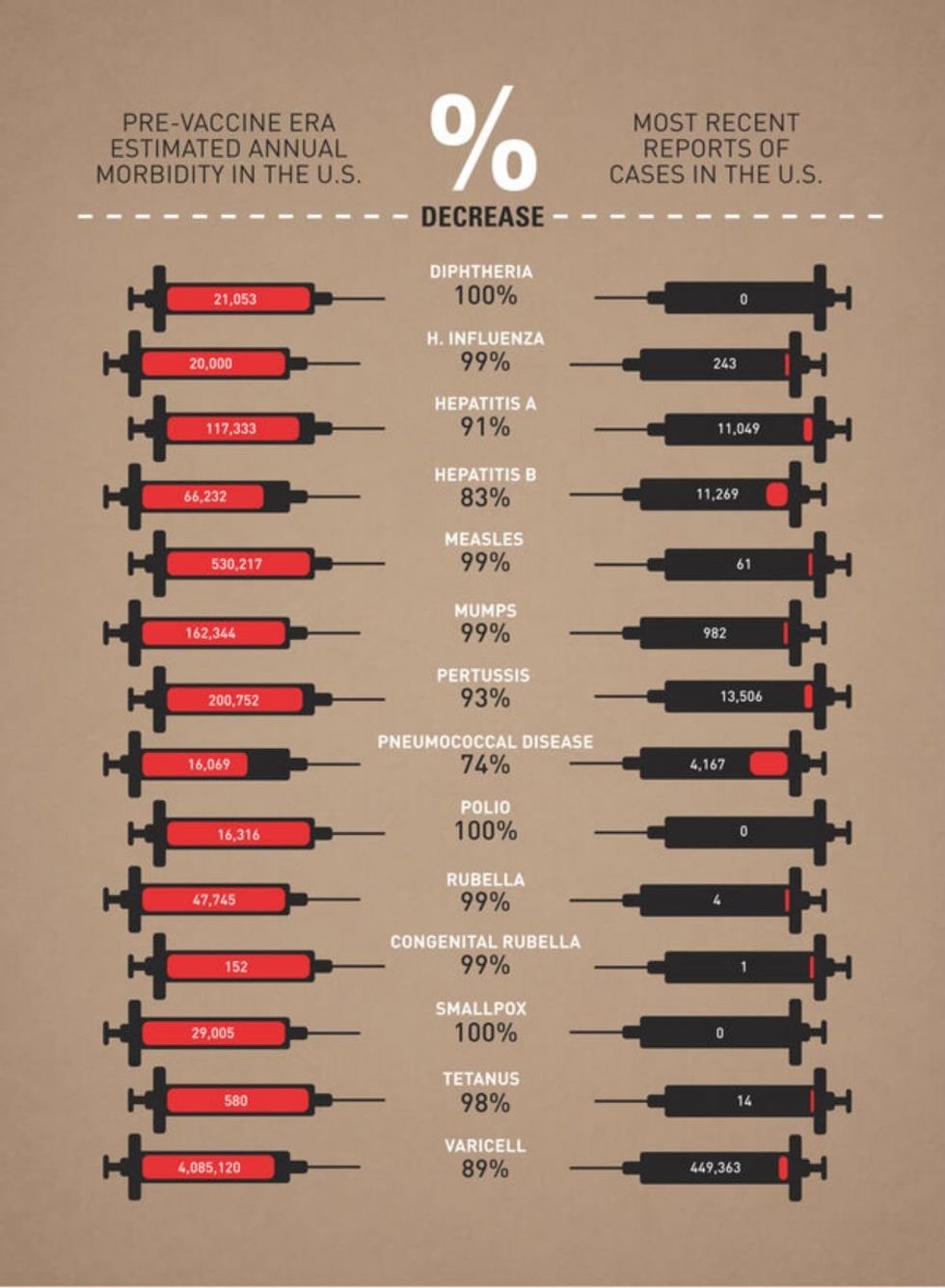
The women of World War II were stone-cold warriors.
Much like their male counterparts, women in the Allied countries were clamoring to get in the game from the moment war broke out. For the most part, the men in charge were like, “We’re, uh, not exactly sure what to do with you.” And the women were like, “Too bad. We’re doing it anyway. Kthxbye!”
These are just a few of them — some famous, some obscure, all ridiculously courageous.
1. Virginia Hall: Allied Spy
Photo via the CIA.
“She is the most dangerous of Allied spies. We must find and destroy her” was an actual thing the Gestapo said about Virginia Hall, an American operative in Vichy France, who helped gather vital intelligence for Britain in the early years of the war.
Despite the fact that her country — the United States — had yet to enter the war. Despite the fact that women weren’t generally considered spy material by the prevailing dudes in charge. Despite walking with a limp on a prosthetic leg, which made her as easily identifiable as, say, James Bond in every movie ever. (Seriously, does anyone in the world not know James Bond is a spy? How is it even possible he’s still undercover at this point? Who can I talk to about this?)
When America did finally enter the war, Hall was forced to escape by herself, on foot, over the Pyrenees mountains, all while still only having one leg. Upon arriving in Spain, she promptly pleaded to be sent back, which she ultimately was — this time to occupied France, where she helped train the French resistance, cut Nazi supply lines, and generally cause mass chaos in preparation for the Allied landing at Normandy. While being literally hunted by Nazis.
Hall is pictured above receiving an award for her service, probably wondering how many Gestapo agents the old dude giving her the award has fled while wearing heels.
2. Jacqueline Cochran: Aviator
Photo via the U.S. Air Force.
Before the Untied States entered World War II, aviator Jacqueline Cochran — who had already proven that she could fly a plane faster than any woman or man alive — politely asked Gen. Hap Arnold to let women fly in the U.S. military, to which he replied, “Ehhhhh, no. Nope. No thanks.”
Then the war started. And Arnold was like, “Um … about that…”
For the next three years, Cochran trained female pilots — who came to be known as WASPs — to pilot American military aircraft. She became the first woman to fly a bomber across the Atlantic Ocean. She supervised the training program, which spanned 120 bases, until 1944 when it was discontinued by the military because of, like, cooties or whatever.
That didn’t stop Cochran, however. After the war, she became the first woman to break the sound barrier. And, according to the National WASP World War II Museum, she “holds more international speed, distance and altitude records than any other pilot, male or female,” to this day.
3. Sophie Scholl: German Dissident
Photo by RyanHulin/Wikimedia Commons.
It’s comforting to think that, if you or I lived in Nazi Germany, we’d have the guts to march right into Hitler Headquarters and slap Hitler in the face personally. In reality, however, we’d most likely be the guy 19 rows deep in the parade, frantically waving our tiny swastika flag, thinking, “Please don’t look at me, pleasedontlookatme, pleasedontlookatme pleasepleaseplease.” (I’m 95% sure I’d be that guy — maybe you wouldn’t be!)
Sophie Scholl wasn’t here for that.
Disgusted by the rumors of mass slaughter on the Eastern Front and the deaths of an ever-growing number of her countrymen, Sophie — only 21 at the time — her brother Hans, and their friend Christoph Probst began distributing leaflets at the University of Munich denouncing the Nazis and calling for resistance among the German people. Their flyers eventually spread around Germany to the University of Hamburg and beyond, and into one of the few genuine flare-ups of internal political resistance against Hitler during the war.
Unfortunately, the Nazis, as you may have heard, were known for being a tad tough on dissent.
Sophie, Hans, and Probst were eventually captured by the Gestapo, tried, and executed for treason. Her last words were: “What does my death matter, if through us thousands of people are awakened and stirred to action?”
You can totally be excused for crying. I know — I hate it when I get something in my eye too.
4. Susan Travers: French Foreign Legion Soldier
Photo by Levin01/Wikimedia Commons.
As an ambulance driver and the only woman in the French Foreign Legion, Travers was stationed at the Free French fort Bir Hakeim in Libya when it was surrounded by German troops (she refused to leave, even when the other female staff were evacuated). Travers and the soldiers inside bravely held out for 15 days — until their supplies ran out and it became clear that no help was coming.
That’s when Travers hopped in her truck, presumably put on her finest Arnold Schwarzenegger voice (unclear how she knew to do this, as this was five years before Schwarzenegger was even born — but lady knew what was up), and said, “Come with me if you want to live.”
The squad launched a daring nighttime escape with Travers at the wheel of the lead vehicle. Her truck took 11 bullets, but she ultimately made it to Allied lines and helped save the lives of 2,500 Free French soldiers in the process.
It is rumored that Susan Travers never secreted a single drop of sweat at any point in the next 71 years. She was just. that. badass.
5. Faye Schulman: Partisan Fighter
Photo by Faye Schulman, via Jewish Partisan Educational Foundation, used with permission.
After her whole family was massacred by the Nazis in the Lenin ghetto in Poland, Faye Schulman fled into the nearby woods, where she joined a group of resistance fighters. A skilled photographer, Schulman participated in a daring raid to rescue her photography equipment and proceeded to take a series of incredible photographs that captured the rarely seen daily lives of partisan fighters during the war.
As the only Jewish woman in the group, Schulman kept her identity secret throughout much of the war, all while documenting the bravery and sacrifice of her cohort. “I want people to know that there was resistance,” she said in an interview after the war. “Jews did not go like sheep to the slaughter. I was a photographer. I have pictures. I have proof.”
6 and 7. Frances Eliza Wills and Harriet Ida Pickens: Naval Officers
Photo by the Department of Defense/Wikimedia Commons.
“Sailors?” you might be thinking. “What’s the big deal? Tons of American women served in the Naval Reserve (WAVES) during the Second World War.” Which is true.
Frances Eliza Wills and Harriet Ida Pickens, however, were the first to do it while black — and contend with the ridiculous amount of racism that came along with that.
In an era when the military was still segregated, Wills and Pickens overcame institutional barriers, a mountain of prejudice, and social expectations just to claim a job that thousands of their white peers were granted simply by showing up. They became the first black female officers in the U.S. Navy and were assigned to teach at the Hunter Naval Training Station in the Bronx.
72 black women in total served in WAVES during the war, thanks in no small part to the efforts of Wills and Pickens.
8. Veronica Lake: Actor/Icon
Photo via Hulton Archive/Getty Images.
Movie star Veronica Lake had the most famous haircut in the world in the early 1940s. Then World War II happened, and she changed it. For patriotism.
Worried the thousands of American women who were copying her signature “peek-a-boo” cut were endangering themselves as they moved into heavy industrial work, Lake publicly restyled her long, flowing, wavy hair — a ‘do that was driving her thriving film career — into a … kind of braided up-thing.
According to an interview she gave many years later, she was told that accident rates fell 22% after her heroic hair appointment.
And because the world can be an awful, unfair place, her job offers started slowly drying up. Though she did film a few movies after the war, her career never really recovered.
No haircut will ever be as patriotic. That’s right. I’m looking at you, red-white-and-blue mohawk.
9. Gertrude Boyarski: Partisan Fighter
Gertrude Boyarski at her 1946 wedding. Photo provided by Jewish Partisan Education Foundation, used with permission.
After fleeing Derechin, a Polish Jewish ghetto, with her parents and siblings, Boyarski — a teenager at the time — watched in horror as each member her family was gunned down one by one in sneak attacks by SS troops and their local allies. Boyarski continued to flee until she eventually linked up with a Russian partisan group, telling its commander, “I want to fight and take revenge for my whole family.”
Believing this to be one of the most Russian things anyone has ever said, the commander admitted Boyarski into the unit.
And revenge she took.
Shortly after joining the group, Boyarski and a friend raided a local village, acquired a crap-ton of kerosene, and burned down a bridge the Germans used to move people and supplies. Even as the Nazis figured out they’d been had and started firing back, Boyarski and her friend continued to curb-stomp the bridge, breaking off pieces with their bare hands and feet, presumably cackling to themselves and high-fiving the whole time.
10. Nancy Wake: Allied Spy
Photo via Australian War Memorial/Wikimedia Commons.
The first line of Nancy Wake’s 2011 New York Times obituary notes that the former New Zealander spy “did not like killing people.” But oh, did she kill people. Occasionally with her bare hands.
Lady was ice-cold.
Known as “The White Mouse” by her German pursuers, Wake spent much of the war as an Allied operative in France, helping escaped POWs and others wanted by the Germans flee to Spain, running messages between the British military and French resistance — and, of course, choking the life out of various Nazis.
“I was not a very nice person,” Wake said once, according to the Times. “And it didn’t put me off my breakfast.”
Wake passed away peacefully in 2011 at the ripe old age of 98 and is presumably reluctantly but efficiently strangling Nazis in the afterlife.
11. Nadezhda Popova: Bomber Pilot
Photo by Kremlin Presidential Press and Information Office/Wikimedia Commons.
By the time the USSR allowed women to join its Air Force, the German Army was already deep in Soviet territory and threatening to overrun Moscow. When word finally came down, Nadezhda Popova was like, “Aw yeah. Strap up, ladies. Let’s go.”
As a member of the feared “Night Witches” squadron, Popova flew 852 missions in an old biplane (mostly at night), was shot down numerous times, and blew up lots of valuable German military equipment in the process.
See that smile? That’s the smile of a woman who knows she could easily take you and all your grandpas one-on-one.
12. Hedy Lamarr: Inventor
Photo via Hulton Archive/Getty Images.
For most of the late 1930s and ’40s, Hedy Lamarr was just your average world-famous actress who appeared in countless films alongside the likes of Charles Boyer, Spencer Tracy, and Clark Gable — and also invented a critically important military technology in her spare time.
Unbeknownst to many who saw her on screen, Lamarr was a passionate inventor — and, as an Austrian immigrant, an ardent Nazi despiser. Working with composer George Antheil, Lamarr discovered an ingenious method of preventing enemy ships from jamming American torpedoes by making radio signals jump between frequencies, rather than stay on a single channel.
To put this in perspective, it’s sort of like if Eva Green built the first drone, or Jessica Chastain came up with the idea for cruise missiles.
As a foreigner, a non-member of the military, and a woman, Lamarr’s invention went largely ignored until the 1960s, when some dude scientists unearthed it and put it to use during the Cuban Missile Crisis (and probably took all the credit for it at parties). It’s also basically the reason we have things like GPS, Bluetooth, and advanced guided missile technology.
The reason Jessica Chastain didn’t have to invent cruise missiles? Hedy freakin’ Lamarr did it first.
13. Violette Szabo: Allied Spy
Photo via the Imperial War Museum/Wikimedia Commons.
Following her husband’s death on the battlefield in North Africa, Violette Szabo volunteered for the British Special Operations Executive and was paradropped into occupied France with orders to generally wreck stuff and raise hell. Szabo did so more than ably — destroying Nazi infrastructure like it was her job — for several months, until she and a fellow resistance fighter drove straight into a German roadblock while out on a mission.
Szabo and her companion leapt out of the car and fled on foot, shooting the whole time. When it became clear that Szabo wasn’t going to escape, she continued to fire at the German soldiers until her partner was safely out of harm’s way. On her way to the concentration camp at Ravensbruck, she and another woman who were chained together dragged themselves through the train in order to bring water to suffering male prisoners during a raid.
Szabo attempted to escape the camp many times, unfortunately to no avail. She was ultimately executed a few weeks before the Allied victory — yet remained a total, committed G to the very end.
14. Veronica Foster: Factory Worker
Photo via Library and Archives Canada/Wikimedia Commons.
Before America had Rosie the Riveter, Canada had Ronnie, the Bren Gun Girl (Canadians get straight to the point). Unlike Rosie, Ronnie was a real-life woman named Veronica Foster, seen here smoking and admiring a big-ass gun she just made.
Ronnie’s no-nonsense, tough-as-nails, gun-constructing demeanor helped inspire millions of Canadian women to get to work in wartime factories. After the war, she took the next logical step in her employment and became a singer in a big band.
Pretty sure that’s the Canadian Dream right there.
15. Lyudmila Pavlichenko: Soviet Sniper
I came here to chew bubble gum and shoot Nazis. And I’m all out of bubble gum. Photo by Mar/Wikimedia Commons.
As a sniper fighting the Nazis in the USSR, Lyudmila Pavlichenko recorded 309 kills — the most of any female sniper in history.
“We mowed down Hitlerites like ripe grain,” she said of her role in the battle of Sevastopol, presumably dropping a mic, kicking a door down, and speeding away in her Escalade. Pavlichenko became a national hero for her efforts and even toured the U.S. in 1942.
Eventually, the Soviets turned the tide on the Eastern Front and marched slowly but surely on to Germany. And the world was never the same.
Thanks in no small part to one woman.
Who shot a lot of Nazis.