The 3 reasons you freeze in the middle of conversation, and how to fix it
This can be especially helpful in the workplace.

Business meeting in progress with focused discussion.
We’ve all been there: sitting in a meeting or group conversation, following along intently…until suddenly someone turns to you with a question. And just like that *poof* your brain pulls the ripcord. The words disappear, our mind goes blank, and whatever comes out of our mouths is a jumble of half-formed sentences held together by pure panic. That’s if anything comes out at all!
It’s embarrassing, yes. But more importantly, it can be discouraging, especially in professional settings where confidence and clarity matter.
Thankfully, communication expert Vinh Giang has an incredibly human (and surprisingly science-backed) explanation for why this happens, along with practical tools we can use to stay calm and speak clearly when it counts.
Cognitive Overload

Your “working memory,” aka the part of your brain that holds onto present moment information, can only maintain about four to seven pieces of different information at a time. In a work meeting, you’re likely already mentally juggling multiple elements—what’s being discussed, filtering what’s relevant, observing and interpreting body language, etc.—and the sudden “extra demand" of now answering a question can push your working memory past its limit, explains Giang.
Fight, Flight, or Freeze

This nervous system response is the biological next step after cognitive overload. When you are put on the spot, and the adrenaline/heart rate/cortisol starts pumping, no resources go towards the part of your brain that helps you think clearly (prefrontal cortex). Instead, everything in your amygdala (the brains’ “alarm system,” as Giang put it) kicks in and causes you to treat the situation like a life-threatening event. So you freeze up the same way you might if you run into a grizzly bear.
On the other hand, you might go into “fight” mode, which in this case, looks a lot like rambling. Also not good.
No Retrieval Cue

Retrieval cues are external or internal triggers that bring back a long term memory. A special candle that smells just like your grandma's lotion, for example, or feeling sad can trigger memories of other times you were sad.
When a question is thrown at you, you don’t necessarily get one of these cues, and your brain scrambles for where to begin.
“It’s like digging through your backpack stuffed with loose papers. All the information is there, but with everyone watching and the clock ticking, you can't seem to find the right page so you fumble,” says Giang.
The biggest takeaway here isn’t that you don’t have the information you need to clearly express yourself, you just don’t have a system for organizing the plethora of information swirling around inside of you. And for that Giang suggested using the PREP (point, reason example, point) framework, which is as follows:
- Point: One main or opinion that kicks things off.
- Reason: Just one explanation as to why you hold that point or believe it is true, using justifications and evidence.
- Example: Data, a story, or concrete illustration to support your reasoning and make your point more persuasive.
- Point: Reiterating your original main point to reinforce your message and provide a strong conclusion.
- YouTube www.youtube.com
Not only this, but giving yourself a second to pause, breathe, and take in the question, repeating or reframing the question to yourself, and slowing down your speech as you answer can be incredibly helpful in clear, concise communication.
At the end of the day, blanking out doesn’t mean you’re unprepared or incapable. It's a sign your brain is working overtime. The good news is you only need a few simple adjustments to turn those high-pressure moments into opportunities for clarity.







 A woman reading a book.via
A woman reading a book.via A woman tending to her garden.via
A woman tending to her garden.via
 "The Magic Words" is a book of poetry prompts from Joseph Fasano.
"The Magic Words" is a book of poetry prompts from Joseph Fasano.  People with dementia are still themselves deep down.
People with dementia are still themselves deep down.  Caregivers try many different ways to communicate with people living with dementia.
Caregivers try many different ways to communicate with people living with dementia.
 Cats can be finicky about how they're held.
Cats can be finicky about how they're held.  Squish that cat.
Squish that cat. 
 Intelligent people are thoughtful.
Intelligent people are thoughtful. People who ask questions are often more intelligent.
People who ask questions are often more intelligent. People who can simplify big ideas concisely are more intelligent.
People who can simplify big ideas concisely are more intelligent.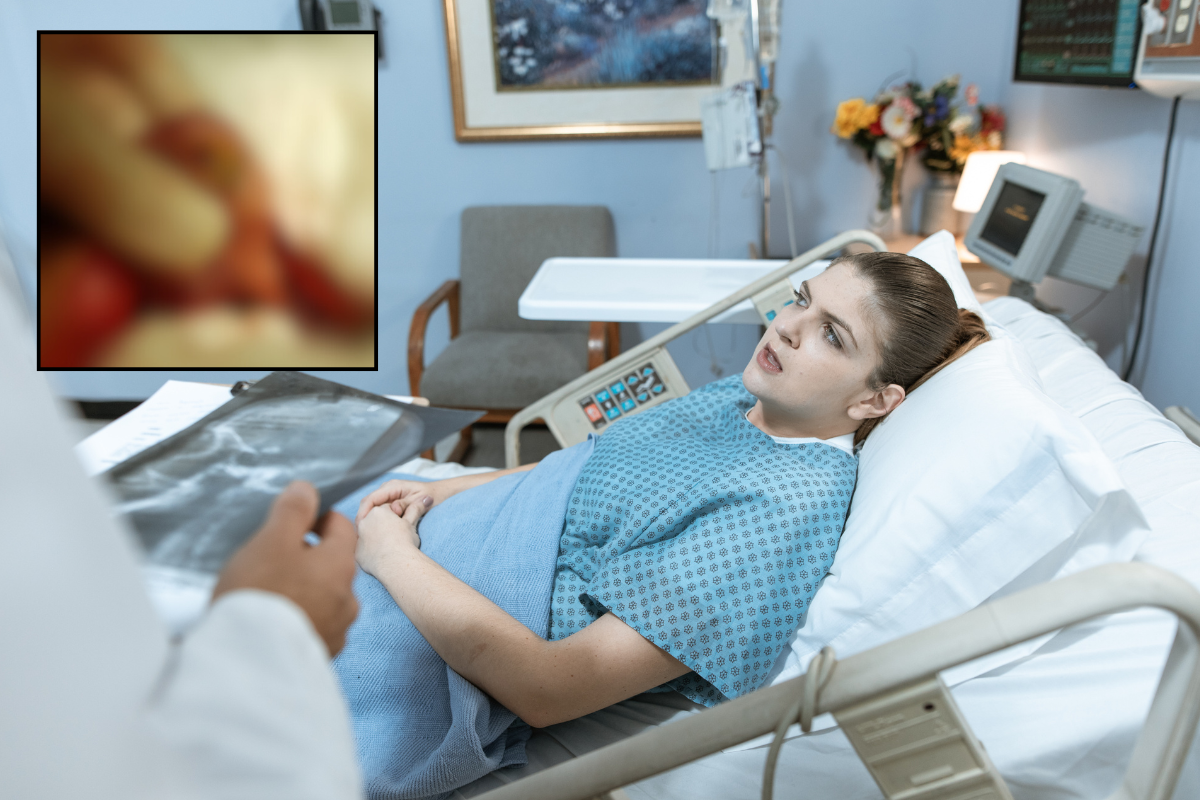
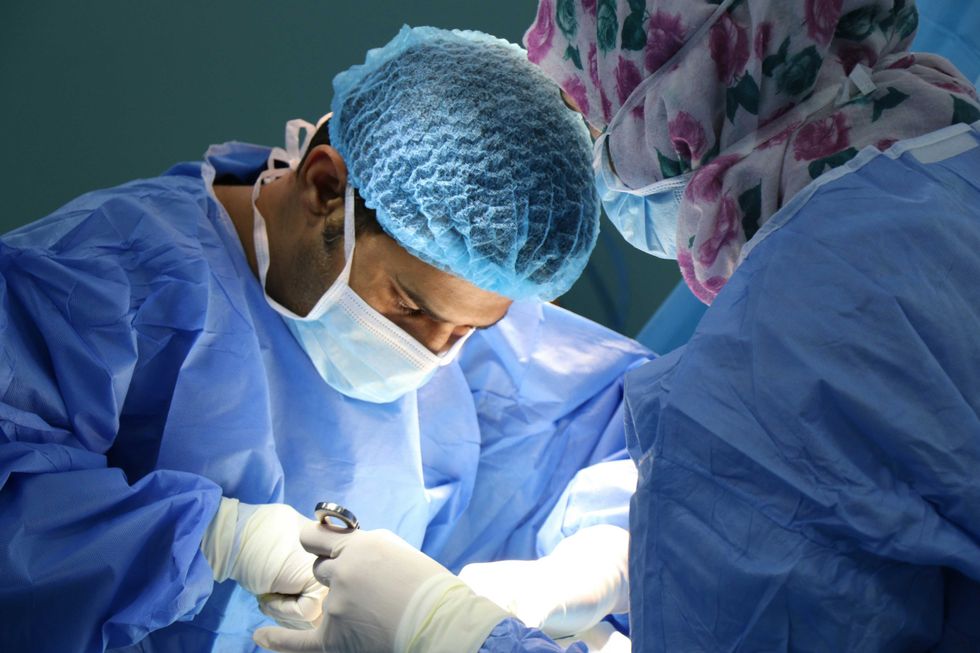 The doctors went in to remove Stuthers' tumor and go more than they bargained for. Photo by
The doctors went in to remove Stuthers' tumor and go more than they bargained for. Photo by 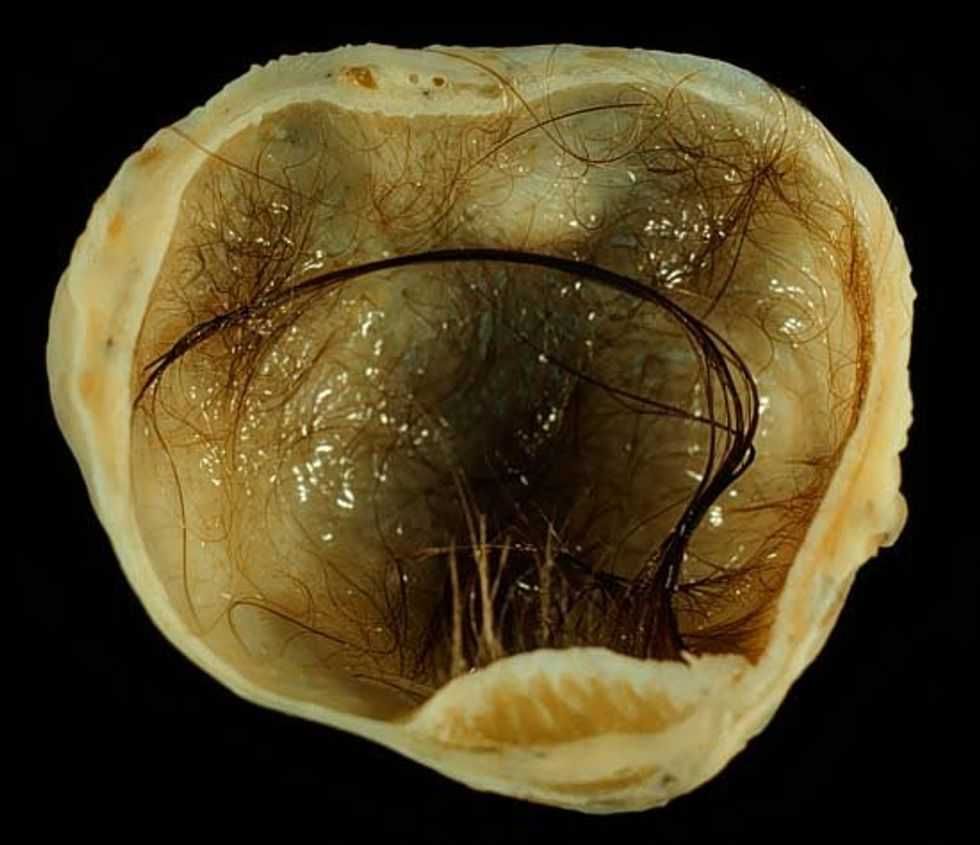 A teratoma with lots and lots of hair growth. Ed Uthman, MD. - Public Domain
A teratoma with lots and lots of hair growth. Ed Uthman, MD. - Public Domain 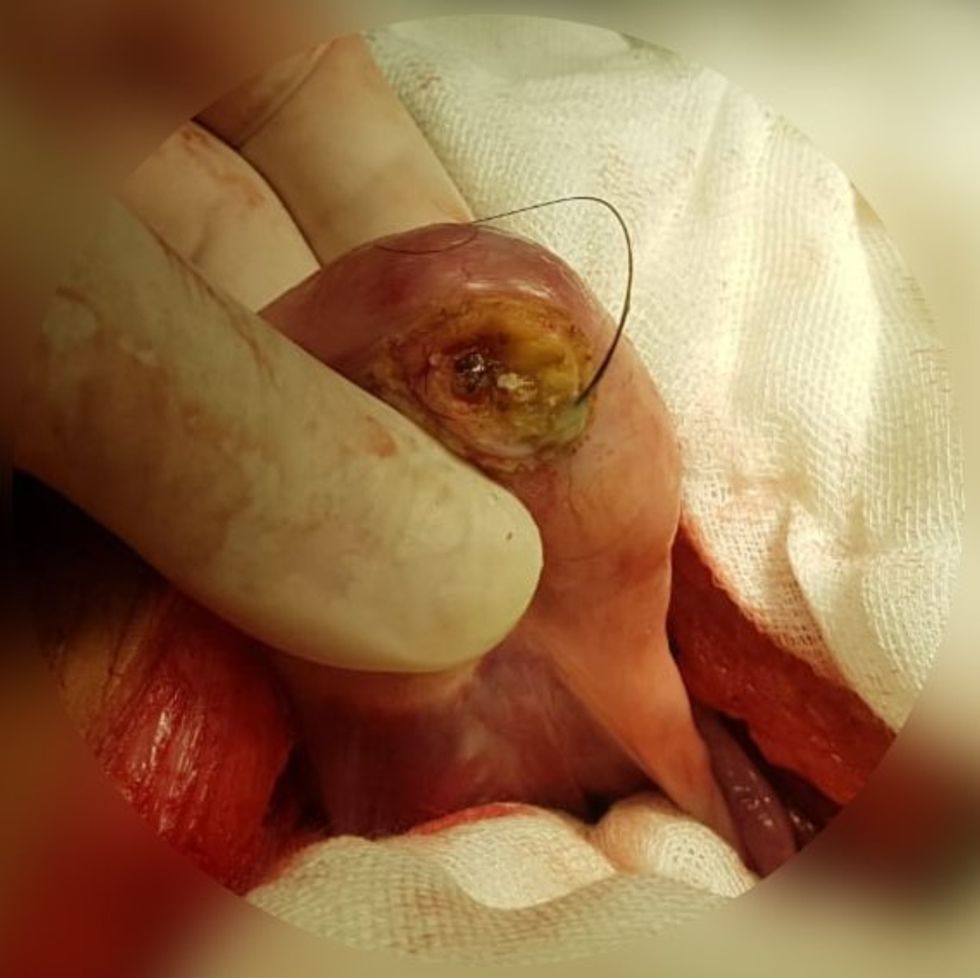 An ovarian teratoma with a long strand of visible hair. E.dronism/Wikimedia Commons
An ovarian teratoma with a long strand of visible hair. E.dronism/Wikimedia Commons