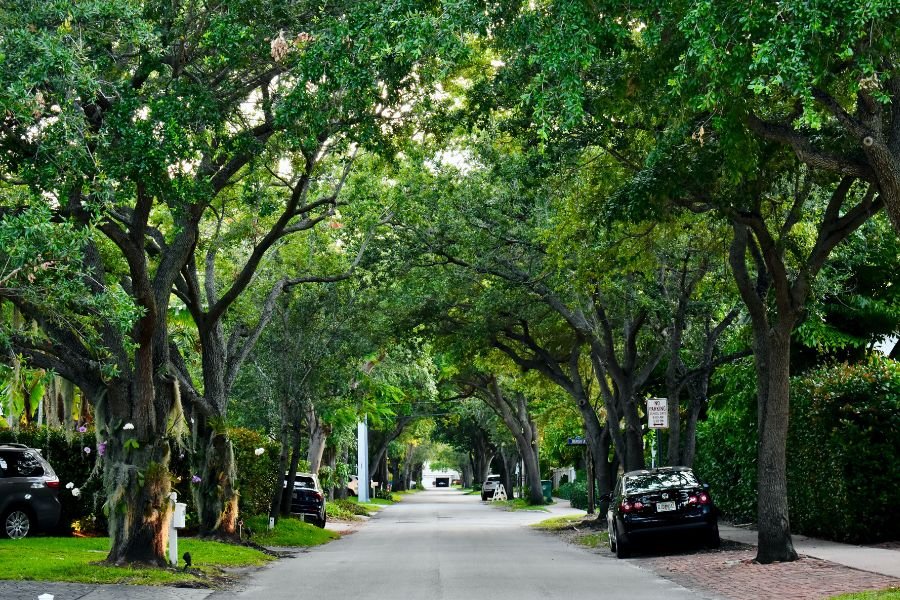
When we talk about environmental justice, we usually talk about how vulnerable communities are disproportionately impacted by things like contaminated water, air pollution, toxic living conditions and lack of access to healthy food. We aren’t usually referring to about how many trees someone has around them on a regular basis, but a push for “tree equity” indicates that maybe we should.
That’s right, tree equity. It’s a real thing.
The impact that trees have on our daily lives is significant. Not only do trees provide natural beauty that brings us joy and comfort, but they absorb carbon dioxide and other air pollutants, release oxygen, provide cooling shade, filter drinking water and support wildlife. Being near trees helps us live healthier lives in various ways, but some people see more of these benefits than others.
In fact, according to the non-profit group American Forests, wealthy areas have 65% more tree cover than lower-income areas nationwide in the U.S., and it’s especially an issue in our cities.
“The inequitable distribution of trees exacerbates social inequities,” American Forests shares on its website. “A map of tree cover is too often a map of income and race—especially in cities. That’s because trees often are sparse in low-income neighborhoods and some neighborhoods of color. In fact, policies from the early 1900s are still shaping the way redlining contributes to periods of disinvestment, exacerbating tree inequity in these neighborhoods.”
The “tree equity” project aims to minimize these disparities so that everyone can reap the health, economic and other benefits trees provide. Through calculating a “tree equity score” derived from tree canopy cover, climate, demographic and socioeconomic data in 486 Census-defined Urbanized Areas, the project aims to prioritize planting trees in neighborhoods that need them the most.
And cities are stepping up to the plate. Washington, D.C., now boasts an overall tree equity score of 91 out of 100—one of the best in the nation—but it took concerted, sustained effort to get there. Decades of disinvestment in the 70s and 80s led to a profound reduction in tree cover in the city, and by the late 1990s, the impact of that disinvestment was clear. In 1999, the Washington Post’s Metro section shared two aerial photos of the city, one from 1973 and one from 1997, showing how the landscape had changed over that time and people were shocked.
“The story needed no words,” shares American Forests. “From the perspective of the 30-meter resolution available at the time, one image was predominantly green, the other looked like a tornado had ripped through a majority of the nation’s capital.”
The stark difference between those images sparked a citywide conversation about priorities, and a push for more vegetation ensued. The city created an Urban Forestry Administration with a robust budget for getting the city’s tree canopy thriving. And according to D.C.’s current tree equity score, it has worked.
On the other side of the country, the other Washington is also investing in trees, which may seem ironic considering its nickname as The Evergreen State and Seattle’s “Emerald City” moniker. Trees have always been a big part of Washington’s identity, but that doesn’t mean its overall tree equity score is good. The interactive tree equity score map shows neighborhoods around Seattle ranging from a perfect score—100 out of 100—all the way down to 16 out of 100.
According to Grist, Washington has initiated the nation’s first statewide tree equity project, the Washington Tree Equity Collaborative, bringing together city governments, Native tribes, community groups, businesses and researchers to expand the tree canopy in Washington’s urban areas with a focus on underserved populations.
Washington’s commissioner of public lands Hillary Franz said in a statement, “We must invest like never before, in order to ensure our most vulnerable communities have cleaner air and are better protected from extreme heat.”
Grist offers a specific example of tree inequity in Seattle: Wealthy neighborhoods along Puget Sound and Lake Washington tend to have a lot of trees, while lower-income areas of south Seattle do not. Some communities will naturally have more trees due to proximity to water or natural topography, of course, but an analysis from Seattle’s Office of Planning and Community Development found that the most disadvantaged communities have been losing tree coverage 11 times faster than the least disadvantaged. That’s an equity issue.
With climate change leading to more deadly heat waves in the American West, trees have become even more vital. The shade provided by trees can lower surface temperatures by double digits, and the evaporative properties of tree leaves can lower overall temperatures by as much as 9 degrees Fahrenheit. Lowering temperatures reduces energy use, which in turn helps lower pollution and increase air quality and even helps reduce the costs of street pavement maintenance since excessive heat makes pavement break down more quickly.
Of coure, the flip side of thee relationship between climate change and trees is that extreme weather events put a lot of stress on trees. Heat waves, droughts, strong storms, fires—not exactly ideal conditions for trees to thrive in overall. Even in areas where climate change may appear to be having a positivite impact on tree growth, researchers have found that pollution and higher temperatures are making trees larger, but weaker.
There’s no question, however, that planting more trees is a good thing. Seattle’s current plan will see three new trees planted for every healthy, site-appropriate tree removed from city property and two trees planted for every tree that dies or is deemed hazardous or invasive. And over the next five years, the city plans to plant 8,000 trees on public and private properties and 40,000 trees in parks and natural areas, with underserved communities being prioritized.
We all deserve the benefits trees have to offer. To learn more about tree equity and projects to build more tree cover and find out how you can help, visit the American Forests website.