Our favorite giveaway is back. Enter to win a free, fun date! 🌊 💗
It's super easy, no purchase or donation necessary, and you help our oceans! That's what we call a win-win-win. Enter here.
This Valentine’s Day, we're bringing back our favorite giveaway with Ocean Wise. You have the chance to win the ultimate ocean-friendly date. Our recommendation? Celebrate love for all your people this Valentine's Day! Treat your mom friends to a relaxing spa trip, take your best friend to an incredible concert, or enjoy a beach adventure with your sibling! Whether you're savoring a romantic seafood dinner or enjoying a movie night in, your next date could be on us!
Here’s how to enter:
- Go to upworthy.com/oceandate and complete the quick form for a chance to win - it’s as easy as that.
- P.S. If you follow @oceanwise or donate after entering, you’ll get extra entries!
Here are the incredible dates:

1. Give mom some relaxation
She’s up before the sun and still going at bedtime. She’s the calendar keeper, the lunch packer, the one who remembers everything so no one else has to. Moms are always creating magic for us. This Valentine’s Day, we’re all in for her. Win an eco-friendly spa day near you, plus a stash of All In snack bars—because she deserves a treat that’s as real as she is. Good for her, kinder to the ocean. That’s the kind of love we can all get behind.
Special thanks to our friends at All In who are all in on helping moms!
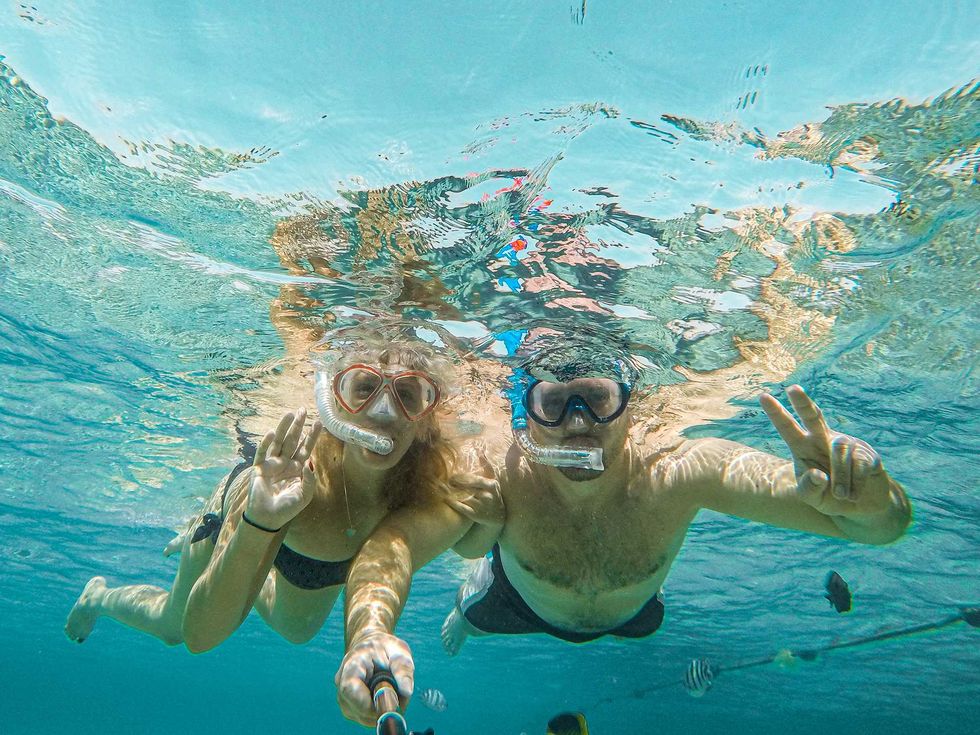

2. Jump in the ocean, together
Grab your favorite person and get some much-needed ocean time. Did you know research on “blue spaces” suggests that being near water is linked with better mental health and well-being, including feeling calmer and less stressed? We’ll treat you to a beach adventure like a surfing or sailing class, plus ocean-friendly bags from GOT Bag and blankets from Sand Cloud so your day by the water feels good for you and a little gentler on the ocean too.
Special thanks to our friends at GOT Bag. They make saving the ocean look stylish and fun!
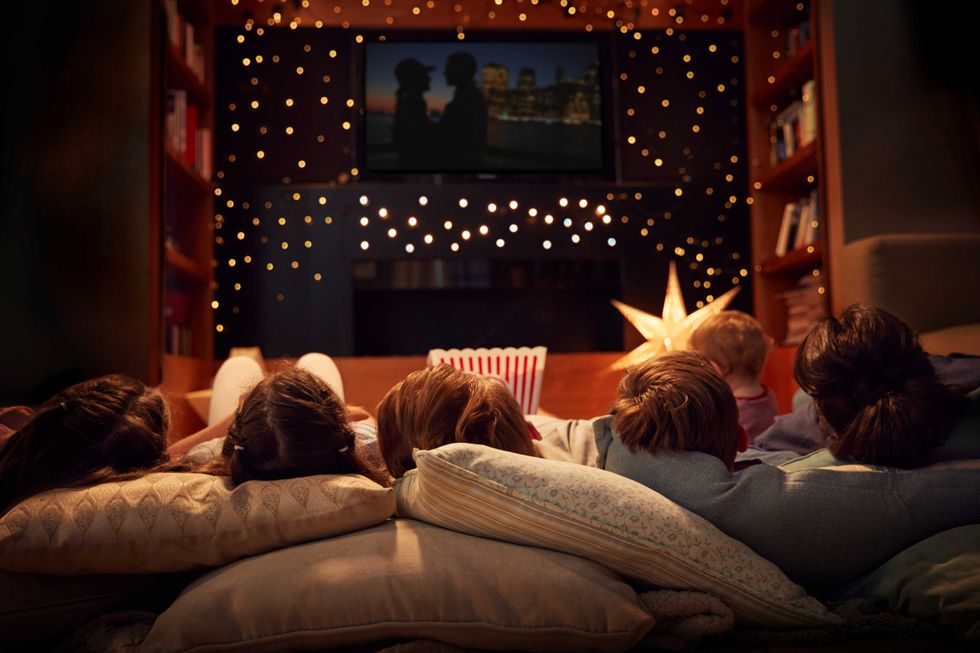

3. Couch potato time
Love nights in as much as you love a date night out? We’ve got you. Have friends over for a movie night or make it a cozy night in with your favorite person. You’ll get a Disney+ and Hulu subscription so you can watch Nat Geo ocean content, plus a curated list of ocean-friendly documentaries and a movie-night basket of snacks. Easy, comfy, and you’ll probably come out of it loving the ocean even more.
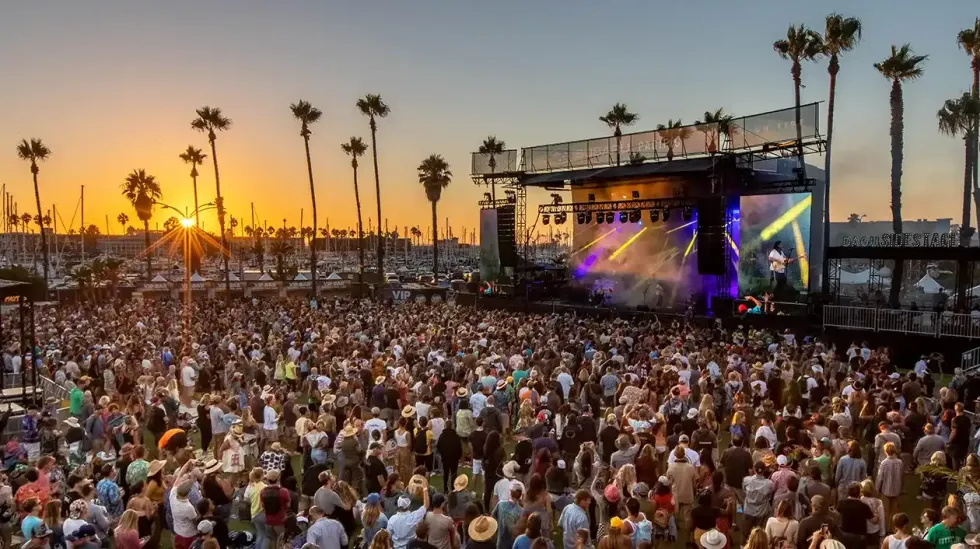

4. Dance all day!
Soak up the sun and catch a full weekend of live music at BeachLife Festival in Redondo Beach, May 1–3, 2026, featuring Duran Duran, The Offspring, James Taylor and His All-Star Band, The Chainsmokers, My Morning Jacket, Slightly Stoopid, and Sheryl Crow. The perfect date to bring your favorite person on!
We also love that BeachLife puts real energy into protecting the coastline it’s built on by spotlighting ocean and beach-focused nonprofit partners and hosting community events like beach cleanups.
Date includes two (2) three-day GA tickets. Does not include accommodation, travel, or flights.
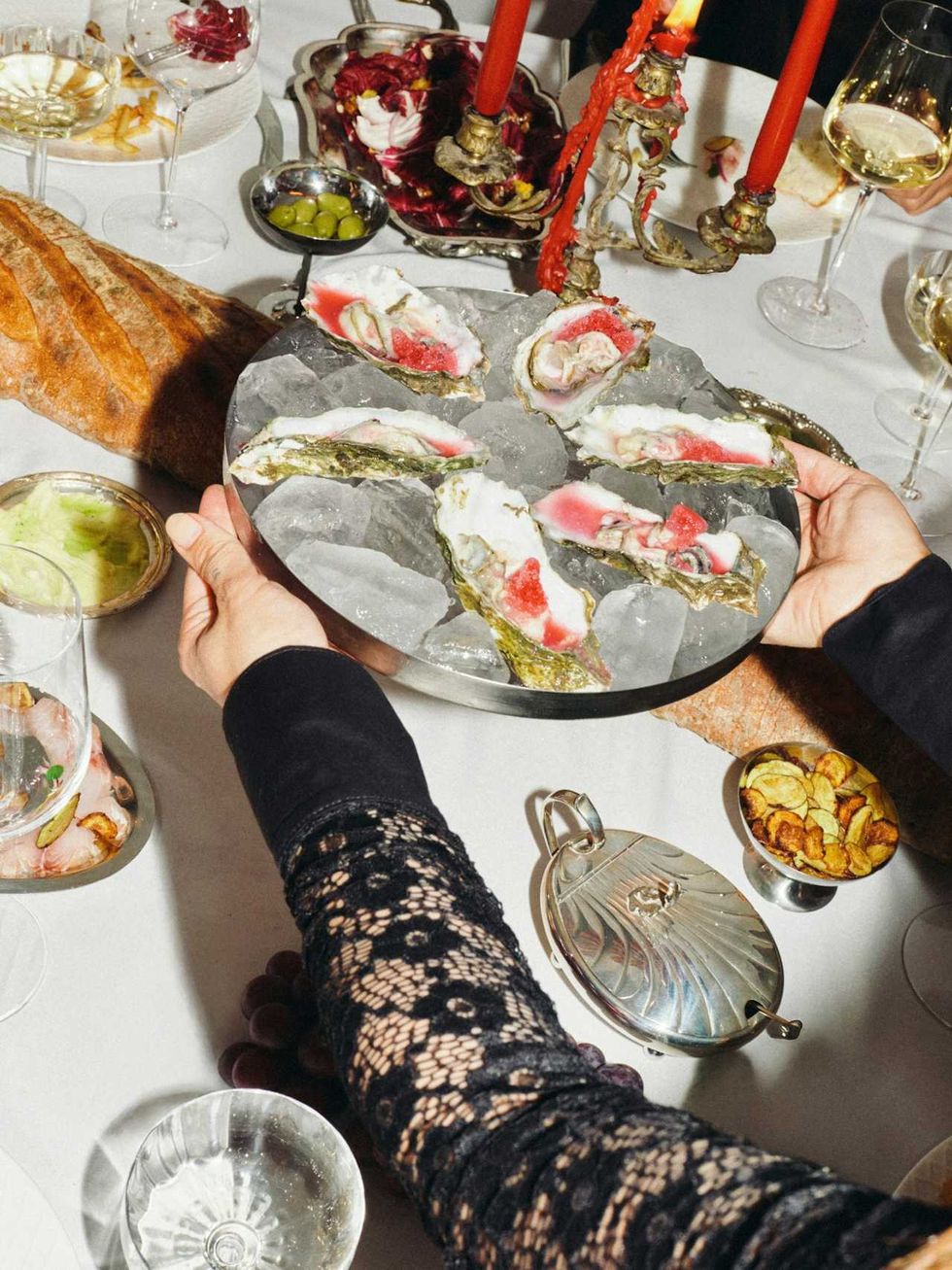

5. Chef it up (at home)
Stay in and cook something delicious with someone you love. We’ll hook you up with sustainable seafood ingredients and some additional goodies for a dinner for two, so you can eat well and feel good knowing your meal supports healthier oceans and more responsible fishing.
Giveaway ends 2/15/26 at 11:59pm PT. Winners will be selected at random and contacted via email from the Upworthy. No purchase necessary. Open to residents of the U.S. and specific Canadian provinces that have reached age of majority in their state/province/territory of residence at the time. Please see terms and conditions for specific instructions. Giveaway not affiliated with Instagram. More details at upworthy.com/oceandate