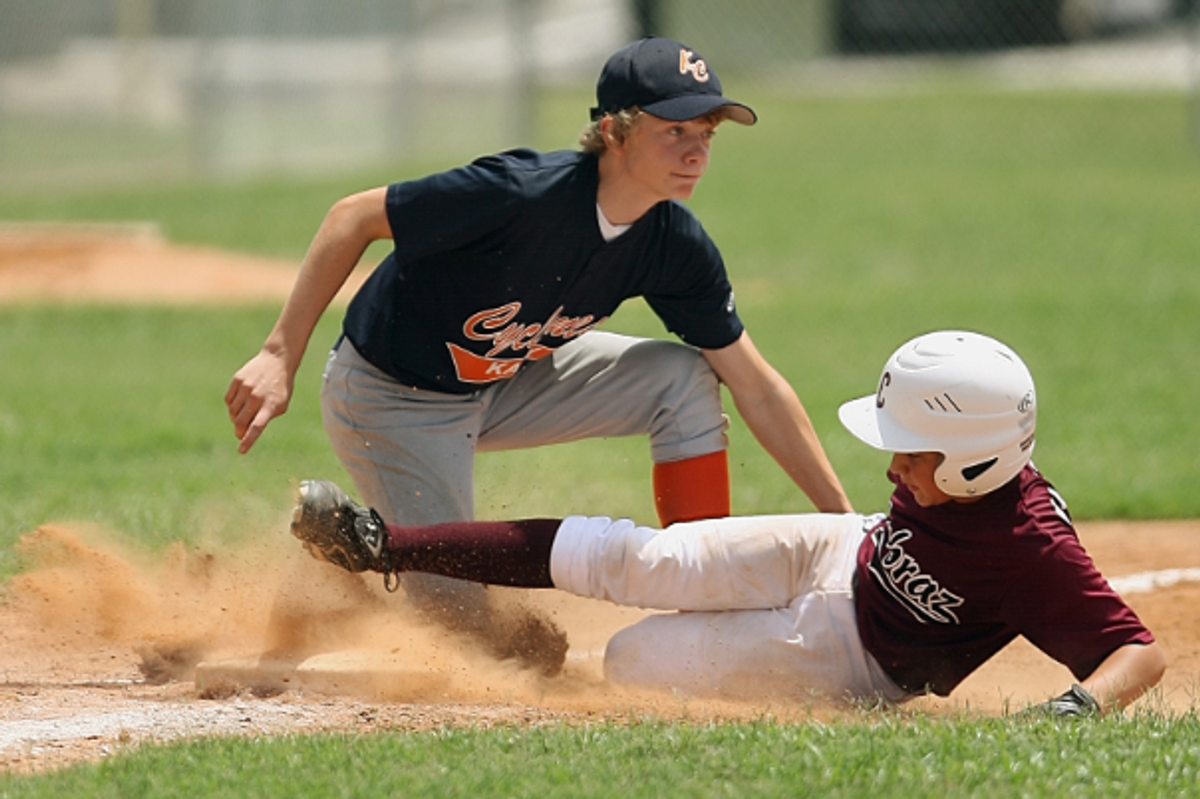 
 Parents posing with their young kids on a basketball court. via
Parents posing with their young kids on a basketball court. via