Most people don’t look at their work calendar on any given day and say, “Yay! I have a meeting!” Most of us just understand and accept that meetings are a part of work life in most industries.
Some people, however, are far more negatively impacted by scheduled meetings than others. For people involved in creating or producing, meetings are actively disruptive to work in a way that isn’t often the case for managers.
A viral post with an explanation from Paul Graham breaks down why.
Graham is a computer scientist, entrepreneur, venture capitalist, and author. In 2009, he described on his website the differences between the way managers and makers utilize work time and how meetings affect their workflow. It’s a brilliant observation that rings true for people in various fields, and understanding this difference can help bridge the gap that often exists between those who work in creation or production and those who manage them.
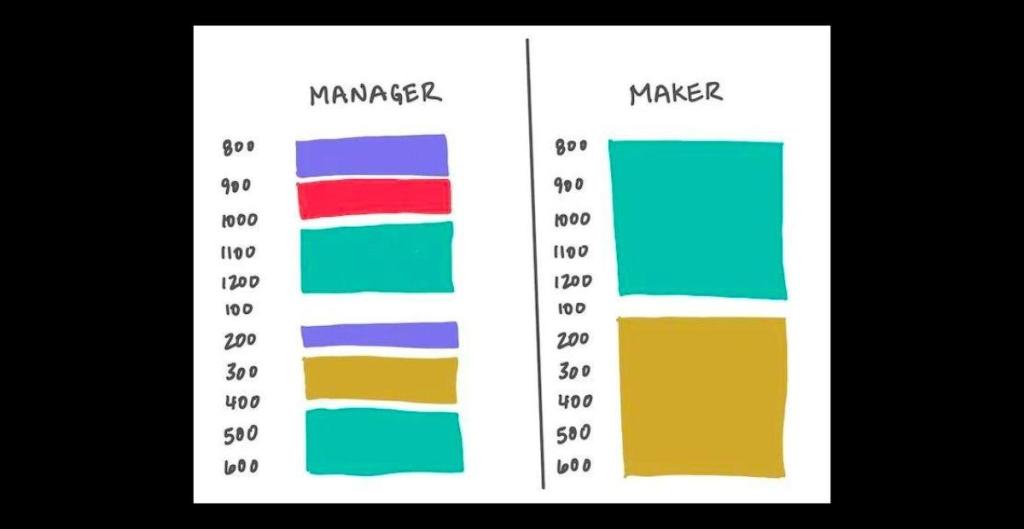
Graham’s explanation was shared by Reese Jones on Facebook with a graphic that shows the difference in how time is seen between managers (people who manage others—the bosses) and makers (writers, artists, programmers—the creators). The manager’s time during the day is split into small blocks, whereas the maker’s is split into two large chunks.
“One reason programmers dislike meetings so much is that they’re on a different type of schedule from other people,” Graham wrote. “Meetings cost them more.”
Graham explained that managers and makers work on two different types of schedules. The manager’s schedule looks more like an appointment book, with the day broken into one-hour intervals.
“You can block off several hours for a single task if you need to, but by default, you change what you’re doing every hour,” he explained. “When you use time that way, it’s merely a practical problem to meet with someone. Find an open slot in your schedule, book them, and you’re done.”
Generally, the folks in power are on this kind of schedule. But those who make things don’t think in hours. Writers, artists, programmers, and others who create for a living work in half-day units at least.
“You can’t write or program well in units of an hour,” wrote Graham. “That’s barely enough time to get started.”
Then he got to the heart of the problem with managers making meetings for makers:
“When you’re operating on the maker’s schedule, meetings are a disaster. A single meeting can blow a whole afternoon, by breaking it into two pieces each too small to do anything hard in. Plus you have to remember to go to the meeting. That’s no problem for someone on the manager’s schedule. There’s always something coming on the next hour; the only question is what. But when someone on the maker’s schedule has a meeting, they have to think about it.
“For someone on the maker’s schedule, having a meeting is like throwing an exception. It doesn’t merely cause you to switch from one task to another; it changes the mode in which you work.”
Bingo. As a “maker” myself, I can attest to this description being spot on for me personally. If I have to attend a meeting, it’s best for it to be right at the beginning or end of those two blocks of time. Tossing one into the middle of the morning or middle of the afternoon is far more disruptive than someone who isn’t a maker might understand.
Many people in the comments complained about meetings being a waste of time, but I don’t think that’s the case all or even most of the time. I see the value in many kinds of meetings and as someone who largely works alone, I actually do sometimes look at the calendar and say “Yay! A meeting!” The issue isn’t so much meetings themselves as their timing.
Graham explained that a meeting can sometimes blow half a day for a maker—not that the meeting itself takes half a day—purely due to the interruption of the workflow.
“Each type of schedule works fine by itself,” he wrote. “Problems arise when they meet. Since most powerful people operate on the manager’s schedule, they’re in a position to make everyone resonate at their frequency if they want to. But the smarter ones restrain themselves, if they know that some of the people working for them need long chunks of time to work in.”
Graham’s post can be read in its entirety here. It’s worth perusing whether you’re a manager or a maker. The more we understand the different ways different people operate, the more we can learn to respect and honor one another’s needs, which ultimately makes us all more successful.
This article originally appeared three years ago.