What the world looks like if all the land ice melts
These maps show the shocking answer to a terrifying "what if" scenario.
A map imagining what the United States would look like partially covered in water
Land ice: We got a lot of it. Considering the two largest ice sheets on earth — the one on Antarctica and the one on Greenland — extend more than 6 million square miles combined ... yeah, we're talkin' a lot of ice. But what if it was all just ... gone? Not like gone gone, but melted?
If all of earth's land ice melted, it would be nothing short of disastrous. And that's putting it lightly. This video by Business Insider Science (seen below) depicts exactly what our coastlines would look like if all the land ice melted. And spoiler alert: It isn't great. Lots of European cities like, Brussels and Venice, would be basically underwater.
I bring up the topic not just for funsies, of course, but because the maps are real possibilities.

How? Climate change.
As we continue to burn fossil fuels for energy and emit carbon into our atmosphere, the planet gets warmer and warmer. And that, ladies and gentlemen, means melted ice.
A 2015 study published by researchers in the U.S., U.K., and Germany found that if we don't change our ways, there's definitely enough fossil fuel resources available for us to completely melt the Antarctic ice sheet.
Basically, the self-inflicted disaster you see above is certainly within the realm of possibility.
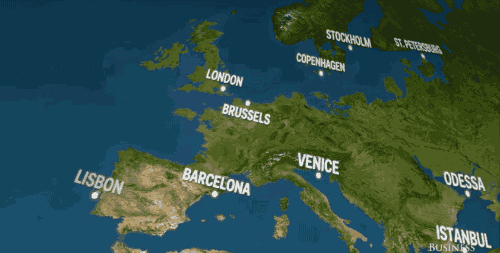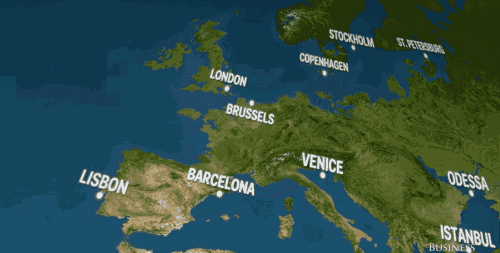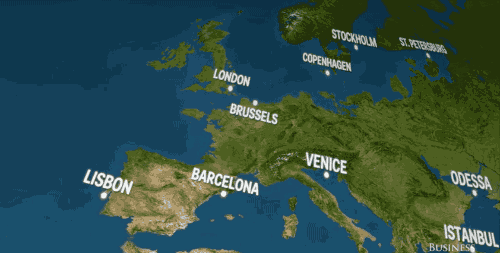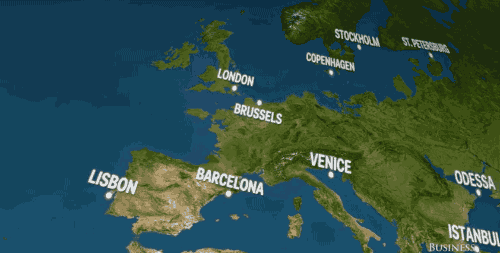
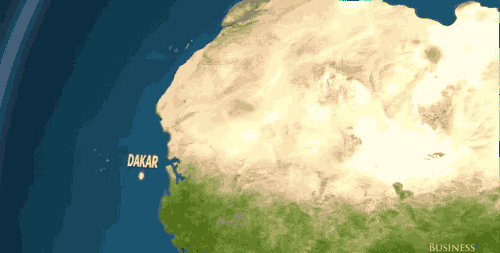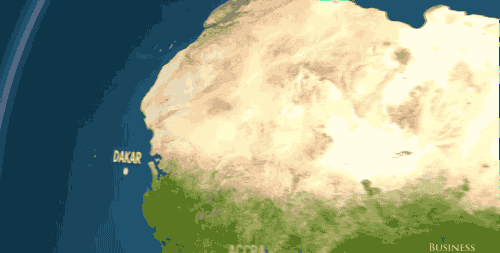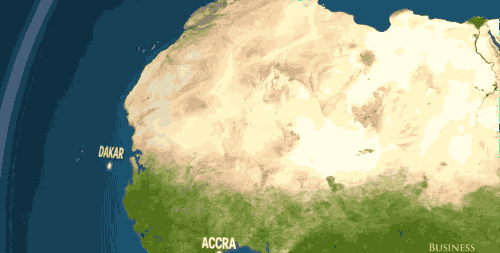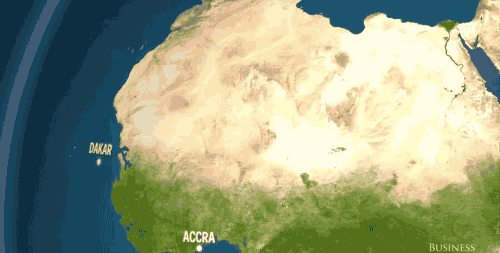
In Africa and the Middle East? Dakar, Accra, Jeddah — gone.
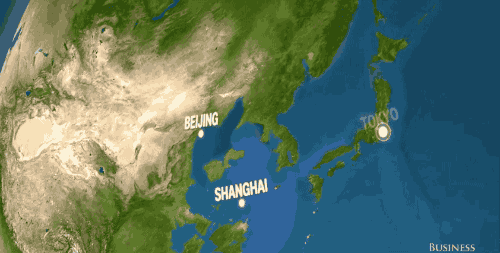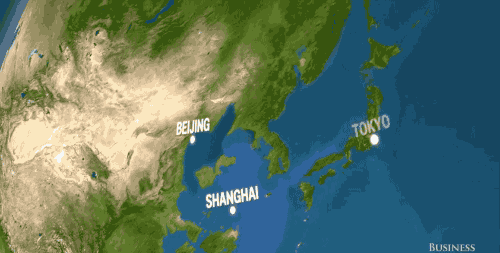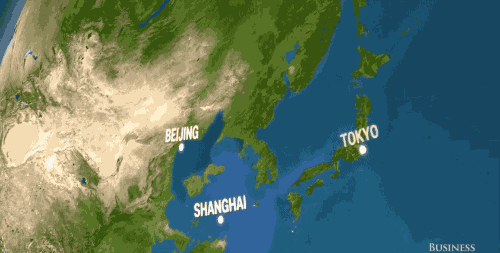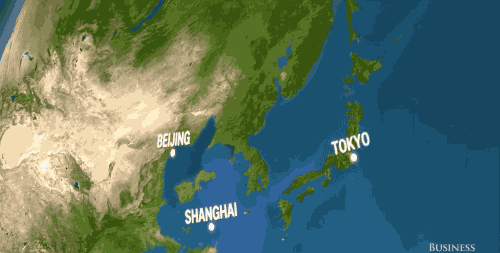
Millions of people in Asia, in cities like Mumbai, Beijing, and Tokyo, would be uprooted and have to move inland.
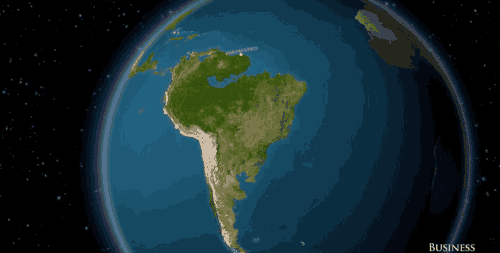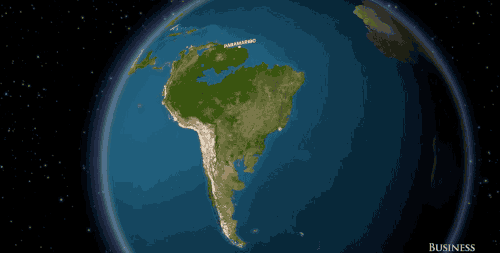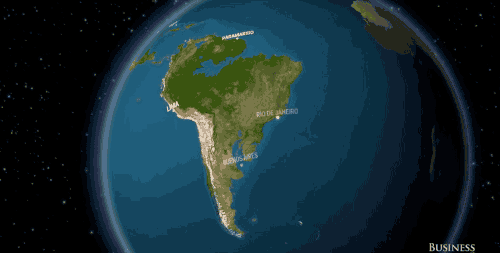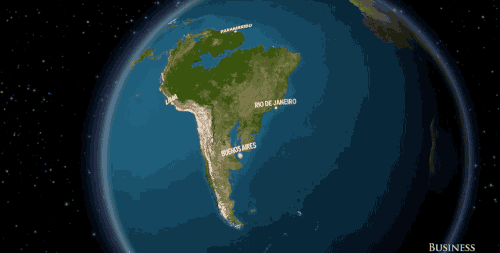
South America would say goodbye to cities like Rio de Janeiro and Buenos Aires.
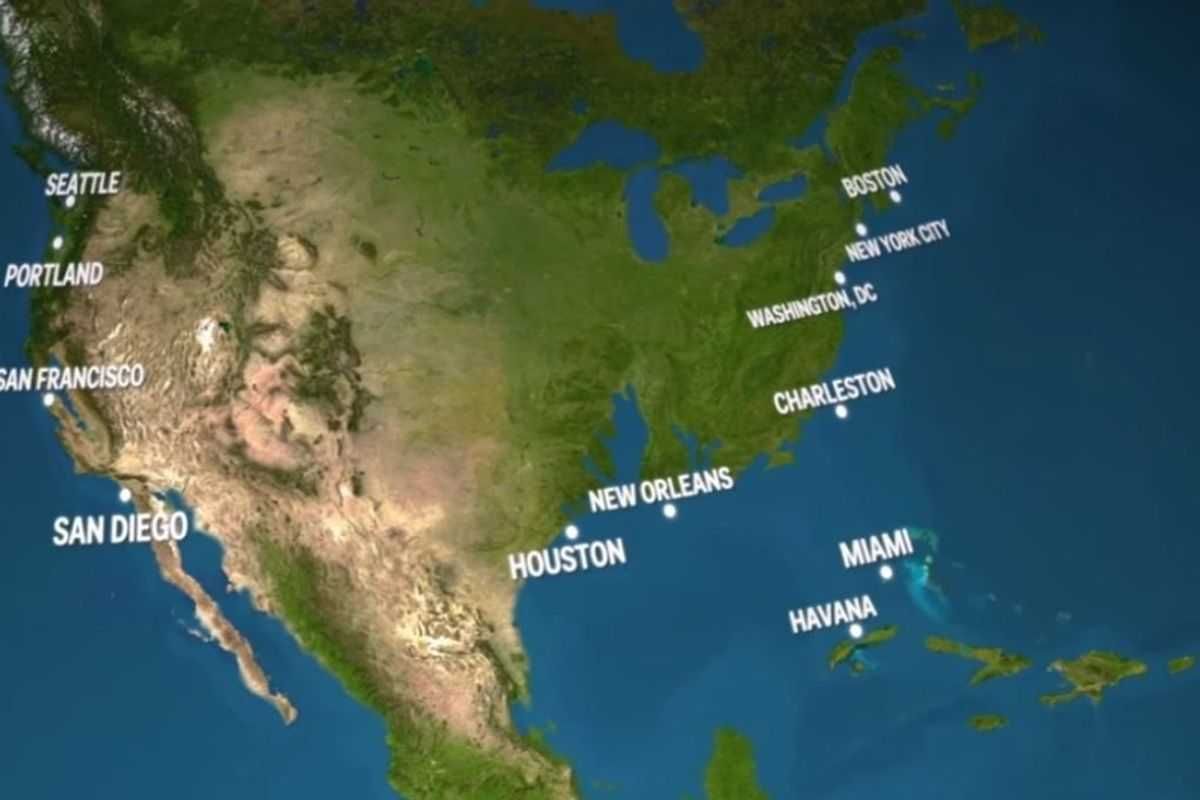
And in the U.S., we'd watch places like Houston, San Francisco, and New York City — not to mention the entire state of Florida — slowly disappear into the sea.
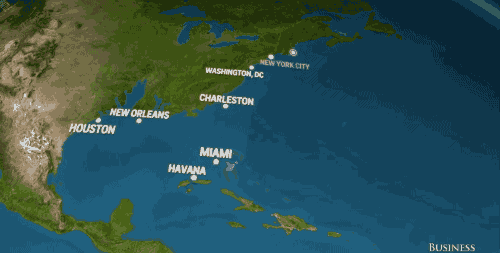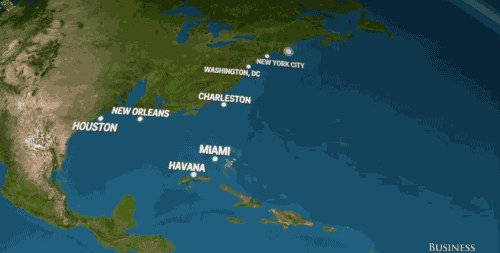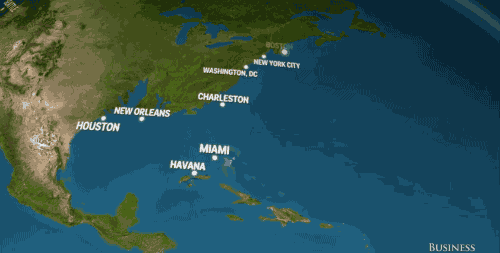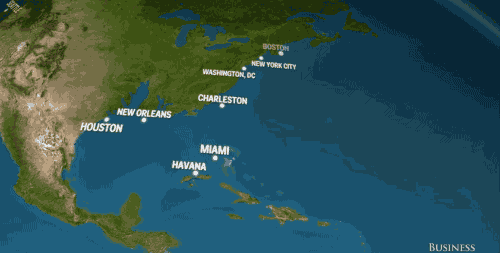
Business Insider based these visuals off National Geographic's estimation that sea levels will rise 216 feet (!) if all of earth's land ice melted into our oceans.
There's even a tool where you can take a detailed look at how your community could be affected by rising seas, for better or worse.
Although ... looking at these maps, it's hard to imagine "for better" is a likely outcome for many of us.
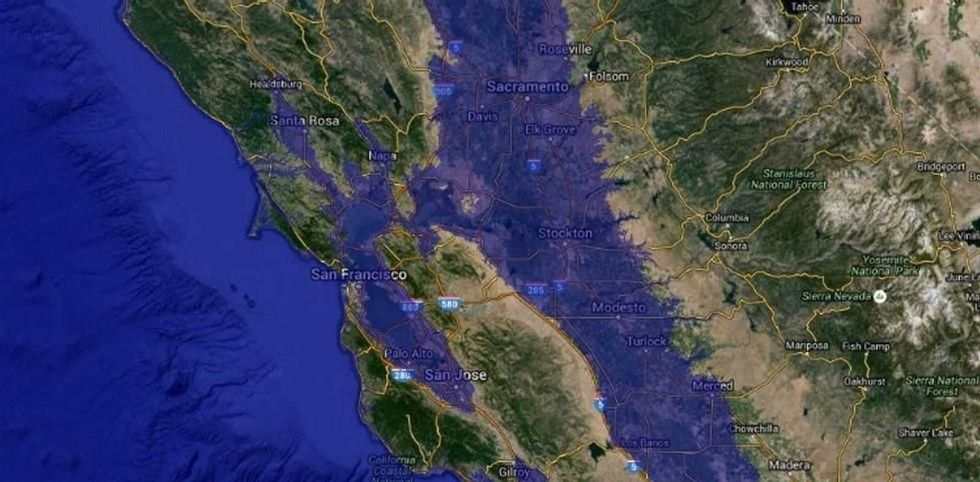
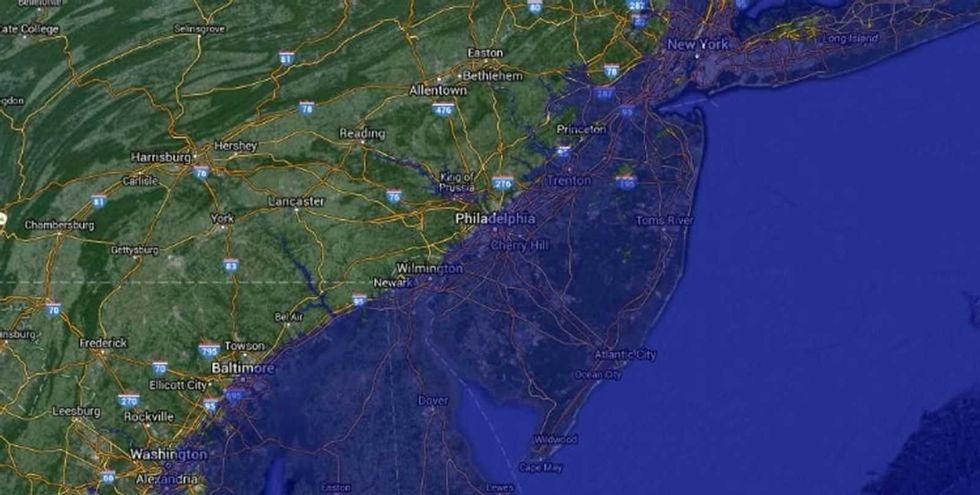
Much of America's most populated regions would be severely affected by rising sea levels, as you'll notice exploring the map, created by Alex Tingle using data provided by NASA.
Take, for instance, the West Coast. (Goodbye, San Fran!)
Or the East Coast. (See ya, Philly!)
And the Gulf Coast. (RIP, Bourbon Street!)
"This would not happen overnight, but the mind-boggling point is that our actions today are changing the face of planet Earth as we know it and will continue to do so for tens of thousands of years to come," said lead author of the study Ricarda Winkelmann, of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research.
If we want to stop this from happening," she says, "we need to keep coal, gas, and oil in the ground."
The good news? Most of our coastlines are still intact! And they can stay that way, too — if we act now.
While world leaders have made pledges and set goals since this article first appeared, the crisis remains. You can help get the point across to them, too.
Check out Business Insider's video below:
climate change, sea level rise, global warming, antarctica, greenland, environment, viral video, science Business Insider Science/YouTube
This article originally appeared eleven years ago.