Seven amazing trends the media ignores that'll make you feel great about the future

Is now the best time to be alive?
Fatal shooting on a movie set. The former president is attacking secretaries of state. The body of a missing man is found to be a murder suspect. Energy prices are rising and could lead to social unrest. Cargo ships are stuck in the harbor.
A quick scan of America's most popular news websites shows a country that appears to be on the brink of chaos. But if you picked up a newspaper in 1972 or 1998 you'd probably come away with the same feeling.
Humans have such unquenchable hunger for hearing about crime, scandals and political turmoil that the news media rarely tells us what's going right in the world.
War always grabs the headline over peace. Economic crises always get more headlines than prosperity, and the storm always receives more press than the calm before it.
At Upworthy, we have a bias toward sharing stories that highlight the best of humanity to help counter the barrage of negativity that comes from traditional media outlets. So we wanted to shine a light on another organization that's doing the same.
Human Progress was created by the Cato Institute after the economic downturn in 2008 to counter the prevailing pessimism of the times. It's a reminder of the power of a free and open society at a time when America's core institutions are being questioned.
Over the past 13 years, the site has compiled a data bank of information from literacy rates and hunger rates to studies on the environment, war, peace and violence. It also recently released a book, "Ten Global Trends Every Smart Person Should Know."
We talked with Chelsea Follett, the managing editor at Human Progress, about the media's negativity bias and why it's crucial to promote the positive trends happening in the world.
Follett doesn't believe that the media is insidious, but that humans have a number of psychological biases that predispose us toward pessimism.
"Historically, obviously our ancestors in a primitive environment who overreacted to danger were more likely to survive than those who underreacted," Follett told Upworthy. "But there is a point where unwarranted panic can actually be detrimental to your survival, if you abandon policies or institutions that are actually working, or that have allowed you to make tremendous progress in the past.
"There's also the nature of the media," she added. "Obviously sudden, noteworthy and rare events are the ones that make headlines, whereas long-term slow, steady, incremental progress is just not as interesting."
Follett says that the American public has been kept in the dark over the incredible steps that the country has made to reduce crime over the past five decades.
"Crime is near historic lows in the United States. It's been falling and falling. We did see a small uptick last year, but we're nowhere close to where it was 30 years ago," she said.
If Follett could shout one truth about human progress from the rooftops, it'd be humans' incredible capacity for innovation.
"You're able to solve so many problems and whatever problems we face whether it's climate change or a global pandemic," she said, "the key seems to be giving people the freedom to cooperate and find solutions."
Here are seven of the most encouraging trends reported by Human Progress.
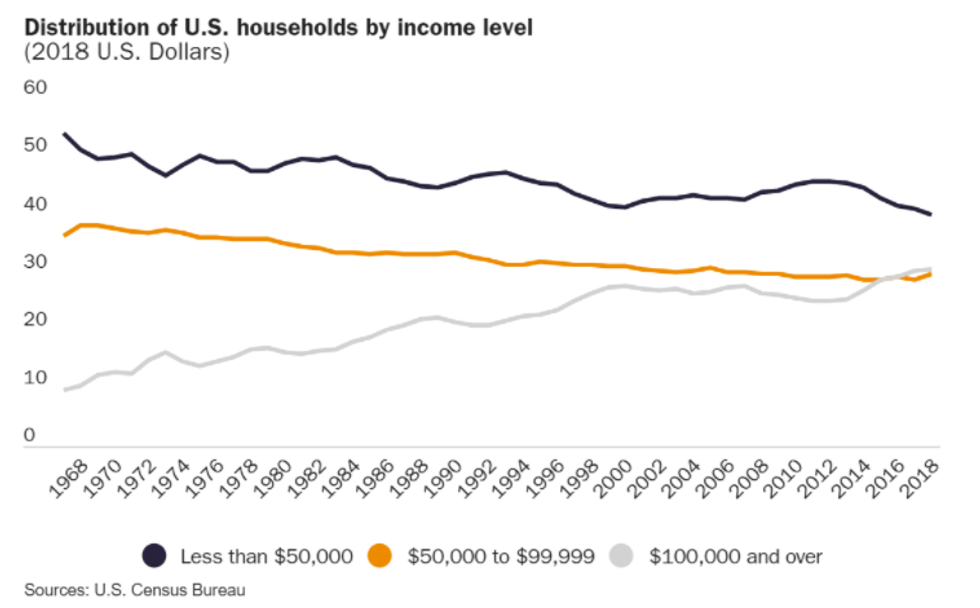
1. The middle class is shrinking, but it's because Americans are getting richer.

The middle class, it turns out, is shrinking. But not because more people are falling into poverty, as some politicians and pundits might have you believe. Rather, it's shrinking because more people are "moving on up," and ascending into a higher income bracket.
The U.S. economy has been on shaky ground since COVID-19 hit, but the overall trend shows more and more Americans are movin' on up.
According to the most recent data from the U.S. Census Bureau, in 2018, more than 30% of U.S. households earned over $100,000 (i.e., the upper class). Fewer than 30% of households earned between $50,000 and $100,000 (i.e., the middle class). The share of U.S. households making at least $100,000 has more than tripled since 1967, when just 9% of all U.S. households earned that much (all figures are adjusted for inflation).
2. Extreme poverty rates are on a steep decline throughout the world.

In 1981, 44.3% of the world lived in extreme poverty (i.e., less than $1.90 per person per day). In 2015, it was 9.6%, a 78% decline.
In East Asia, a region of the world that includes China, 80.6% of people lived in extreme poverty. Today, 4.1% do—a 95% reduction. Even in sub-Saharan Africa, a relatively underperforming region, the share of the population living on less than $1.90 per day dropped by 38%.
Why are people in developing nations doing so much better these days? A major reason is a rise in international trade. The movement of capital, people and goods around the globe has increased dramatically since the '80s.
Extreme poverty is also on the decline due to an increase in the "rule of law" in developing nations to protect people and their property. Improvements in public health, infrastructure and technology have also been a big aid to developing nations.
3. Far fewer people are dying in war.
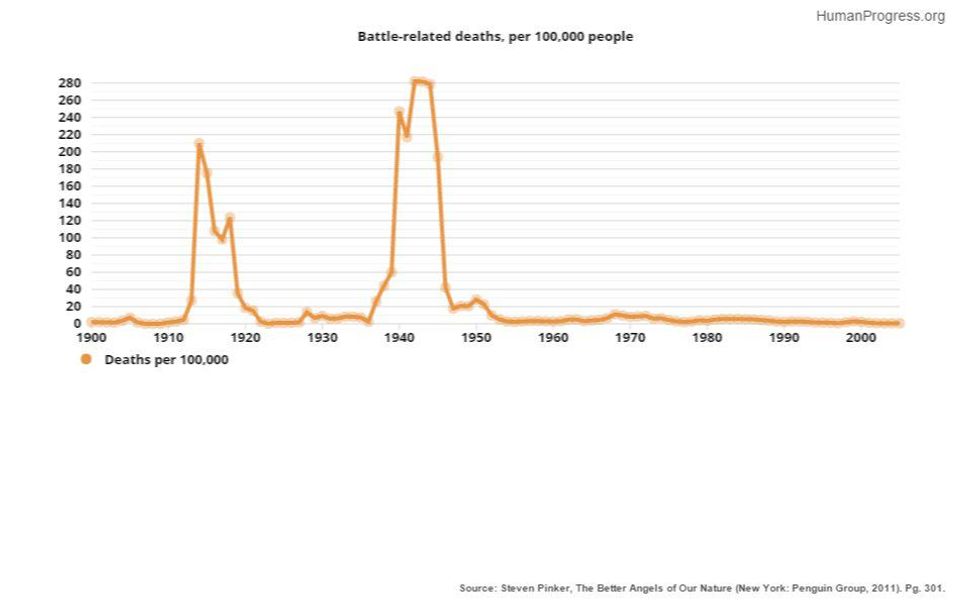
While war deaths are certainly more visible than ever, with television and the internet bringing scenes of flag-draped coffins into our living rooms, far fewer people ever see battle firsthand. After adjusting for population growth, the data shows that despite the noted exception of the World Wars, battle deaths have become rarer since 1900.
In fact, today there are fewer military personnel as a share of the population than at any time since 1932. The world may seem chaotic, but the data shows a more optimistic story.
4. America's incarceration rate is at the lowest level since 1995.
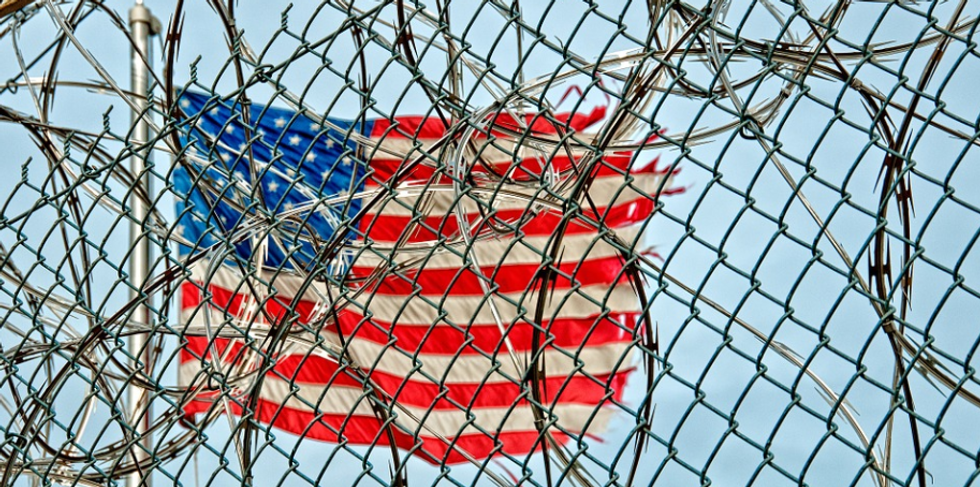

The United States incarcerates a larger percentage of its population than any other country. Mass incarceration is responsible for destroying families and reducing mobility for marginalized groups.
The good news is that in 2019, the U.S. incarceration rate fell to its lowest level since 1995, according to recently published data from the Bureau of Justice Statistics (BJS), the statistical arm of the Department of Justice.
At year-end 2019, an estimated 6,344,000 persons were under the supervision of adult correctional systems in the United States, about 65,200 fewer persons than the year before.
A major reason for the decline in incarcerated Americans is the steep decline in violent and property crimes over the past few decades. The nationwide arrest rate has also been falling steadily.
5. Violent crime has dropped like a rock.
Even though the news media and politicians would like people to think otherwise, the number of Americans who've reported violent crime has been cut in half since 1990. The problem is that regardless of how much safer America has become, public perception has only gone in the opposite direction.
One study out of California found that the more local news one consumes, the greater one's perception of risk and fear.
"The news is not going to report on things that are going really well very often," Meghan Hollis, a research scholar at the Ronin Institute for Independent Scholarship, told FiveThirtyEight.
"You can have people perceiving areas of cities as much more violent than they actually are because that's what they see in the news," she said. "It really amplifies that view of criminal activity beyond what it really is."
6. COVID-19 forced many to work from home where they are happier and more productive.

via Pixabay
Many people were forced into working from home due to the pandemic, but it looks like the unforeseen change may have incredible benefits for workers and employers everywhere.
Research has found that remote workers are happier, more productive, take fewer breaks and have greater loyalty to their employers. So the dramatic rise in telework amid the pandemic has the potential to make a positive difference in many people's lives, reshaping everything from how we work to where we live.
7. We're making tremendous progress in the fight against malaria, AIDS and other diseases.
While the world has been focused on eradicating COVID-19, we've also been making huge strides in the fight against malaria and AIDS. Thanks to better treatments and preventive measures, the malaria death rate dropped from 12.6 per 100,000 in 1990 to 8.2 per 100,000 in 2017.
The number of people who die of AIDS every year, as well as the number of those infected, is now half of when the disease was at its peak. The HIV pandemic peaked in the mid-2000s when some 1.9 million people died of AIDS each year. In 2017, less than 1 million died from the sickness. In the mid-1990s, there were some 3.4 million new HIV infections each year. In 2017, there were only 1.8 million new infections.
- Trump Administration surprisingly approves the largest solar project ... ›
- I'm honestly fed up with all the bad news, so I illustrated 50 of the ... ›
- 7 things that made us happy this week - Upworthy ›
- People share good things happening in America - Upworthy ›

 A Generation Jones teenager poses in her room.Image via Wikmedia Commons
A Generation Jones teenager poses in her room.Image via Wikmedia Commons



 A woman getting her nails painted.via
A woman getting her nails painted.via 
