We’ve been “locked down” for nearly two months, and people are are understandably tired of it. Millions of Americans are out of work, which means many have also lost their employer-provided health insurance. Our economy has slowed to a crawl, businesses are shuttered, and everyone is worried about the sustainability of it all.
“We can’t let the cure be worse than the disease,” people say. The president himself has repeated this line, the implication being that the impact of the lockdowns will be worse than the impact of the virus. Just today in his press briefing the president mentioned suicides and drug overdoses as tragic consequences of the lockdowns, stating that more Americans could die of those causes than the virus if we fall into an extended economic depression.
Is that true, though? While no one can predict the future, death statistics and economic history in the U.S. do not support that idea at all. Not even close.
Let’s start with suicides. During the two worst years of the Great Depression, 20,000 Americans per year took their own lives. That’s tragic—but it’s nowhere near the number of Americans that have died of COVID-19 just in the past month.
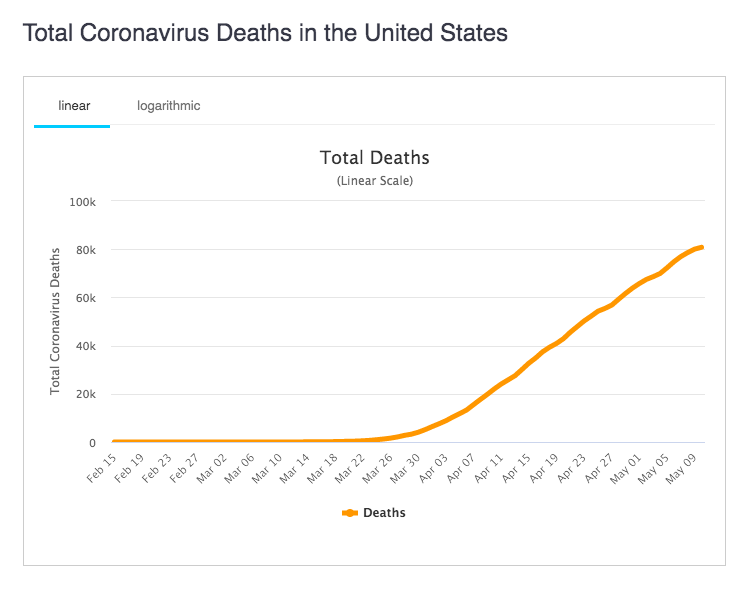
Of course, the U.S. population has nearly tripled since the Great Depression, so we can’t compare that number directly. But even if we triple those Great Depression suicides to 60,000 a year to account for population change, that’s still not as many Americans as have died of COVID-19 in just the past 5 weeks.
Using a different calculation, there was a 25% increase in suicides during the Great Depression. With ~48,000 suicides in the U.S. in 2018, a 25% increase would also put the annual number at 60,000. No suicide number is a good number, of course. But by no math in the universe is an extra 12,000 deaths per year anywhere near the 80,000 Americans who have died of COVID-19 in the past two months.
Our COVID-19 deaths have averaged around 2000 per day for weeks while under lockdown. At no time in our history, through bad economic depressions and horrific world wars, has 2000 Americans died of suicide per day. Even if our suicide numbers tripled—a 12 times greater increase than during the worst years of the Great Depression—that would still be less than 400 people dying of suicide per day. A terrible number, but not nearly as terrible as 2000 per day.
What about drug overdoses? Well, that’s a little trickier to gauge. I’ve not seen any statistics about drug overdoses during the Great Depression, and we already had an opioid crisis flourishing before the pandemic hit. I imagine it’s probably harder for people to get the drugs to feed an addiction right now, so I’m not convinced that there would be an enormous increase in drug overdoses. But for the sake of argument, let’s say drug overdoses doubled. Highly unlikely, but let’s go with it.
In 2018, the last year for which we have statistics, 184 people per day died of drug overdose. If we double that, we’re talking around 370 people per day—still less than one-fourth the number of Americans dying of COVID-19 per day in the past month.
Even added together, those extreme suicide and drug overdose scenarios don’t add up to our current COVID-19 situation. And once again—those numbers are with lockdowns in place.
What about starvation, though? Surely millions would die of starvation or malnutrition in a tanked economy, right? Well, no—for a couple of reasons.
1) The reality is if anyone starves to death in the U.S., a country that has the ability to produce more than enough food to feed our population, that’s a mismanagement of resources, not an inevitable outcome of an economic crash.
2) Americans didn’t die of starvation in large numbers during the Great Depression.
In fact—are you ready for a rather mind-blowing statistic—the overall health of Americans didn’t decline during the Great Depression at all. It improved.
People lived years longer during the Depression. Life expectancy rose. Mortality rates dropped in every category (except suicide) across practically every demographic.
In fact, this pattern shows up consistently during economic booms and recessions. More people die—and die at younger ages—during economic booms. Vice versa during recessions. Counterintuitive? Yes. But that’s what the data shows. (Here’s the 2009 study that shows these trends during the Great Depression.)
We could debate the reasons for this, but it doesn’t really matter. The point is, if the “cure” is a lockdown that results in an economic depression and the “disease” is the virus spreading unchecked, we have no evidence that the cure is or could be worse than the disease, at least not in terms of death counts.
Now clearly, there are huge problems with a tanked economy. Mental health issues increase. Life is hard. People struggle and suffer and we certainly should not minimize that. BUT…
Mass death and mass illness also cause suffering and mental health issues, while also hurting the economy.
I’ve seen people say we open back up, shoot for herd immunity, and just accept the fact that people will die. But that notion completely ignores the economic impact of having a big chunk of the population too sick to work. As we hear more and more people describe their COVID-19 journeys, it’s becoming clear that even infected people who don’t have to be hospitalized can still be very ill for weeks.
Let’s do some quick herd immunity math. Reaching herd immunity means 70% of the population would have to get the virus. (Some say 60%, some say 80 or 90%—let’s go with the middle.) That’s 229 million people in the U.S. We don’t have a good enough hold on this virus to know how many people have already have it or how many would be asymptomatic, but a current guess for asymptomatic cases is 25% to 50%. Let’s go with the higher.
That would mean 114.5 million Americans being symptomatically ill. It’s impossible to know how severe each person’s case would be, but if even half of those with symptoms got flu-level ill, that would be 56 million people too sick to work for weeks. Some would have lingering health issues afterward to boot. What would that kind of mass illness to do to the economy?
And we haven’t even gotten to the people dying yet. We don’t have an accurate mortality rate, but let’s go with a conservative 0.5% death rate (meaning 99.5% of people who get it, survive it). We’re still talking 1,135,000 deaths if we shoot for 70% herd immunity at that death rate. That basically means we’d all know people who died of this disease.
I’m pretty sure mass grieving over a huge death toll in a short period of time isn’t great for the economy, either. (Perhaps instead of deciding how much death and illness we’re willing to tolerate, we could take this opportunity to fundamentally rethink how our economy works? Just a thought.)
Granted, all of these numbers are based on data that keeps changing as we learn more about the virus and its impact. We don’t know enough yet to say anything for sure. We don’t even know if people are truly immune yet. We do know the virus is real, and that it’s more contagious and more deadly than the flu. Everything else is a best guess.
Essentially, there are no good options before us at the moment that don’t involve great losses of one kind or another. But by no historical or statistical measure do we have evidence that the cure worse than the disease—at least with the data we have right now.