These 14 photos of beautiful American wildlife remind us why we need to protect them.
When you think of an endangered species, what comes to mind?
African elephants or wild tigers in India? What about pandas in China?
But the truth is, we don’t have to look that far away to find endangered and vulnerable animal species. We have a bunch right here at home in the U.S. And a lot of them are threatened with extinction because of the things that we do to them, like build roads through their habitats or pollute the places where they live.
A Florida panther in a tree. Photo by Mark Lotz/Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission/Flickr.
Since 1973, these animals have enjoyed some protections thanks to the Endangered Species Act (ESA). Over 1,600 vulnerable plant and animal species in the United States are covered by this federal law, which provides for their conservation and protection by restricting human activities that threaten them and making it a crime to harm or kill one of the species on the list.
Since it was signed into law, the ESA has helped several species recover — including the bald eagle, which was removed from the endangered species list in 2007 because its population had sufficiently recovered.
Photo via the U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service Midwest/Flickr.
The law also benefits people because when it protects animals and their habitats, it helps provide us with clean air and water too.
So, what are some of the North American animals under threat today and what is being done to help protect them?
Here are just a few of the animals on that list:
1. The gray wolf was mostly exterminated from the lower 48 states because humans hunted and killed them out of fear or to protect livestock.
Today, conservationists are working to help wolf populations recover in a few places — reintroduction projects have helped return wolves to some of their former homes.
2. Loggerhead sea turtles are the most common marine turtle species seen in U.S. waters, but they're threatened by pollution, shrimp trawling, and development in their nesting areas.
Photo via iStock.
3. The black-footed ferret is the only ferret native to North America but there are only about 370 left in the wild.
Photo via U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service.
They are one of the most endangered carnivore species in the world because of disease, lack of habitat, and because humans poisoned their number one prey — prairie dogs. Once thought to be completely extinct, they were brought back with captive-breeding efforts.
4. The Florida panther once lived in the woodlands and swamps of the Southeast. Today, it is one of the most endangered mammals on Earth with only 100 left in the wild.
The panther's population was decimated after European settlers arrived in the 1600s because they destroyed and fragmented its habitat. The Florida panther is considered an "umbrella species" because protecting this apex predator also keeps its ecosystem healthy and balanced.
5. The North Atlantic right whale gets its name because it was once considered the "right" whale to hunt.
This whale species lives along the Atlantic coast of North America and is still one of the most endangered whale species in the world, even though it has been protected from whaling since the 1930s. Today, it is threatened by ship collisions, entanglement in fishing nets, and ocean noise.
6. The San Joaquin kit fox is a tiny fox — about the size of a domestic cat — and it is one of the most endangered animals in California.
They were once relatively common in California, but after a lot of their grassland habitat was converted into farms and orchards, their population declined. Today, only about 7,000 remain.
7. The piping plover is a small shore bird that lives along the Atlantic and Gulf coasts, as well as in the northern Great Plains.
Photo via iStock.
Piping plovers are very sensitive to the presence of humans and too much disturbance on the beach can cause them to abandon their nests. They are also threatened by habitat loss and predators.
8. The Columbia Basin pygmy rabbit is found only in the state of Washington, where its sagebush habitat has been mostly converted to agricultural land or destroyed by human developments.
9. Pronghorns have the longest land migration in North America but this migration is endangered. They are also the fastest land animal on the continent but they are experiencing increasing run-ins with humans and property developments. And two subspecies of pronghorn are already listed on the ESA.
Photo via iStock
10. California condors are the largest bird in North America, with average wingspans of nine-and-a-half feet. For most of the 20th century, their population declined so quickly, they almost went completely extinct.
Photo via iStock.
Many of the birds were killed by poison ingestion and illegal egg collection — which can be devastating because they only lay one egg every two years. At the lowest point, in 1987, their numbers dropped to only 10 birds. Today, thanks to captive breeding, there about 127 birds in the wild — but their fate is still uncertain.
11. The whooping crane is the tallest bird in North America and it is critically endangered.
Photo via iStock.
In the 1800s and 1900s, the species was almost wiped out by habitat loss and hunting — and by 1941, only 15 birds remained. Conservationists worked with local, federal, and international governments to try to save the species, and while they aren't out of the woods just yet, their numbers are slowly growing.
12. Monarch butterflies spend most of their lives migrating across North America, and this journey has become more dangerous for them over recent years.
Photo via bark/Flickr.
Illegal logging, deforestation, agriculture, forest fires, climate change, and increased development all pose threats to this butterfly's migration. Despite the fact that the population of monarch butterfly has declined by 80%, it is not currently protected by the ESA — though the U.S. Fish & Wildlife Service is in the process of determining whether that will soon change.
These are just a few of the many endangered or threatened wildlife species in North America — and if they are going to continue to survive, they need our help.
They need laws, like the ESA, to protect them, they need scientists working on conservation efforts to keep them alive, and perhaps most importantly, they need support and engagement from people to help work toward their recovery.
There has been a lot of pressure lately to weaken federal wildlife protection laws like the ESA or to de-list animals before they are fully recovered. If laws are weakened, if conservation budgets are cut, or if policy falls short, it will become even more important for us to step up and take preservation into our own hands to make sure that these animals stay safe. After all, without us, they could go extinct.
But with an engaged and informed public, we can keep fighting the good fight to protect these species for generations to come.
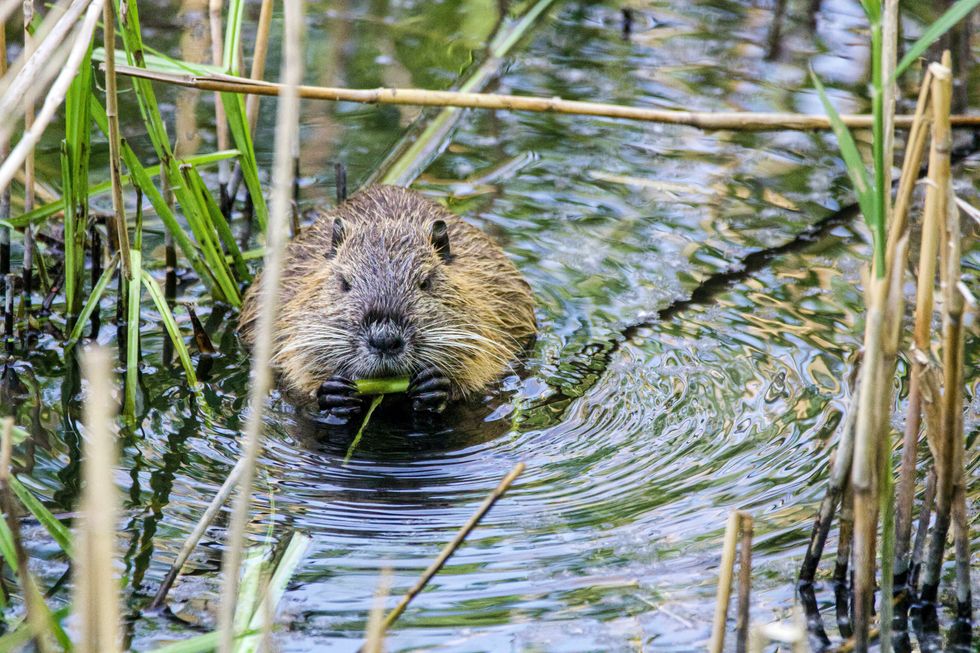





 Beaver in water. Photo by
Beaver in water. Photo by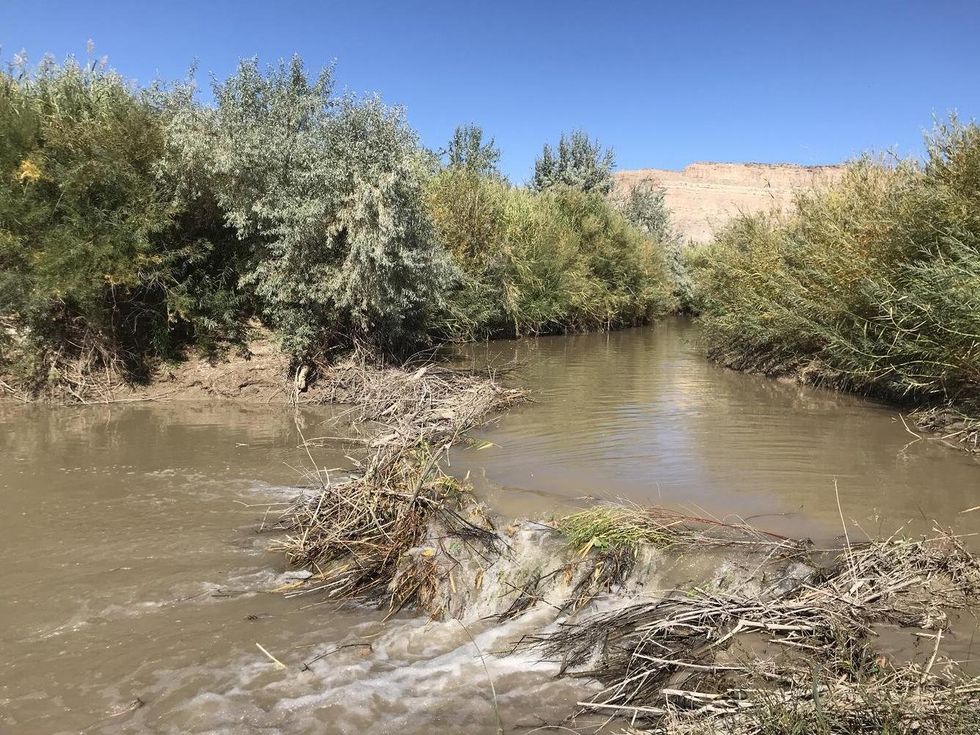  An actual beaver dam on the now-thriving Price River
An actual beaver dam on the now-thriving Price River Simpsons Gif
Simpsons Gif Aging happens in bursts, scientists find.
Aging happens in bursts, scientists find. Research shows the body goes through specific changes in our 40s and 60s.
Research shows the body goes through specific changes in our 40s and 60s.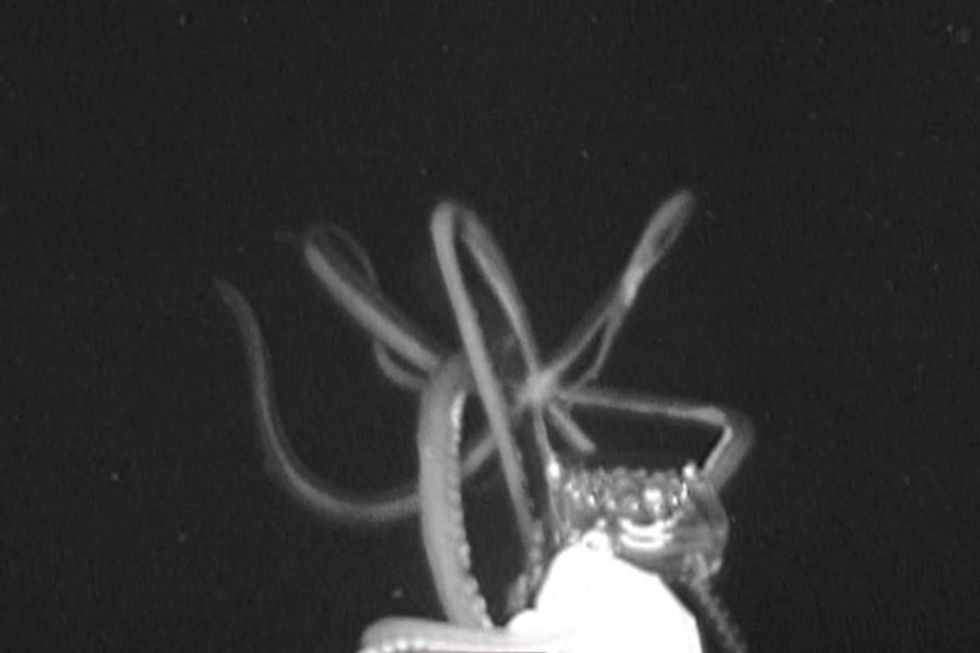 Medusa image of giant squid in Gulf of Mexico off of Mississippi Gulf CoastPhoto credit:
Medusa image of giant squid in Gulf of Mexico off of Mississippi Gulf CoastPhoto credit: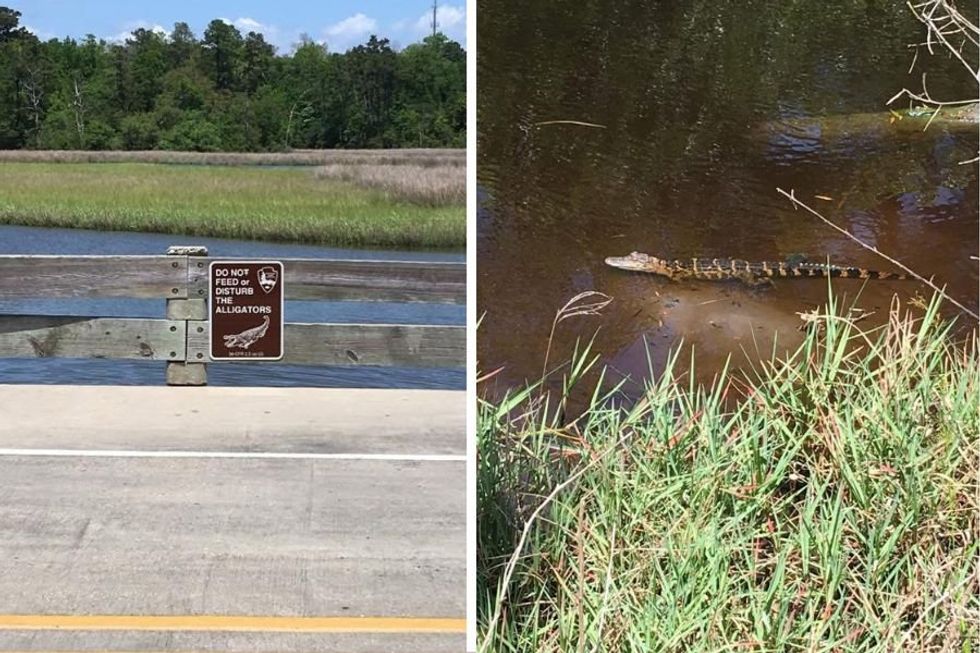  Sign warning against feeding alligators next to alligator in Mississippi marshlandsCourtesy of Jacalyn Wetzel
Sign warning against feeding alligators next to alligator in Mississippi marshlandsCourtesy of Jacalyn Wetzel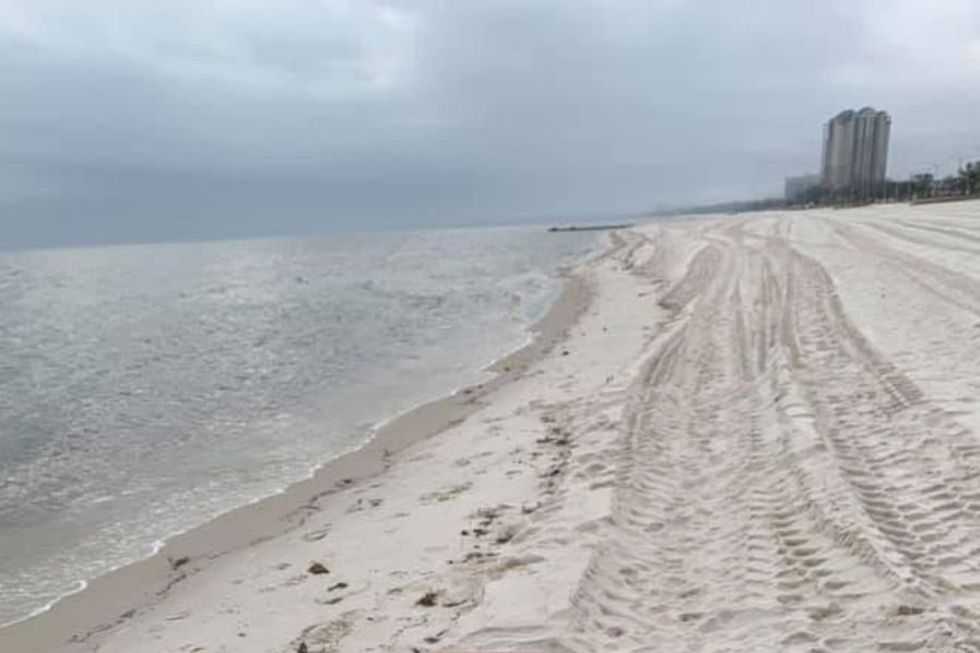 Mississippi Gulf Coast beach in BiloxiCourtesy of Jacalyn Wetzel
Mississippi Gulf Coast beach in BiloxiCourtesy of Jacalyn Wetzel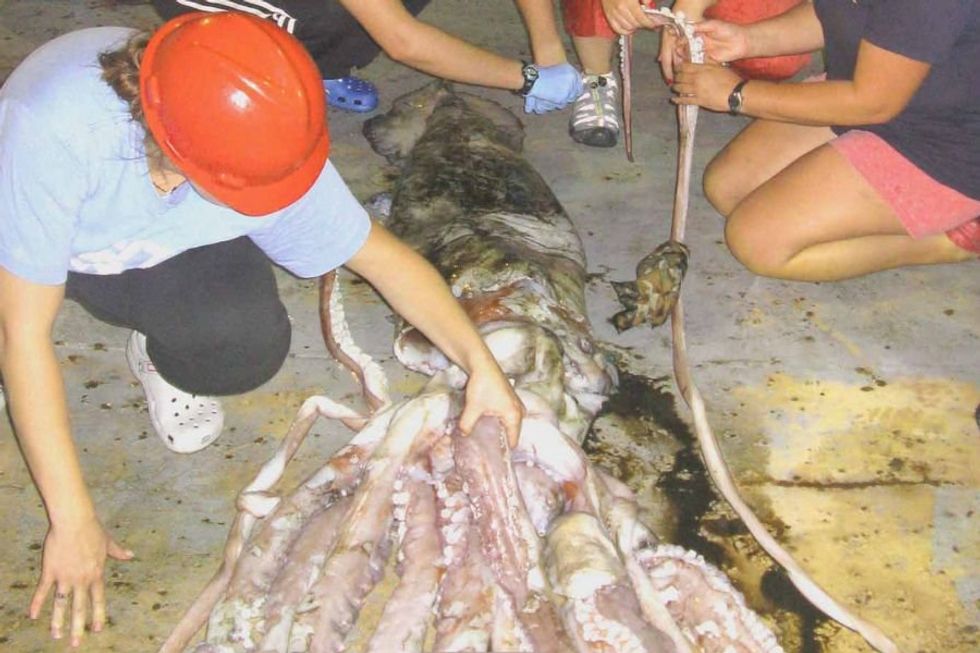 2009 photo of giant squid caught in Gulf of Mexico near Mississippi GulfPhoto credit:
2009 photo of giant squid caught in Gulf of Mexico near Mississippi GulfPhoto credit:
There's a reason why some people can perfectly copy accents, and others can't
Turns out, there's a neurodivergent link.
A woman in black long sleeve shirt stands in front of mirror.
Have you ever had that friend who goes on vacation for four days to London and comes back with a full-on Queen's English posh accent? "Oooh I left my brolly in the loo," they say, and you respond, "But you're from Colorado!" Well, there are reasons they (and many of us) do that, and usually it's on a pretty subconscious level.
It's called "accent mirroring," and it's actually quite common with people who are neurodivergent, particularly those with ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder). According Neurolaunch, the self-described "Free Mental Health Library," "Accent mirroring, also known as accent adaptation or phonetic convergence, is the tendency to unconsciously adopt the accent or speech patterns of those around us. This linguistic chameleon effect is not unique to individuals with ADHD, but it appears to be more pronounced and frequent in this population."
Essentially, when people have conversations, we're constantly "scanning" for information—not just the words we're absorbing, but the inflection and tone. "When we hear an accent, our brains automatically analyze and categorize the phonetic features, prosody, and intonation patterns," writes Neurolaunch. For most, this does result in copying the accent of the person with whom we're speaking. But those with ADHD might be more sensitive to auditory cues. This, "coupled with a reduced ability to filter out or inhibit the impulse to mimic…could potentially explain the increased tendency for accent mirroring."
While the article explains further research is needed, they distinctly state that, "Accent mirroring in individuals with ADHD often manifests as an unconscious mimicry of accents in social situations. This can range from subtle shifts in pronunciation to more noticeable changes in intonation and speech rhythm. For example, a person with ADHD might find themselves unconsciously adopting a Southern drawl when conversing with someone from Texas, even if they’ve never lived in the South themselves."
People are having their say online. On the subreddit r/ADHDWomen, a thread began: "Taking on accents is an ADHD thing?" The OP shares, "My whole life, I've picked up accents. I, myself, never noticed, but everyone around me would be like, 'Why are you talking like that??' It could be after I watched a show or movie with an accent or after I've traveled somewhere with a different accent than my 'normal.'
They continue, "Apparently, I pick it up fast, but it fades out slowly. Today... I'm scrolling Instagram, I watch a reel from a comedian couple (Darcy and Jeremy. IYKYK) about how Darcy (ADHD) picks up accents everywhere they go. It's called ADHD Mirroring??? And it's another way of masking."
(The OP is referring to Darcy Michaels and his husband Jeremy Baer, who are both touring comedians based in Canada.)
Hundreds of people on the Reddit thread alone seem to relate. One comments, "Omfg I've done this my whole life; I'll even pick up on the pauses/spaces when I'm talking to someone who is ESL—but English is my first language lol."
Sometimes, it can be a real issue for those around the chameleon. "I accidentally mimicked a waitress's weird laugh one time. As soon as she was out of earshot, my family started to reprimand me, but I was already like 'oh my god I don’t know why I did that, I feel so bad.'"
Many commenters on TikTok were shocked to find out this can be a sign of ADHD. One jokes, "Omg, yes, at a store the cashier was talking to me and she was French. She's like 'Oh are you French too? No, I'm not lol. I'm very east coast Canada."
And some people just embrace it and make it work for them. "I mirror their words or phrase! I’m 30. I realized I start calling everyone sweetie cause my manager does & I work at coffee shop."